With the rise in demand for and competition among digital products, product managers need to have a strategy for managing their digital products’ lifecycles. Digital product lifecycle management involves consistently updating and improving the product based on user feedback, research, and market trends to keep it competitive, relevant, and profitable over time.
In this blog post, we will discuss managing a digital product lifecycle in detail, along with defining the different stages involved. Understanding these stages’ nuances can help product managers make informed decisions about product development, marketing, and strategy to ensure that their product remains competitive and profitable.
What is a digital product lifecycle?
A digital product lifecycle is a framework for describing the stages of a digital product’s life from its conception to retirement. It is divided into several phases, each with its own set of goals and activities.
To successfully introduce a digital product, it’s crucial to have a strategy for managing its lifecycle. Digital product lifecycle management involves consistently updating and improving the product based on user feedback, research, and market trends to keep it competitive, relevant, and profitable over time.
We will talk more about managing a digital product lifecycle in the latter section along with defining its stages in detail.
Digital product lifecycle stages
Each stage in the digital product lifecycle has unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities that product managers need to consider to maximize their product’s success. By understanding the nuances involved and the best practices for these stages, product managers can make informed decisions about product development, marketing, and strategy to ensure that their product remains competitive and profitable.
A product’s life cycle in the market actually begins once it has been deemed feasible and profitable enough to be developed, promoted, and released into the market. This progression sets the stage for how the product is marketed to consumers.
Furthermore, the initial launch of a product should increase demand and popularity, potentially replacing older products. As the product gains traction, marketing costs decrease along with associated production costs.
In such a case, managing the lifecycle stages can help increase profitability and maximize returns. But failing to do so may result in the product falling short of its potential and having a shorter shelf life.
Here are the different stages of a digital product lifecycle:
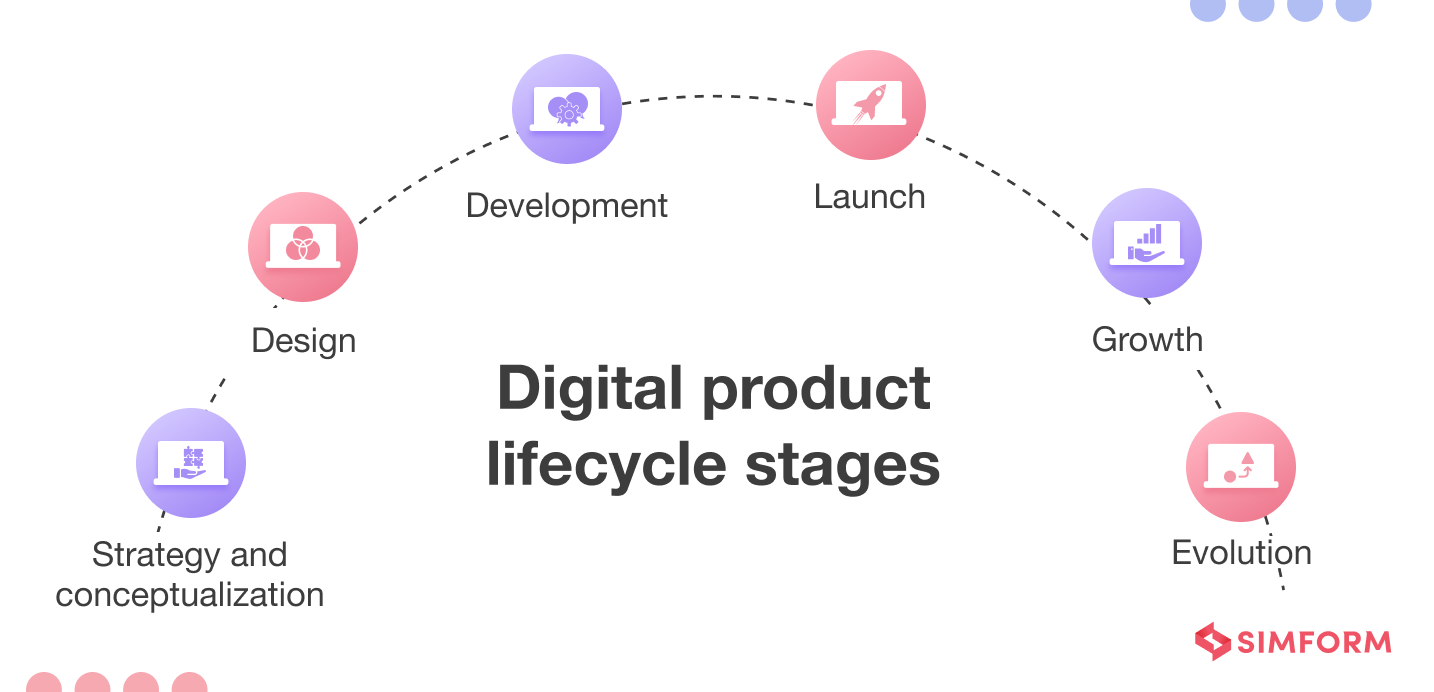
1. Strategy and conceptualization
The product strategy is the foundation of the digital product lifecycle. It involves defining the product’s vision, mission, and goals. A digital product strategy assists an organization to define the value it wants to deliver to its customers through digital tools.
Conceptualization is when the idea for the actual product is born. During this phase, product managers work on defining the product’s concept and creating a business plan. They conduct market research to identify potential opportunities, evaluate the competition, and gather insights into customer needs and preferences.
Based on this research, product managers create a product concept that outlines the product’s purpose, value proposition, target audience, and potential benefits. This phase also involves assessing the feasibility of the product by evaluating technical, financial, and resource constraints.

With a digital product strategy in place, businesses can implement a more aligned and straightforward approach to product development. Typically, product managers should aim for the following outcomes at the end of this phase:
- Creation and validation of user persona, which includes identifying their interests, concerns, needs, and goals
- Benchmarking and competitive analysis to identify competitors, market trends, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
- Defined value proposition and vision to highlight the promise of value the product offers and how it solves users’ needs and improves their lives
- Creation of a product strategy canvas to provide a 360-degree view of the product and business, including the definition of the business model and pricing
- Establishment of a set of objectives and key results, known as Product OKRs to focus on and track progress
2. Design
In the design phase, product managers work on creating a blueprint or prototype for the digital product. They collaborate with designers and development teams to create a user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design that aligns with the product strategy and meets the target audience’s needs. This includes designing the product’s layout, navigation, functionality, and visual elements.
Product design is built on the foundation of identifying the right market opportunity and defining the problem clearly. It then becomes a foundation itself for developing a sustainable solution and validating the same with the targeted user persona.
Digital product design can be narrowed down to three elements: System, interface, and process. Let’s have a quick overview of these elements:
- System Design
Before you start thinking about how your digital product should look, devise a plan stating how it should work to address the customers’ pain points. System design is about planning and organizing a solution to a problem before actually building it.
- Interface Design
Interface design involves layout, typography, color scheme, icons, buttons, and other graphical elements that visually represent the product’s features and functionalities. A well-designed interface enhances the user experience and influences how users perceive the product’s quality and value.
- Process Design
Process design involves identifying the steps an end-user must take to arrive at the desired outcome while using the product. Here you consider your customers and business needs and strike a balance between them.
At the end of the design phase, you should aim to produce:
- A list of required resources for project execution
- Story Sitemap
- A working prototype
- Clear product execution roadmap for developing Minimal Marketable Product (MMP)
- MMP wireframes
- Product design style guide
3. Development
In this stage of the digital product lifecycle, the focus is on actually building the product based on the design and specifications developed in the previous phase. Here the product team typically follows an agile methodology, which involves breaking down the development process into smaller, iterative cycles called sprints. Each sprint typically lasts for two to four weeks and involves developing a specific set of features or functionalities.
The development stage involves several key steps, including:
- Writing the code required to implement the product’s features and functionalities
- Testing the code to ensure that it works as intended and meets the desired quality standards
- Integrating the various components of the digital product to ensure that they work together seamlessly
- Deploying the digital product to a test environment to ensure that it works as expected
- Testing the digital product with a group of users to ensure that it meets their needs and is easy to use
- Identifying and fixing any bugs or issues that are identified during the testing process
- Refining the product based on feedback from users and stakeholders
The development stage is critical as it ensures that the digital product is built according to the design specifications and meets the needs of the target audience. It is an iterative process that requires continuous testing and refinement to ensure that the digital product meets the desired quality standards and is ready for release.
4. Launch
Once your product has undergone multiple testing and optimization phases, you can release its features simultaneously or go for a phased launch. A phased launch involves a gradual release of a product and its features, which allows for ongoing improvement.
There are different strategies you can adopt for the product launch:
- Soft Launch -This involves making the MVP available to a small group of early adopters within the target market.
- Hard Launch – Here, the MVP is released to the general market with a comprehensive marketing campaign
- Dark Launch—With this method, the MVP has already been launched, but new features are quietly introduced to a specific percentage of users to observe their response to the changes.
The launch phase in the digital product lifecycle also involves creating a marketing strategy and advertising campaign to promote the digital product. A well-executed launch can generate a significant amount of buzz and interest, leading to increased sales and adoption of the digital product.
Introducing a product is merely the beginning, as the ultimate goal for any business after the launch is to achieve growth, which we will discuss next.
5. Growth
During the growth phase, the digital product gains momentum in the market, and its user base grows rapidly. It marks an increase in sales and profitability. Here the business can start to benefit from the savings in production scale, obtaining a significant increase in its solution’s market share.
The growth phase is a critical phase in the digital product lifecycle as it determines the long-term success of the digital product. It requires a focus on user acquisition, retention, and monetization, as well as scaling and optimizing the product to meet the needs of the growing user base.
The goal of the growth phase is to establish the digital product as a market leader and position it for continued success in the future.
6. Evolution
To stay relevant, businesses need to adopt a growth mindset for their digital offerings, and continuously improve and add new features throughout the life cycle of the product.
To keep up with market growth, businesses should modernize their old existing systems using the latest technologies. This helps them stay ahead, improve efficiency, and maintain their competitive advantage.
Companies must choose the right approach based on project requirements to modernize applications. These approaches are rehosting, refactoring, re-architecting, or replacing legacy apps with SaaS-based systems for improved efficiency and user experience.
Best practices for digital product lifecycle management
Digital product lifecycle management encompasses the manner and time in which products are presented to the market, from development to growth, maturity, and evolution. It involves technology to help you develop, manage, and leverage your products to maximize profits.
An effective digital product lifecycle management (digital PLM) strategy offers a myriad of benefits to companies, like better decision-making, enhanced customer experience, increased efficiency, and compliance with prevailing industry standards.
Here we have outlined four best practices to help companies derive the most value from their digital PLM process:
1. Clearly define product strategy
Define a clear product strategy that aligns with your business goals, customer needs, and market trends. This works as a guiding light that positively impacts your decisions about product development and ensures it remains relevant and competitive.
A detailed product strategy includes:
- Digital product vision
- Plan to make the best of market opportunity
- Build timeframes for development
- Understand critical requirements for achieving goals like cost reduction or product performance improvement
Listing the goals and objectives in this way clearly indicates which processes should be prioritized and which ones can be delayed a little.
2. Review and update product strategy frequently
Saturation is unavoidable if you stick to the product strategy that you made initially. New technology trends are emerging at an unprecedented rate and your product will eventually exit the market if it fails the test of time.
Here are some steps you can take to keep your product strategy updated and aligned with the latest trends:
- Keep a close eye on industry news, competitor activity, and emerging trends.
- Regularly analyze customer feedback to identify pain points and areas for improvement.
- Conduct regular market research to identify new opportunities and understand your target audience better.
- Continuously review and analyze product metrics such as user engagement, retention rates, and customer satisfaction.
3. Create a clear project plan
When implementing a PLM strategy, creating a project plan that includes future milestones for your product is best. Set deadlines for completing these milestones as well.
Establishing clear deadlines can enhance workflow efficiency and boost team productivity. Further, assigning a point of contact is essential to understand and solve any queries related to the implementation.
However, make sure that you review and update your product roadmap regularly to ensure that it aligns with your product strategy and incorporates the latest market trends and customer needs.
4. Select and train professionals accordingly
It’s essential to train employees on the usage and benefits of these solutions before implementing them. Also, you need to show why the new solution is different from the existing one.
Here web-based and classroom instruction can aid understanding and promote success. This increased understanding can improve efficiency and better control over the entire development process and data.
Optimize the lifecycle of your digital product with Simform
The process of digital product lifecycle management never ends. Understanding and managing the same is crucial for business leaders to meet market needs using appropriate resources and tactics based on the product’s stage.
This is where digital product engineering services come into the picture. Partnering with an experienced product development and management partner equips you with a range of technical expertise and support throughout the product lifecycle, from conception to delivery and evolution.
As a leading digital product engineering company, we have the skill and extensive experience to prioritize scalability, security, reliability, resilience, and fault tolerance to ensure steady product growth. Connect with our experts for a free consultation on 360-degree product development and growth strategy for your digital solution.