Imagine having a personal assistant who never sleeps, never gets tired, and can handle an infinite number of tasks on its own. That’s the power of AI agents, the superheroes of the artificial intelligence era.
With the advent of agents such as AutoGPT, BabyAGI, AgentGPT, etc., a whole new chapter has been added to the AI horizon. These innovative platforms are creating new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike. With the continuous evolution of AI, there will be endless possibilities for using autonomous AI agents. But, hey, first of all,
What is an AI agent? What is an autonomous AI agent?
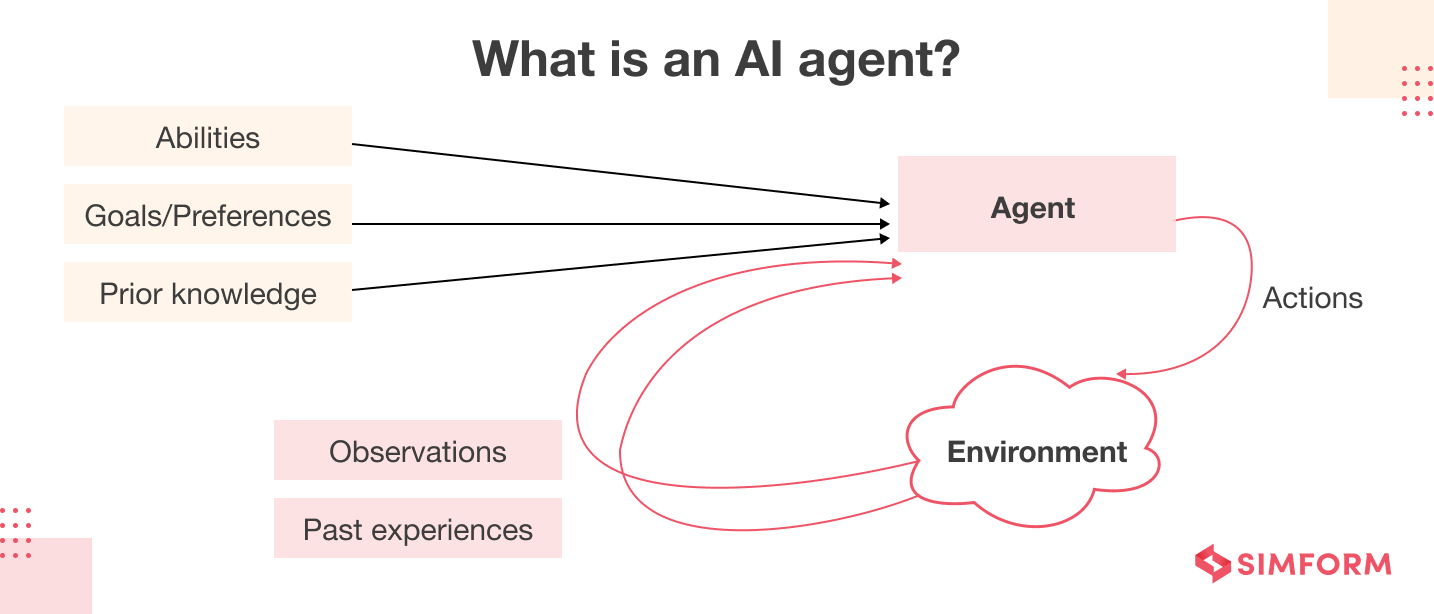
An AI agent is a software program designed to interact with its environment, perceive the data it receives, and take actions based on that data to achieve specific goals. AI agents simulate intelligent behavior, and they can be as simple as rule-based systems or as complex as advanced machine learning models. They use predetermined rules or trained models to make decisions and might need external control or supervision.
An autonomous AI agent is an advanced software program that can operate independently without human control. It can think, act, and learn on its own, without needing constant input from humans. These agents are widely used in different industries, like healthcare, finance, and banking, to make things run smoother and more efficiently. They can adjust to new situations, learn from their experiences, and make decisions using their own internal systems.
For example:
- AutoGPT is an AI agent that can generate human-like text responses. It can comprehend the context of the conversation and generate relevant responses accordingly.
- BabyAGI is an autonomous AI agent that can independently learn and perform tasks like understanding natural language, analyzing images, identifying objects, following simple commands, etc.
- AgentGPT is an intelligent virtual agent designed to interact with customers and provide them with personalized recommendations. It can understand natural language and provide relevant responses based on customer queries.
Both AI tools and AI agents can perform tasks autonomously to an extent. So what sets them apart? What qualifies an AI tool as an agent? Let’s find out!
Characteristics of an AI agent
While AI tools and agents are software programs designed to automate tasks, specific key characteristics differentiate AI agents as more sophisticated AI software.
You can consider an AI tool as an AI agent when it has the following characteristics:
- Autonomy: An AI virtual agent is capable of performing tasks independently without requiring constant human intervention or input.
- Perception: The agent function senses and interprets the environment they operate in through various sensors, such as cameras or microphones.
- Reactivity: An AI agent can assess the environment and respond accordingly to achieve its goals.
- Reasoning and decision-making: AI agents are intelligent tools that can analyze data and make decisions to achieve goals. They use reasoning techniques and algorithms to process information and take appropriate actions.
- Learning: They can learn and enhance their performance through machine, deep, and reinforcement learning elements and techniques.
- Communication: AI agents can communicate with other agents or humans using different methods, like understanding and responding to natural language, recognizing speech, and exchanging messages through text.
- Goal-oriented: They are designed to achieve specific goals, which can be pre-defined or learned through interactions with the environment.
So far, we have a basic understanding of an agent in AI or intelligent agent definition. But how does an AI agent work? Let’s break it down in the next section as we understand the structure of an agent.
Understanding the structure of an AI agent
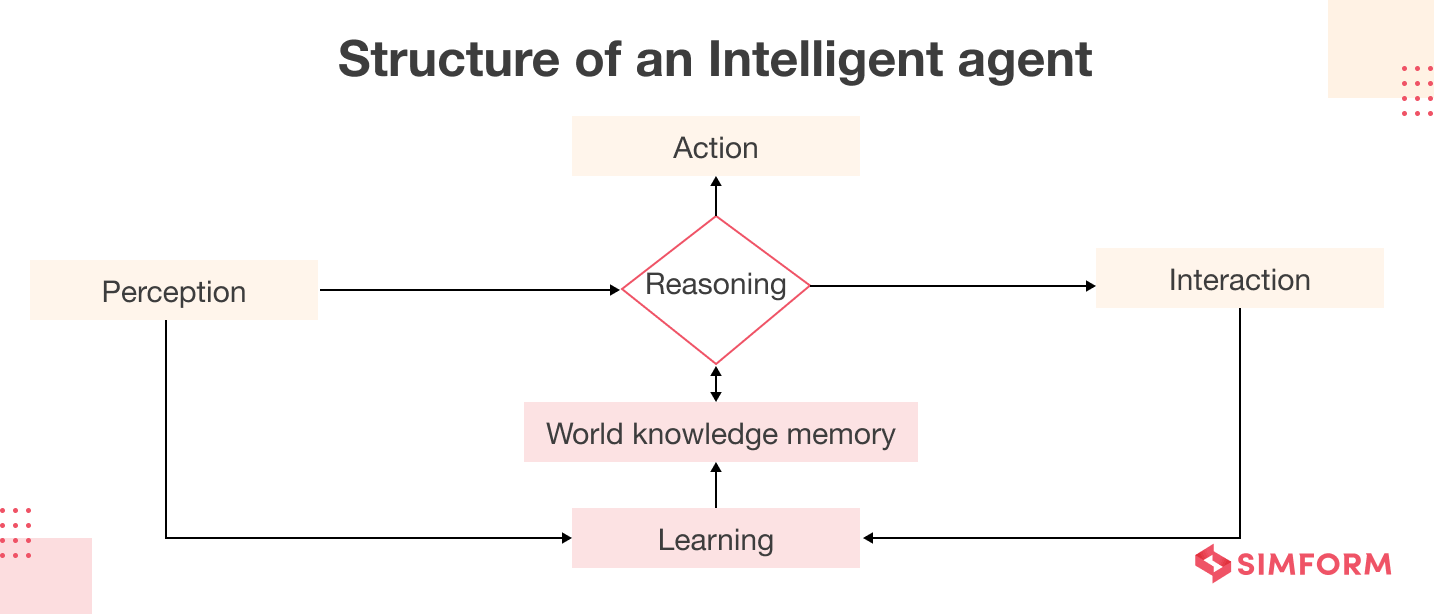
At its core, an AI agent is made up of four components: the environment, sensors, actuators, and the decision-making mechanism.
1. Environment
The environment refers to the area or domain in which an AI agent operates. It can be a physical space, like a factory floor, or a digital space, like a website.
2. Sensors
Sensors are the tools that an AI agent uses to perceive its environment. These can be cameras, microphones, or any other sensory input that the AI agent can use to understand what is happening around it.
3. Actuators
Actuators are the tools that an AI agent uses to interact with its environment. These can be things like robotic arms, computer screens, or any other device the AI agent can use to change the environment.
4. Decision-making mechanism
A decision-making mechanism is the brain of an AI agent. It processes the information gathered by the sensors and decides what action to take using the actuators. The decision-making mechanism is where the real magic happens.
AI agents use various decision-making mechanisms, such as rule-based systems, expert systems, and neural networks, to make informed choices and perform tasks effectively.
5. Learning system
The learning system enables the AI agent to learn from its experiences and interactions with the environment. It uses techniques like reinforcement learning, supervised learning, and unsupervised learning to improve the performance of the AI agent over time.
By understanding the environment, sensors, actuators, and decision-making mechanisms, developers can create AI agents to perform specific tasks accurately and efficiently. As AI technology evolves, we can expect new types of AI agents with even more sophisticated structures and capabilities.
With the AI agent definition and intelligent agent purpose known to you, it’s time to dive deeper into the agent function and analyze how an AI agent works in our upcoming section.
How does an AI agent work?
An AI agent works by perceiving its environment, processing information, and taking action to achieve specific goals or tasks. The process usually involves the following steps:
Step 1: Perceiving the environment
An autonomous AI agent first needs to gather information about its environment. It can do so using sensors or collecting data from various sources.
Step 2: Processing input data
The agent takes the knowledge gathered in Step 1 and prepares it for processing. This may include organizing the data, creating a knowledge base, or making internal representations that the agent can understand and work with.
Step 3: Decision-making
The agent uses reasoning techniques like logic or statistical analysis to make an informed decision based on its knowledge base and goals. This can involve applying pre-determined rules or machine learning algorithms.
Step 4: Planning and executing an action
The agent makes a plan or a series of steps to reach its goals. This may involve creating a step-by-step strategy, optimizing resource allocation, or considering various limitations and priorities. Based on its plan, the agent executes all the steps to achieve the desired goal. It can also receive feedback or new information from the environment, which can be used to adjust its future actions or update its knowledge base.
Step 5: Learning and Improvement
After taking action, the agent can learn from its own experiences. This feedback loop allows the agent to improve performance and adapt to new situations and environments.
In conclusion, autonomous AI agents collect and analyze data, preprocess it, make decisions based on machine learning algorithms, take action, and receive feedback. Now, let us simplify the working of an autonomous AI agent by taking the example of AutoGPT and BabyAGI, the modern-day and most commonly used autonomous agents.
What is AutoGPT?
AutoGPT is like a smart assistant that can handle tasks on its own. It uses the power of GPT-4 and GPT-3.5, the Large Language Models (LLMs), to complete tasks without needing constant instructions. Unlike other models that rely on specific prompts, AutoGPT comes up with its own prompts to achieve its goals. Interestingly, its abilities go beyond the fed database; it can also search the web or other external sources to gather and filter out authentic information.
How does AutoGPT work?
Because AutoGPT is a recursive AI model, it overcomes traditional AI limitations by using its own results to tackle complex tasks. Here is how the model processes input and delivers relevant output:
1. Giving it a name and a role: When you start AutoGPT, give it a name and tell it what it needs to do. This helps the system understand the task and make decisions accordingly.
2. Training on the provided data: AutoGPT begins by learning from the information you provide. It studies the data to understand its patterns and details, helping it grasp the task better.
3. Generating prompts: With its knowledge base in place, AutoGPT develops its own prompts based on what it needs to achieve. These prompts serve as the basis for its decision-making, guiding it through the tasks.
4. Collecting data independently: AutoGPT doesn’t rely only on the initial data. It autonomously searches the internet and other sources, gathering more information to improve its understanding and accuracy.
5. Evaluating and filtering data: The system carefully examines the collected data, checking its authenticity and relevance. It removes any incorrect or low-quality information, making sure its knowledge base is reliable.
6. Continuous improvement: AutoGPT believes in constant refinement. It learns from the results it generates and uses feedback to adapt and enhance its future responses. This ongoing process helps the system refine its strategies and improve over time.
7. Generating the output: Finally, AutoGPT produces its output based on its reasoning process. It combines what it has learned, the filtered data, and the context to generate a well-informed and suitable response to the given task.
AutoGPT unveils itself as an independent problem-solver with impressive decision-making skills. It showcases the sheer power of AI, providing a glimpse into the potential of intelligent systems that effortlessly handle complex tasks with minimal human input. Arguably, AutoGPT paves the way for a future where machines become trusted partners in navigating our intricate world.
What is BabyAGI?
BabyAGI is a fascinating concept in the field of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). It’s based on generative AI and focuses on recreating the cognitive abilities seen in young children. This research project focuses on building AI systems capable of learning and gaining knowledge from diverse sources, just like young children do!
More specifically, BabyAGI is an advanced computer program that operates with a remarkable level of autonomy. It can work independently, accomplishing tasks without users having to provide specific instructions. BabyAGI is built upon a combination of powerful programs, including Chat GPT-4, LangChain, and Pinecone.
When an AI uses other programs or tools to accomplish tasks, it is known as Stacking. Baby AGI is one of the more robust Stacking tools created and built on Chat GPT-4. You can use this technology for various applications, including language translation, image recognition, and decision-making processes. BabyAGI is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the AI industry.
How does BabyAGI work?
Baby AGI is a Python script that leverages the capabilities of OpenAI and Pinecone APIs, along with the LangChain framework, to manage and execute tasks. Its process involves generating tasks based on high-level objectives predefined by the user.
Using OpenAI’s natural language processing (NLP) abilities, the BabyAGI system creates new tasks aligned with the objectives. Moreover, it uses PineCone to store task results and the LangChain framework to make decisions.
Here’s how the system operates in a loop with four steps:
- 1. Retrieve the first task from the task list.
- 2. Send the task to the execution agent, which utilizes the OpenAI API to complete the task based on the available context.
- 3. Store the result in Pinecone for future reference.
- 4. Generate and prioritize new tasks based on the previous task’s objective and outcome.
This continuous loop ensures that tasks are consistently executed, prioritized, and updated based on the desired objective.
While the development of a true BabyAGI is still a long way off, there’s daily progress towards a more comprehensive performance. AI experts are actively researching and experimenting to create an AI system that can truly understand and navigate the world like a young human.
What are the type of AI agents?
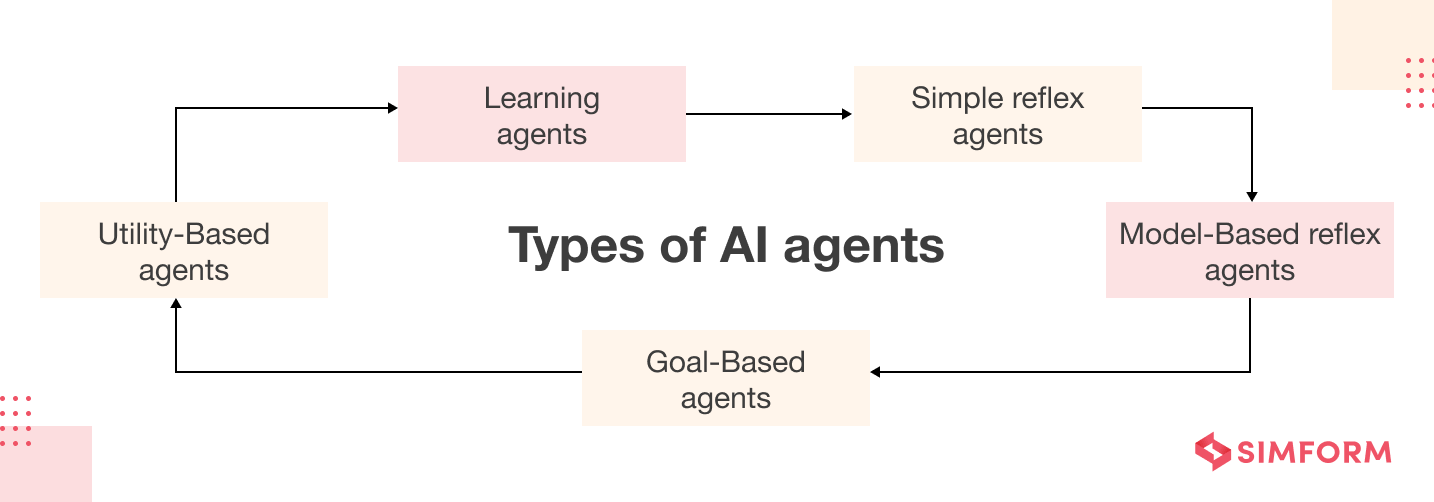 Here are the five main types of AI agents:
Here are the five main types of AI agents:
- Simple reflex agents are programmed to respond to specific environmental stimuli based on pre-defined rules.
- Model-based reflex agents are reactive agents that maintain an internal model of the environment and use it to make decisions.
- Goal-based agents execute a program to achieve specific goals and take actions based on evaluating the current state of the environment.
- Utility-based agents consider the potential outcomes of their actions and choose the one that maximizes the expected utility.
- Learning agents execute machine learning techniques to improve their decision-making over time.
Components of AI agents
AI agents comprise many key components that work together to perceive, reason, and act in their environment. Understanding these components will help you grasp how AI systems function and make decisions.
Sensors: These allow the models to gather information from its surroundings, much like human senses. For a robot, sensors might include cameras for vision, microphones for hearing, or touch sensors for physical interaction. In software agents, sensors could be data inputs or API connections.
Perception module: This processes the raw sensor data into meaningful information. It involves tasks like image recognition, speech-to-text conversion, or data preprocessing. The perception module essentially interprets the world for the AI.
Cognitive architecture: It encompasses the AI’s knowledge base, reasoning mechanisms, and learning algorithms.
- The knowledge base stores information and rules the AI uses to make decisions.
- Reasoning mechanisms allow the AI to draw conclusions and plan actions based on knowledge and current perceptions.
- Learning algorithms enable the AI to improve its performance over time by adjusting its knowledge and decision-making processes.
Decision-making: It uses processed information and cognitive architecture to determine the best course of action. Depending on the AI’s design and purpose, this might involve techniques like search algorithms, planning systems, or neural networks.
Actuator: It carries out the chosen actions. In a physical robot, actuators might be motors or mechanical parts. For software agents, actuators could be functions that modify data, send messages, or control other systems.
These components are continuous: sense, perceive, think, decide, and act. Understanding this structure can help you better conceptualize how AI agents operate and interact with their environment.
What are the advantages of using AI agents?
AI agents offer businesses the potential to streamline operations, make informed decisions, improve customer experiences, and drive growth and competitiveness in the digital age.
1. Increased efficiency
AI agents can automate repetitive tasks, allowing businesses to complete them faster and more accurately. This efficiency improvement frees employees’ time to focus on more business-critical tasks and improves productivity.
2. Better decision-making
AI agents can analyze large amounts of data and provide valuable insights to support decision-making processes. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning, AI agents can identify patterns, trends, and correlations that humans may overlook.
3. Improved customer experience
AI agents can provide personalized and timely interactions with customers, enhancing their experience. They can offer instant support, answer queries, and provide recommendations, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Cost savings
By automating tasks, AI agents can reduce the need for human resources and manual labor, resulting in cost savings for businesses. They can handle high-volume, repetitive tasks without fatigue or errors.
Most common challenges you may face while using an AI agent
Autonomous AI agents have become increasingly popular in recent years, with many brands implementing them for various purposes. However, several challenges come with using these agents. Some of the most common challenges are:
- Data bias: An autonomous artificial intelligence agent program relies heavily on data to make decisions. If the data they use is biased, it can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Amazon’s AI recruiting tool was biased against women, leading to a skewed hiring process.
- Lack of accountability: Proactive agents can make decisions without human intervention, so holding them accountable for their actions can be difficult. Uber’s autonomous vehicle that struck and killed a pedestrian in 2018 raised questions about who was responsible.
- Lack of transparency: The decision-making processes of a learning agent can be complex and opaque, making it difficult to understand how they arrive at certain decisions.
- Ethical considerations: A rational agent can make decisions with ethical implications, and it can be challenging to program them to make ethical decisions. Microsoft’s chatbot, Tay, was shut down after it started making racist and sexist comments.
- Security risks: Software agents can be vulnerable to cyber attacks, compromising their decision-making processes or leading to data breaches.
- Lack of adaptability: Autonomous AI agents act according to their training data, which means they can struggle to adapt to new situations or contexts.
What are the applications of AI agents?
Autonomous AI agents have numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Healthcare: Autonomous artificial intelligence agents can assist in diagnosing, treating, and monitoring patients. IBM Watson Health is an AI agent that can analyze medical data to identify potential health issues and recommend treatment options.
- Finance: They can analyze financial data, detect fraud, and make investment recommendations. Charles Schwab uses an AI agent called Intelligent Portfolio to create and manage portfolios based on customers’ investment goals.
- Retail: Agents can provide personalized recommendations, improve supply chain management, and enhance customer experience. Amazon’s Alexa is an AI agent that can recommend products, place orders, and track shipments.
- Manufacturing: Intelligent agents can optimize production processes, predict maintenance needs, and improve product quality. General Electric uses an AI agent called Predix to monitor machines in real-time to predict and prevent equipment failures.
- Transportation: Autonomous AI agents can assist in route planning, traffic management, and vehicle safety. Tesla’s Autopilot helps drive a vehicle autonomously and helps the driver park, lane change, and safe driving.
- Education: They can provide personalized learning experiences, automate administrative tasks, and analyze student performance. Pearson’s AI agent, Aida, can provide feedback to students and suggest personalized learning paths.
- Agriculture: AI agents can optimize crop production, monitor soil quality, and predict weather patterns. John Deere uses an AI agent called See & Spray to detect and target weeds without affecting crops.
What does the future hold for AI agents?
The future of autonomous AI agents is full of exciting possibilities. As organizations realize the potential for enhanced efficiency and productivity, the use of autonomous agents is expected to soar.
A significant trend on the horizon is the customization of AI agents to meet the specific needs of businesses. As these agents become more common, it will be crucial to tailor their algorithms, data inputs, and outputs to align with each organization’s unique goals and processes.
The decision-making capabilities of AI agents are also set to undergo significant enhancements. With their increasing sophistication, these agents can effortlessly analyze vast amounts of data, providing predictions and recommendations that would otherwise require considerable human effort.
However, as the influence of autonomous agent programs expands, ethical considerations come to the forefront. Questions surrounding privacy, bias, and accountability emerge as the deployment of these agents becomes more widespread. Balancing the tremendous potential of these AI systems with the ethical implications they pose will be a critical aspect of their future development.
Want to integrate AI agents into your existing ecosystem?
From virtual assistants to chatbots and self-driving cars, agents in artificial intelligence are changing how we live and work. It isn’t an overstatement that AI agents are the future, and businesses that fail to adapt will be left behind.
Simform is an experienced AI/ML solutions company that helps businesses integrate AI agents into their ecosystems.
We can help you develop cutting-edge agent solutions that help you streamline your processes, cut operational costs, and get a competitive edge in the market. Don’t get left behind in the race to the future. Connect with our industry experts to learn how they can help you make the most of AI agents for your business.