The digital product development process involves market research to validate the product idea and prototyping, building, and testing the product. It also includes the activities associated with making the product live and maintaining it.
Each stage in the product development process requires a specific skill set and various resources. So it’s a significant investment, and organizations must plan it meticulously.
But why do you need digital product development?
A PWC survey estimates a 19% increase in the efficiency of business operations and a 13% reduction in production costs after building digital products for both internal and external users.
These numbers emphasize how digital product development is critical for companies looking to increase productivity, reduce costs, and better serve their customers.
This article will focus on the digital product development process, its stages, and the requirements of each stage. Let’s begin by understanding what digital product development exactly means.
What is digital product development?
Digital products are assets created using programming code, offering a specific benefit or value to the end user who interacts with them. These assets comprise mobile, desktop, web applications, digital dashboards, and control applications, among many others.
A piece of software can be considered a digital product if it,
- Provides a solution or service to a specific user need or problem
- Is developed with a customer-centric approach, meaning the software is designed and developed with the user’s needs and preferences in mind
- Has a clear value proposition and revenue model that justifies its development and ongoing maintenance costs
Some benefits of digital product development:
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Cost-effective compared to traditional product development
- Scope for customization and personalization
- Greater accessibility and reach to a broader audience
- Ability to collect and analyze valuable data insights
- Improved customer experience and satisfaction
- Ability to scale the business to meet growing demand
- Greater flexibility to adapt to changing market trends and user needs
A quick glance at the digital product lifecycle
Before we dive into the subject of digital product development, let’s quickly go over the concept of the lifecycle of a digital product. Every product undergoes its unique expedition in the market, known as the product life cycle.
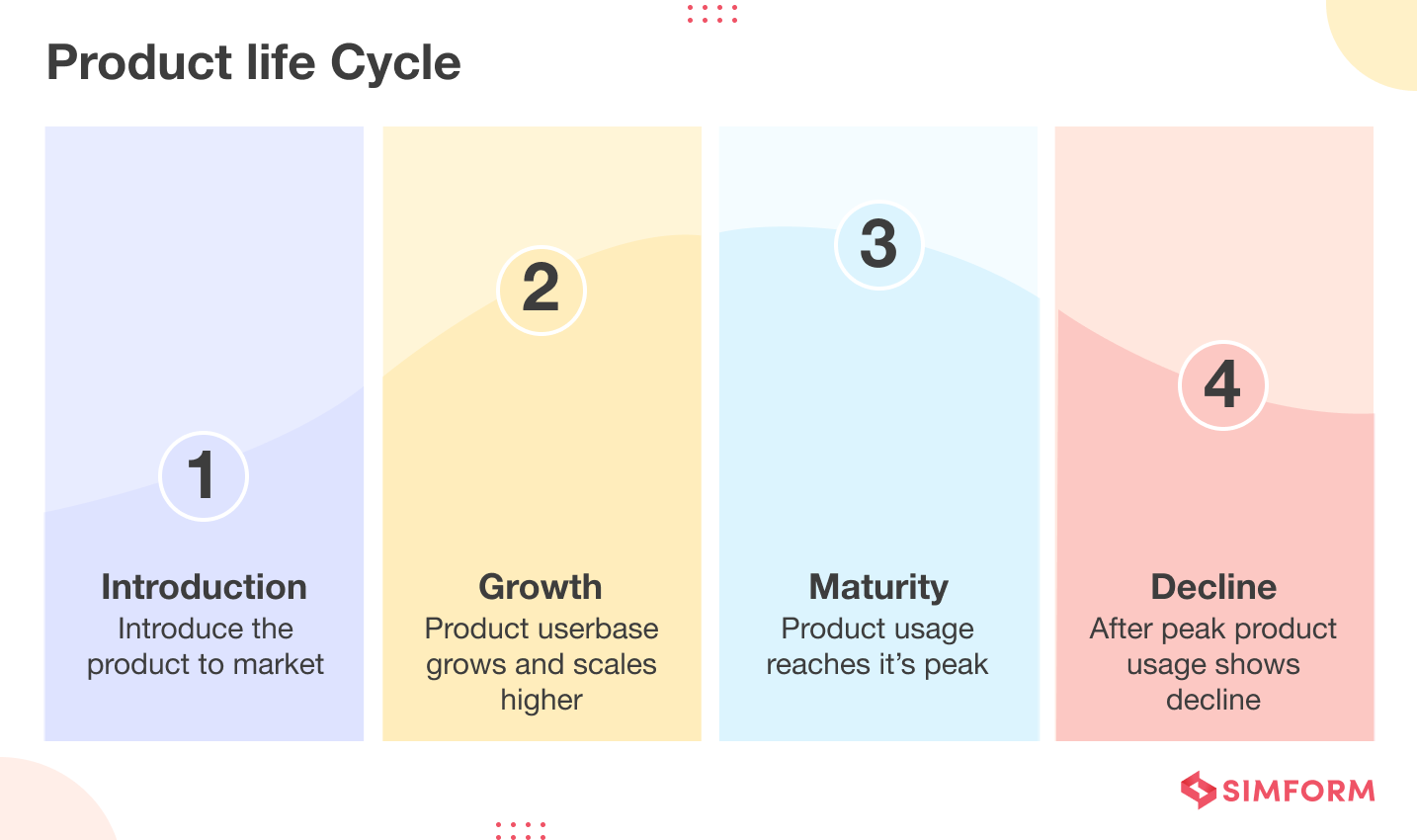
The product lifecycle typically entails four phases: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
- The introduction is when a product is launched into the market.
- The growth phase is when the market adoption of a product is picking up.
- The maturity phase is when the sales growth declines and the product reaches its market saturation point.
- The decline phase is marked by decreased sales and the product replacement in the market with better alternatives.
A thorough understanding and planning of the digital product lifecycle
- Helps businesses conduct more targeted and effective market research
- Guides product designers on how to design the product in a way that is adaptable to the changing needs of the market
- Assists engineering teams identify the potential issues that may arise during the different stages of the lifecycle so they can keep those considerations in mind while developing the product
Overall, understanding the digital product lifecycle can help optimize the development process, ensuring that you build relevant and profitable products throughout their lifecycle.
6 stages of digital product development
#1. Research and analysis
The first stage of digital product development is researching the market and identifying a problem to solve. This also involves conducting user research to determine your target audience’s needs.
Conduct market research
There are many ways to conduct market research, but using an agile approach makes more sense. Its continuous nature makes market research different from the conventional approach. The entire research process will have several iterations, continuously improving the data quality.
Understand the target audience
Understanding your target audience’s characteristics and behavior will enable your design and development teams to create a product that resonates with the audience and provides a valuable user experience. Here are some ways to gain insights into your target audience:
- Conduct market research to gather data about your potential customers’ demographics, behaviors, needs, and preferences.
- Create buyer personas that include demographic information, behaviors, goals, and pain points.
Analyze competitors
Before you even begin to ideate your digital product, conduct a thorough competitive analysis to identify the market gaps and understand customer needs. Here are some steps to follow when analyzing your competitors:
- Identify your direct and indirect competitors.
- Analyze your competitors’ product offerings, including features, functionalities, and pricing.
- Study your competitors’ marketing strategy, including their messaging, channels, and tactics.
- Evaluate your competitors’ user experience, including their website, app, and other digital touchpoints.
- Identify gaps in the market that your competitors are missing out on.
Conduct user research
Comprehensive user research helps ensure that your digital product will meet the needs and expectations of your potential users. It also helps validate assumptions and improve usability.
Here is how to conduct user research:
- Define the research goals and objectives.
- Choose a suitable method for research, such as surveys or interviews.
- Recruit participants aligned with your target audience.
- Develop a questionnaire to gather data.
- Use observation and recording tools to capture user behavior.
- Analyze the research data to identify patterns.
#2. Ideation and concept development
Before starting the ideation process, it is essential to understand the digital landscape. Knowing your target audience, market trends, and industry standards is crucial in creating a successful digital product.
Use mind maps
Using mind maps is a great way to encourage brainstorming and come up with new digital product ideas. Mind mapping facilitates the visualization of complex ideas and helps organize them into a well-defined product strategy.
The best way to do it is to start with a central idea and branch out to related concepts. For example, let’s say you want to build an eCommerce application for printed t-shirts
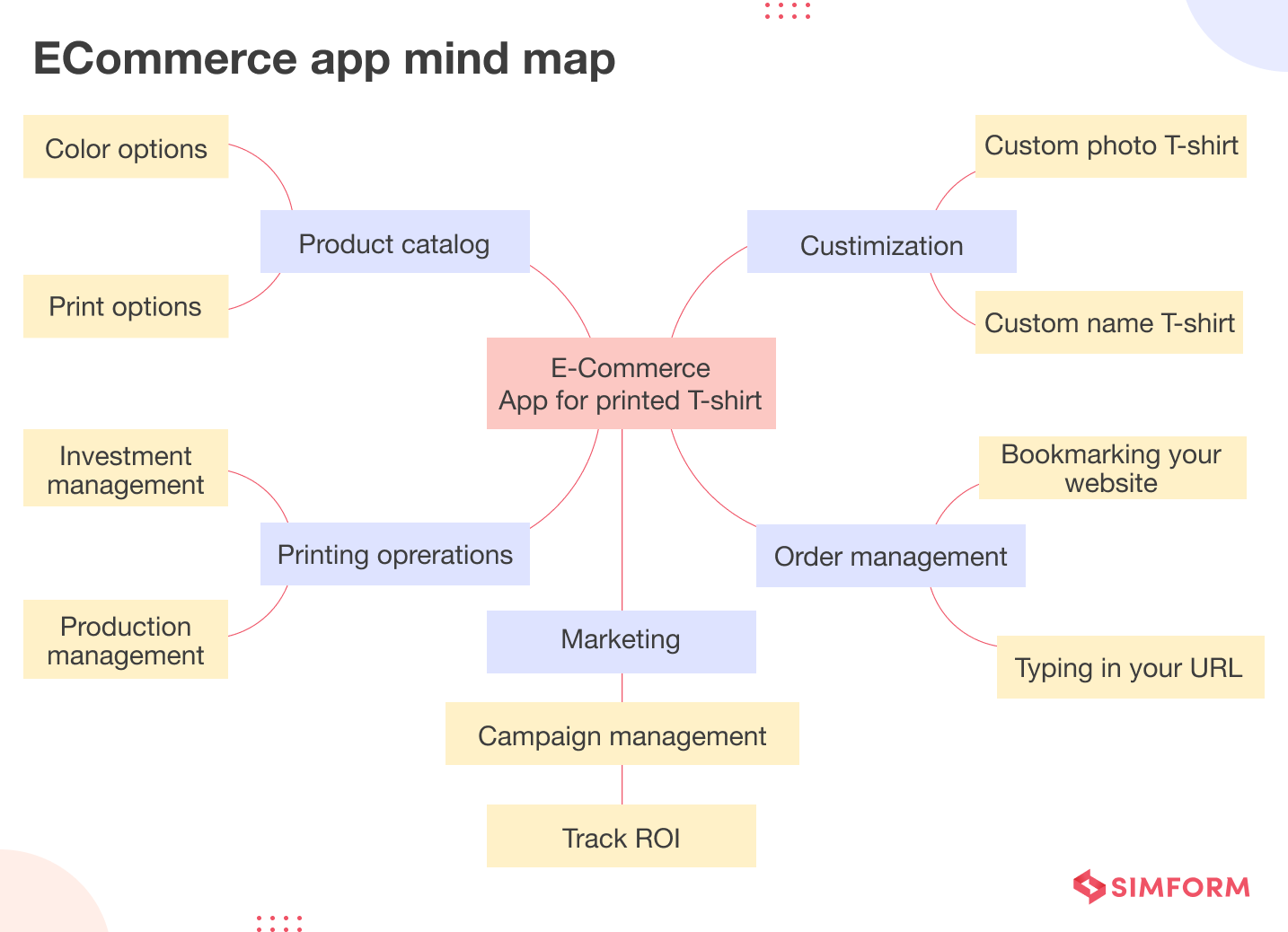
The mind map will help you keep the central idea of the eCommerce app at the core, branching out into different functions like catalog, order, customizations, and operations management.
Refine ideas and develop a product concept
After the ideation process, the next step is concept development, which begins with refining ideas. Several ideas on the mind map have a specific hierarchy representing priority.
However, you must refine and align these ideas with your organizational goals. Here’s how to do that:
- Have a list of potential ideas, and prioritize them based on factors such as feasibility, user demand, potential revenue, and market competition.
- Align ideas with the target audience’s characteristics, behaviors, and preferences.
- Test ideas through surveys, focus groups, and prototyping.
- Get feedback from your potential users, industry experts, and stakeholders
Once initial ideas are refined, concept development becomes easy. Concept development involves several key steps:
- Define the problemthat your digital product aims to solve. This will offer clarity of project requirements and scope.
- Craft user personas that help teams understand the user’s needs, goals, and behavior to develop a product that meets their requirements.
- Create user journey maps tovisualize the user’s experience with the digital product. This involves creating a timeline of user interactions and identifying pain points to improve the experience.
You have researched the market, done competitor analysis, and created the product concept, but the design stage is where all these activities act as valuable input. WHY SO?
As Steve Jobs and Jonathan Ive would have said, “ A design is not just about looks and how it will look on the surface. It needs to reflect the essence of a product.”
#3. Design and prototyping the digital product
The design stage begins with some basic questions which help define the vision of the digital product,
- Why do you need the digital product?
- What will the product achieve?
- How will you achieve the digital product’s vision?
- Who will use the product?
- How will the product solve the user’s problem?
You must have found answers to some questions, like who will use the product and what problems it will solve, by the end of the first two stages – market research and concept development.
However, you will need more data for the product design process to produce desired results.
An ideal product design process involves:
- Specifying design specifications which include a digital product overview, target audience, user requirements, branding style, and other specific needs.
- Creating wireframes based on the design specifications to help bring the product vision to life. Wireframes also offer visualization of a digital product’s functionality and layout before any actual design work takes place.
- Designing UIs and creating high-fidelity prototypes that involve several wireframes refinements, ultimately improving the design’s fidelity.
Lastly, a digital product design process requires usability testing to ensure high-fidelity prototypes deliver what you aim for.
Conduct usability testing
Usability testing is a process of observing, watching, listening, and taking notes while the user interacts with the prototype to identify problems with the design. Such tests will have participants complete specific tasks using the prototype.
There are different types of usability tests,
- Formative usability testinghelps to “form” the design for a digital product. It allows you to understand whether a user likes or dislikes the product and if they need it.
- Summative testing assesses the product design, which is a summation of the effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction that a user experiences. It helps to validate or verify how effective repeatable processes are.
- Qualitative vs. quantitative testing helps you research user behavior while interacting with the digital product and complex data. It allows you to understand what prevents users from completing a task and what percentage of users could complete specific tasks.
- Moderated vs. unmoderated tests are two types of usability testing: one requires a moderator/facilitator, while the other is an automated process.
A design without execution is just an idea on paper!
Elon Musk says Twitter had many employees but little product developmenthttps://t.co/fdfvb69aQd
— FOX Business (@FoxBusiness) April 18, 2023
As the above tweet puts it- ‘You need product development efforts even if you are a giant like Twitter!’
#4. Development stage
Digital product development begins by defining what processes and technologies you need to execute the design. Defining the processes requires clarity on which development approach you will use.
There are two significant digital product development approaches that you can use,
- Waterfall approach
- Agile development
Adopting the right development methodology: Waterfall vs. agile
A waterfall approach is a conventional approach where you must follow a specific sequence of processes before creating a finished product. Each stage begins only after the previous stages have been completed.
On the other hand, the agile approach follows a non-linear process flow. It has several incremental iterations, each of which is tested to get feedback for improvement of the digital product.
This iterative development process enables continuous improvement in the digital product by offering better quality, flexibility, and reduced performance bottlenecks.
We always recommend adopting an agile approach and working with a DevOps culture to ensure development efficiency and improved productivity. Agile methodologies enable development teams to respond quickly to changing requirements and deliver value to customers in a timely manner.
Meanwhile, DevOps culture focuses on collaboration between development and operations teams, allowing for continuous code integration, delivery, and deployment.
Once you have determined which development approach your teams will adopt to build the digital product, the next step is to find the appropriate tech stack that aligns with the design specifications and the project’s technical requirements.
Building an appropriate technology stack
A tech stack for digital product development includes technologies for frontend, backend, database infrastructure, testing, and deployment. The tech stack you use will significantly impact the product’s performance, scalability, security, and development time.
Several factors need consideration when choosing a tech stack for digital product development. For example, if you choose a front-end technology for UI development, you must check whether it is compatible with your backend. Further, you also need to consider the underlying architecture a frontend framework offers.
Other factors you should consider are,
- Scalability – can the tech stack handle growth?
- Flexibility – can the tech stack adapt to changing needs?
- Developer Skill Set – do your team members have expertise in the chosen tech stack?
- Budget – can you afford the necessary licenses and support?
- Time to Market – can the tech stack help you launch quickly?
- Security –does the tech stack have robust security features to protect your product and users?
Setting up the infrastructure for your development process
Setting up infrastructure is a crucial step for digital product development because your teams will need to store, analyze, and process lots of data during the entire lifecycle. An eCommerce business’s storage of users’ financial data is a simple example.
Infrastructure requirements increase as the business scales, so you need to ensure higher flexibility. One way to ensure your infrastructure can meet changing business needs is to use cloud infrastructure.
A few reasons why you should consider opting for cloud infrastructure:
- Higher scalability with on-demand resource scaling capabilities
- Better cost efficiency due to the reduced need for physical servers
- Improved accessibility with remote access to cloud-based resources
- Enhanced reliability with built-in redundancy and backup options ensuring uptime
- Easy collaboration across cloud-based services and platforms, improving productivity and remote capabilities
- Robust security with effective identification and access management (IAM)
Developing the digital product
This is the stage where your team finally begins to code for your digital product. However, we recommend building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) first and testing it before investing resources into building the final product.
It will help you ship a minimal product, test it and get feedback for incremental improvements.
Developing the digital product will require several iterations in an agile development approach. With each iteration, you can leverage testing and quality assurance to ensure continuous improvement.
#5. Testing and QA stage
Testing during digital product development requires effective planning, building test cases, and executing and analyzing the result. The testing process involves conducting various tests on the product to validate its functionality and performance.
Different types of tests that you can conduct are unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing. Each type of testing focuses on different aspects of the product and helps identify issues or bugs that need to be addressed.
On the other hand, Quality Assurance(QA) involves establishing standards and processes to ensure the product meets the required quality standards. This includes defining testing protocols, setting quality metrics, and monitoring the product at every stage of development.
Some key tips for testing and QA are:
- Define the goals and requirements for the software being tested to ensure that the product meets the needs of its users.
- Develop detailed test cases that cover all possible scenarios and edge cases to ensure that the software is thoroughly tested.
- Use automation tools to automate repetitive testing tasks, such as regression testing, to increase efficiency and reduce errors.
- Test your digital product in real-world environments that replicate the conditions in which it will be used.
- Keep a detailed record of any issues found during testing and track them through to resolution.
- Involve stakeholders, such as end-users and business owners, in the testing process to ensure that the product meets their expectations.
#6. Launch and maintenance of digital products
You begin this stage by establishing a clear roadmap and timeline for launching and maintaining your digital product. This includes defining the product’s goals, scope, and target audience, as well as outlining the features, functionality, and design requirements.
That’s where Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) comes to the fore. CI/CD helps automate the deployment process, making deployment of updates faster.
The process of launching your digital product should include the following steps:
- Establish a clear roadmap and timeline for the launch of the digital product.
- Define testing and quality metrics by identifying the test environments, tools, and techniques needed to ensure the product is tested thoroughly.
- Set up monitoring tools like analytics and error tracking to track the product’s performance.
- Once the digital product is launched, leverage CI/CD pipelines for regular updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements.
Common digital product development challenges you may encounter
Developing a digital product can be complex and fraught with challenges. Some of the major digital product development challenges are:
1. Lack of comprehensive market research
Developing a product without conducting sufficient and accurate market research is one of the biggest mistakes most product companies fall prey to. A product not in sync with the market demand will not generate revenue.
Before developing a digital product, it is important to identify the target audience, their pain points, and their needs.
2. Budget constraints
Digital product development can be an expensive process. A limited budget can restrict the scope of the product and hinder its functionality. In such situations, it helps prioritize features and functionalities necessary for the product.
3. Unclear requirements
Unclear requirements can lead to delays in the development process and cause stakeholder miscommunication. Ensure your teams clearly understand the product requirements before starting the development process.
4. Integration with legacy systems
Many businesses have legacy systems that they rely on for their daily operations. Integrating a new digital product with existing systems can be a major challenge. Businesses must ensure that the new product can seamlessly integrate with legacy systems without any disruptions.
5. Ensuring cybersecurity
Digital products are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, which can compromise sensitive data and cause reputational damage. Cybersecurity measures should be implemented to protect the product from potential threats.
6. Limited technical expertise
Developing a digital product requires technical expertise that may not be available in-house. Businesses may need to hire external developers or partner with a development company to overcome this challenge.
7. Changing technology landscape
The technology landscape is constantly evolving. Businesses need to ensure that their digital product remains relevant and up-to-date in the face of changing technologies.
8. Shortening the time to market
The time to market for a digital product is critical. The longer it takes to develop and launch a product, the greater the risk of losing market share to competitors. Rapid development methodologies such as Agile can help businesses reduce the time to market.
How Simform helped reduce TAT by 70% with digital product development
Developing a digital product needs consistent efforts across the stages, including the ideation stage, conceptualization, design, and development. You must ensure digital product development and deployment is up to the mark to deliver seamless performance.
This was the same challenge a leading manufacturer faced while digitally transforming its processes. Simform helped the transmission parts manufacturers by creating database-driven solutions to digitize and automate their RFQ lifecycle.
We leveraged Azure Cloud and automated rules to reduce the turnaround time for generating quotations. We also helped them choose the right tech stack with our CTO-as-a-Service offering.
As a result, the client can now work with better processes and generate faster quotations with a 70% reduction in turnaround time.
If you are looking for solutions to improve your processes or serve your customers better, we would love to help you! Just share your requirements here, and our consultants will get in touch with you to discuss the project viability and cost estimations.
