What a year it had been! 2023 will be forever etched in history as the moment when generative AI made its grand entrance—opening up game-changing new technological possibilities one after another!
Soon, the names like ChatGPT and DALL-E were universally recognized. Industry sectors, including healthcare, banking, and high tech, quickly warmed up to exploring new opportunities.
Meanwhile, before we knew it, AI-generated content filled the Internet. Deepfakes and voice clones became widespread, raising various ethical concerns. Sure, challenges and concerns are inevitable, but should they stop businesses from assessing the impact and benefits generative AI can bring? Most certainly not!
But then, adopting generative AI can be a complex process, as it requires a thorough understanding of its potential applications and limitations. Observing and understanding the way other businesses are moving forward can give companies valuable insights.
And so, we surveyed 656 business leaders across 8 key sectors to benchmark current and planned adoption of generative AI, summarize beneficial use cases and business impacts so far, and provide balanced, data-driven insights around priorities and safeguards needed moving forward.
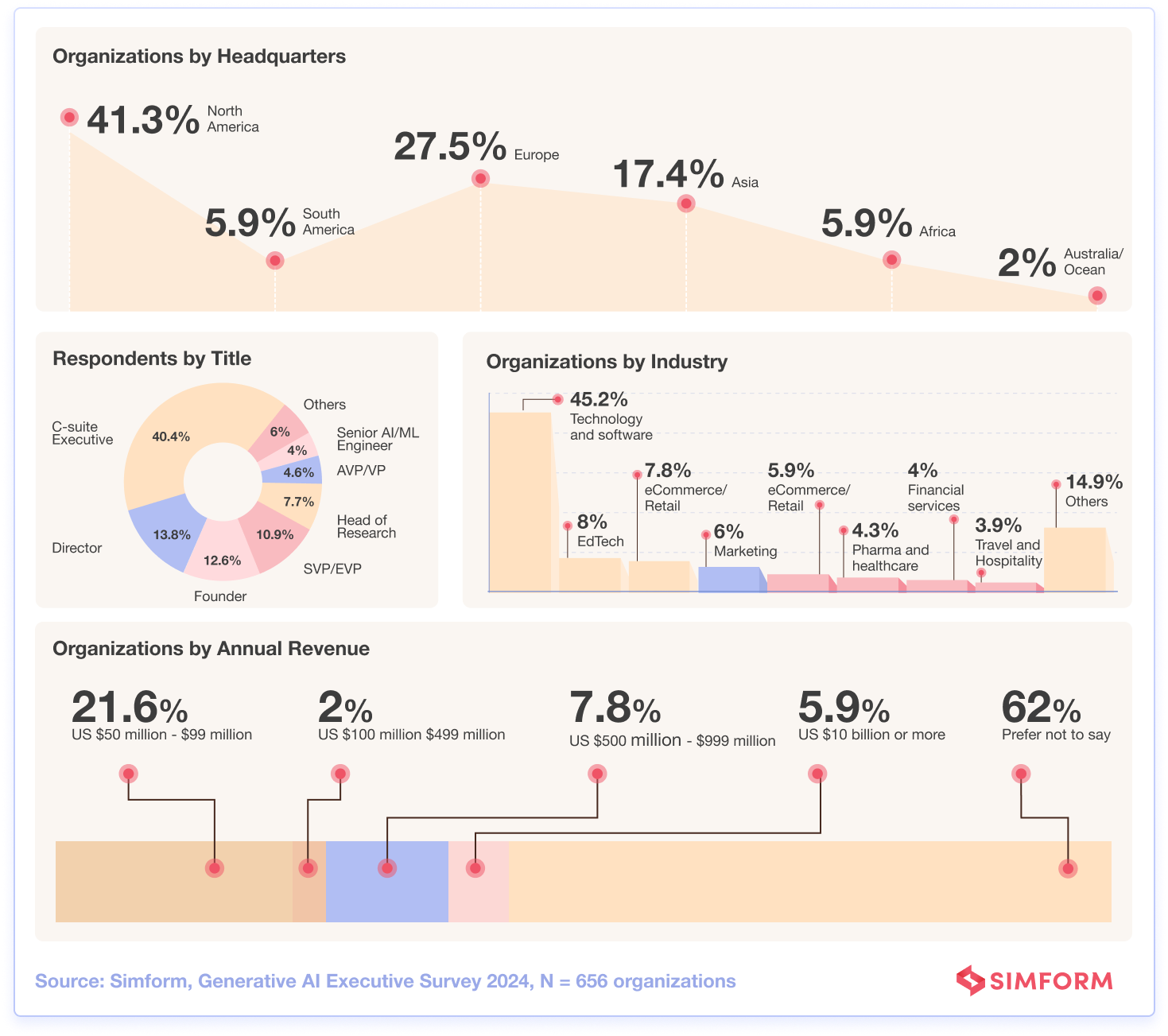
Survey highlights
- Almost 8 in 10 tech leaders regularly incorporate generative AI into their work.
- 14.6% of the participants utilize generative AI for more than 5 business functions.
- 90.2% of the executives use ChatGPT, followed by Dall-E employed by 53.7%.
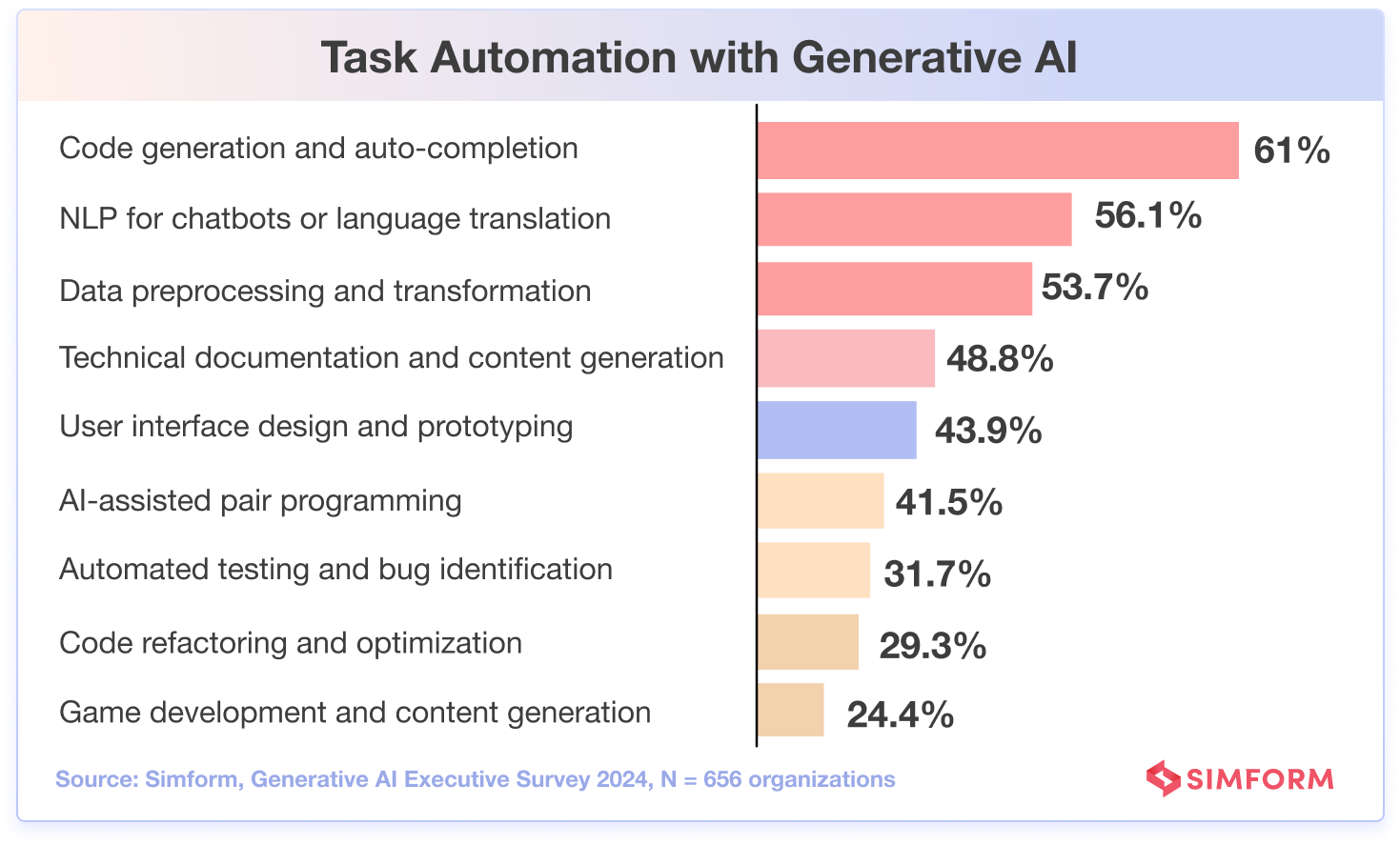
- 61% of organizations use GenAI for tasks like code generation and auto-completion.
- Nearly 1 in 3 respondents use generative AI for Marketing and Communications.
- Prompt engineering is considered as the top competency required to handle generative AI projects by 53.7% of the respondents.
- The most difficult positions to fill are those of Machine Learning engineers for 48.8% of organizations.
- Acquiring generative AI expertise is the top challenge that 43.9% of organizations face.
- 68.3% of organizations prioritize in-house training as a key strategy for addressing the knowledge and skills gap.
- Nearly 7 out of 10 industry professionals intend to improve training data and transparency to tackle AI ethics issues.
- Over a third of surveyed organizations will only consider using LLMs if comprehensive data privacy measures are implemented.
- The primary metric for measuring ROI is ‘Efficiency and Productivity Gains’ for 56.1% of the participants.
- 63.4% of the surveyed organizations use ‘Accuracy and Reliability of Predictions’ KPI to evaluate the success of generative AI projects.
- 47.2% of the companies conduct regular audits of their generative AI projects.
Check out the illustration of the Survey Highlights, here.
Generative AI is an enabler, not a threat!
Executives across industries are now well past recognizing the shift— they are actively adopting and deploying generative AI solutions to not fall behind. Various large enterprises and SMEs are game for these AI-driven innovations and corporate leaders are seeking ways to implement it within their business processes.
1. Majority of executives use generative AI regularly at work
According to Simform’s survey, over three-quarters(78.1%) of the tech leaders regularly use GenAI for work.
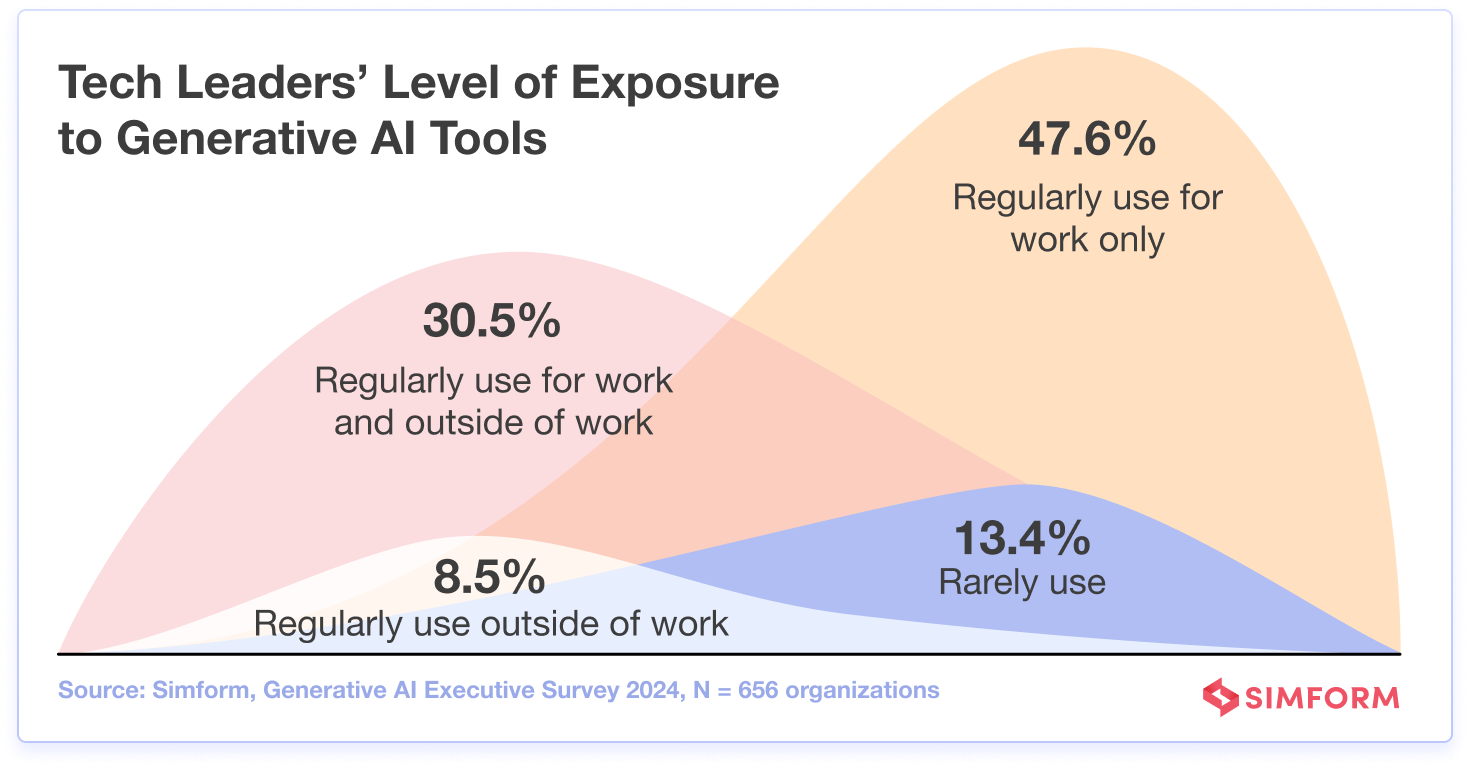
In fact, 30.5% of the executives regularly use generative AI for work and outside of work, and Michael Maximoff, Co-Founder and Managing Partner at Belkins, is one of them.
“Personally, I employ a somewhat limited approach to generative AI and I never use this technology to do my work for me, rather, I treat it as a highly intelligent modern-day assistant and companion that helps me take care of monotonous tasks, do my research faster, and spark/generate ideas for everyday work and life stuff.”
– Michael Maximoff, Co-Founder and Managing Partner at Belkins
As AI becomes an increasingly integral tool for executives in the workplace, its applications are truly expanding.
2. Organizations have started integrating generative AI into business functions
Not every company is sold on GenAI. While 14.6% of organizations have recently started exploring this technology’s capabilities, 14.6% are using GenAI for more than 5 business functions!
However, a whopping 70.7% of organizations apply GenAI for up to 4 business functions.
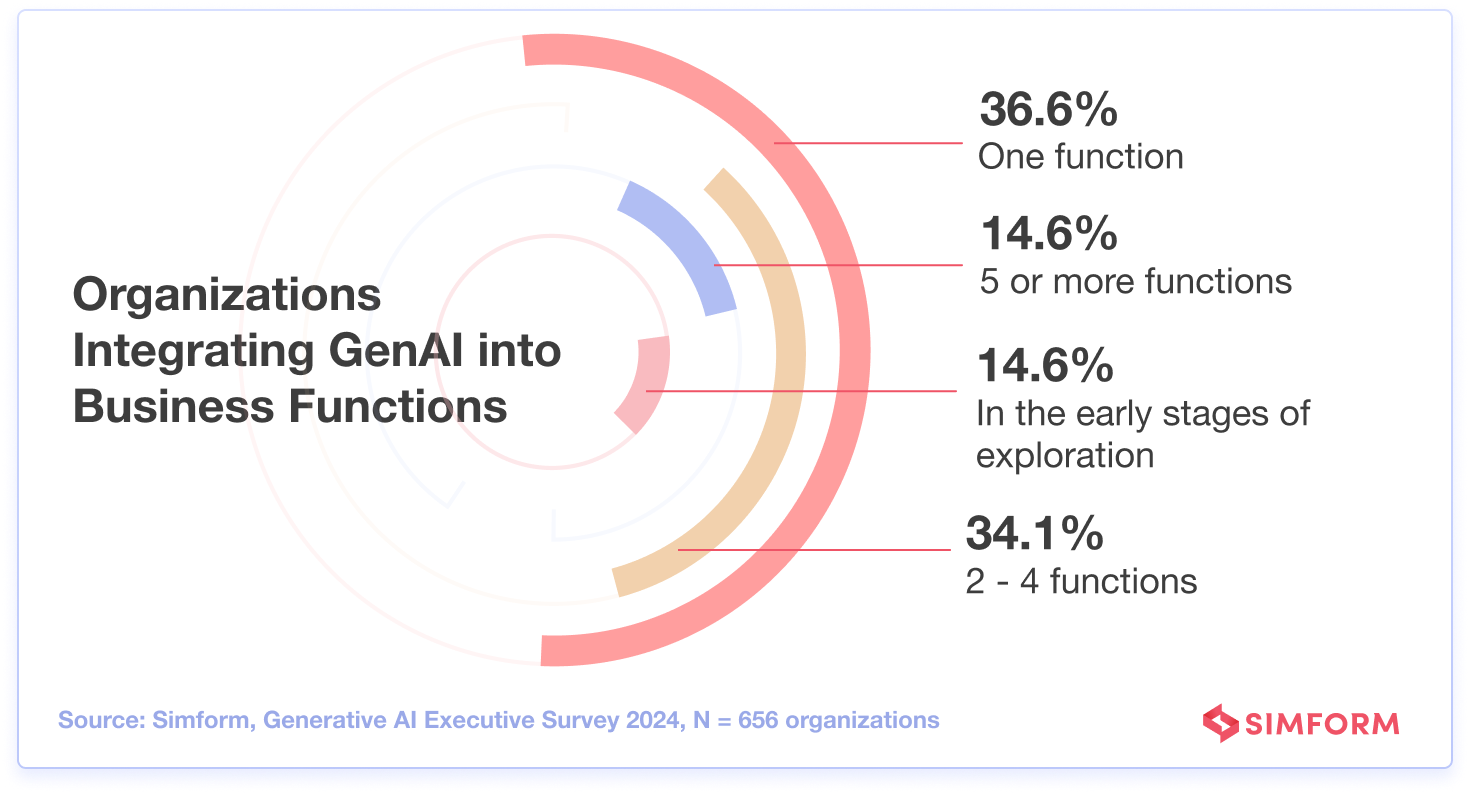 As organizations explore the potential of GenAI in their operations, experts like Teresha Aird recommend a measured approach to adoption.
As organizations explore the potential of GenAI in their operations, experts like Teresha Aird recommend a measured approach to adoption.
“The best approach is to start small and scale gradually. Begin by implementing GenAI in one operational area, such as customer service or marketing, and monitor its impact. This provides a test-case. A controlled environment for you to better understand the nuances and potential of GenAI for your business. Once it’s been proven effective, you can then replicate and adapt the strategy across other areas – tailoring it to the specific needs and challenges of each department.”
– Teresha Aird, the Co-Founder and CMO at Offices.net
Sharing Teresha’s perspective, Alexander De Ridder also advocates for a phased implementation of generative AI as the optimal place to start.
“Prove value in one area, then expand. It is key to integrate AI seamlessly with existing workflows, like an AI operating system enabling a retailer to automate customer inquiries, boosting efficiency and customer satisfaction. Tailor AI solutions to specific operational needs for maximum impact.”
– Alexander De Ridder, CTO & Co-Founder at SmythOS
With the implementation of generative AI within their business functions, organizations are ultimately striving to unlock new avenues for efficiency and growth.
3. Businesses aim for a bullseye by automating with generative AI
Organizations looking to adopt generative AI must have well-defined goals in place to ensure successful integration with existing processes. Clearly stated objectives allow enterprises to diversify their business portfolio strategically with innovative products while boosting overall value.
With the increasing adoption of generative AI, 26.6% of organizations aim to optimize business processes and employee productivity.
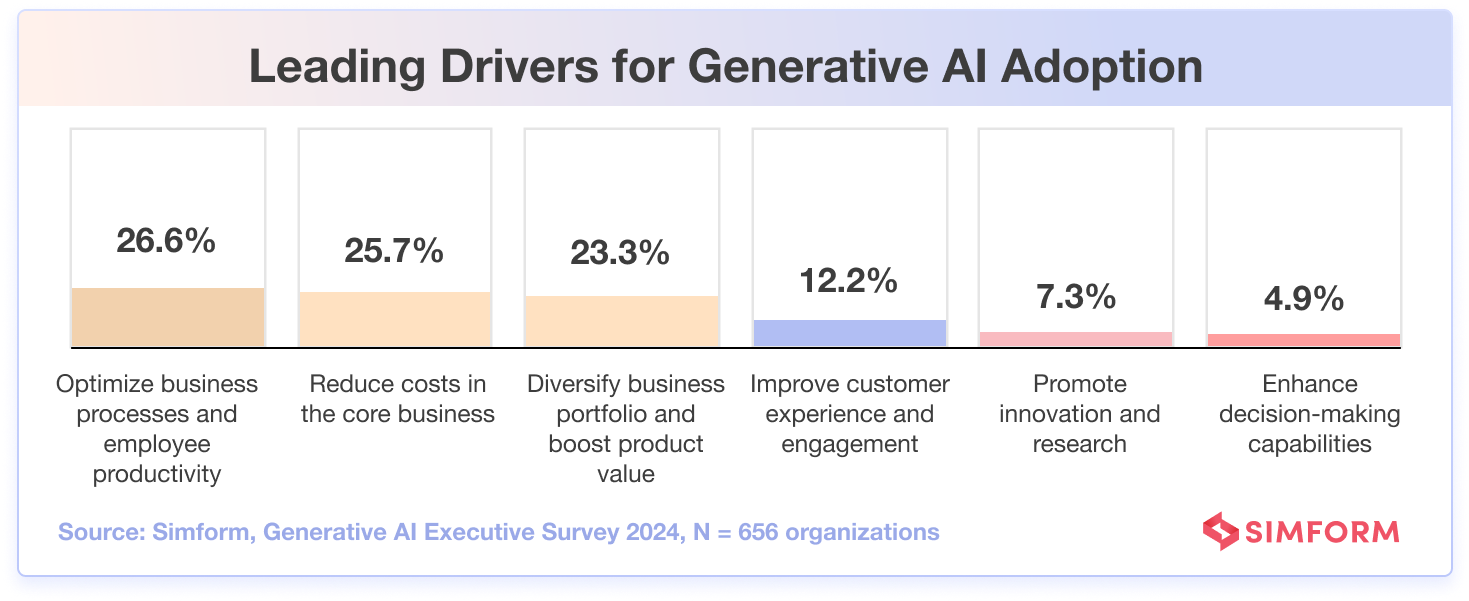
Meanwhile, when the business landscape evolves the way it does these days, there’s a constant need to trim expenses. In fact, our survey reveals that 25.7% of organizations expect generative AI to enable cost reduction at the core of their business.
Though it makes up a small part, 7.3% of businesses want generative AI to help them boost innovation and research efforts. Professionals in various industries, including fashion, leverage this technology to gain valuable insights and improve operations.
Damian Kwinta, a dedicated SEO & PR Manager with a rich background in technical documentation and process optimization, channelize his passion for the fashion industry,
“The use of generative AI in improving business processes and employee performance is like having a backstage pass to every fashion show – you get insights and access like never before. We’ve employed AI tools for market analysis, trend forecasting, and even in crafting engaging content. This approach has not only streamlined our operations but also given our team more room to innovate and create.”
– Damian Kwinta, SEO & PR Manager at prm.com
A versatile marketing professional, Paul Chow, also shares Damian’s perspective. As a 3D printing expert, he specializes in woodworking, CNC machining, and 3D modeling. They’ve been using generative AI for over a year now at 3DGearZone.
“The idea is to let AI handle the more tedious aspects of 3D modeling so our designers can focus on creativity and innovation. We use a variety of AI 3D object generators. They help us quickly whip up prototypes, play around with different design scenarios, and even suggest tweaks based on material strengths. It’s been a game-changer, sped up our design cycle, and also opened doors to explore designs that were previously too complex or time-consuming.”
– Paul Chow, CTO at 3DGearZone
In general, businesses are now incorporating generative AI into their daily operations and embracing it as a facilitator rather than a menace for diverse business functions.
Generative AI use cases sparking “what ifs” and “why nots” in the boardrooms
4. GenAI tools see uptick in adoption by businesses despite risks
As one might expect, ChatGPT is the breakout star, used by 9 in 10 people we surveyed, but DALL-E’s image magic is quickly gaining fans as well, being used by over half of them.
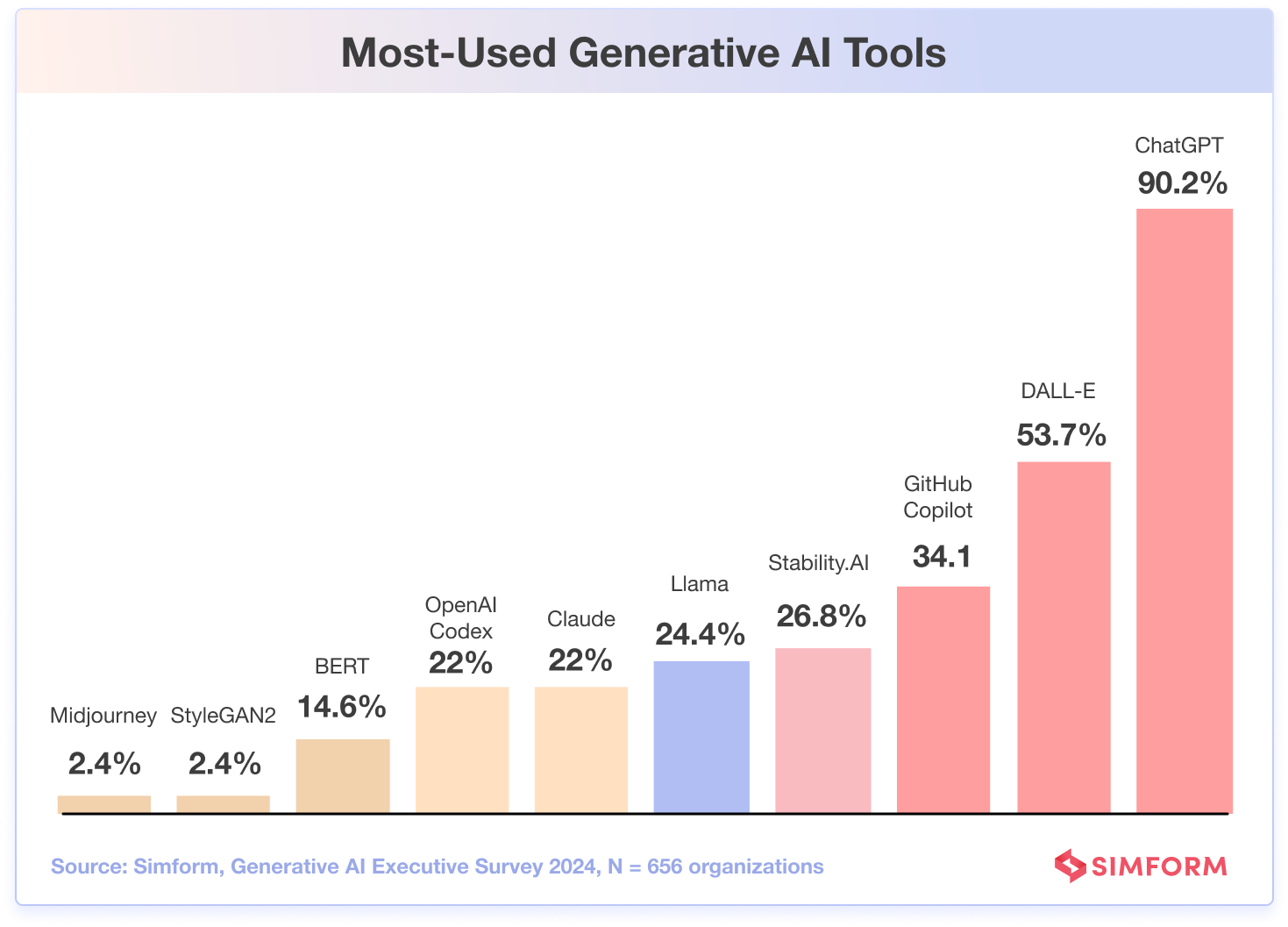
There is ongoing debate about whether ChatGPT will replace the Google Search Engine. ChatGPT certainly has taken over some traffic, but, at least for now, we can say that it’s difficult to turn the search engine market upside down. Still, developers are flocking to ChatGPT, and as Sheldon Chi, an ex-Google engineer who helps people prepare for system design interviews, points out:
“Google and Stackoverflow are no longer my go-to source for most technical questions, ChatGPT is.”
– Sheldon Chi
Businesses are also exploring other tools to enhance their development processes while being aware of the challenges they may face.
For example, a regular user of generative AI tools, Adam Kukołowicz, Co-owner and CTO at Bulldogjob, expresses,
“GenAI tools are now key in my workflow. Using GitHub Copilot or similar tools is like having a junior developer who types very fast to pair programs with. However, it’s important to note that for complex problems, the time spent creating accurate and detailed prompts for GenAI tools can sometimes be as much, or more, than solving the problem itself.”
– Adam Kukołowicz, Co-owner and CTO at Bulldogjob
In data analysis, generative AI tools take on an integral role of extracting actionable insights out of unstructured documents, allowing professionals like Thomas Wood to significantly enhance general decision-making processes.
“One of our primary objectives is to improve business processes by automating data management tasks that are traditionally performed by humans… For example, in a clinical trial, authors draft a document known as a protocol that outlines the trial details. However, assessing a protocol for cost or risk can be quite challenging. We develop AI solutions to extract valuable data from such protocols. We primarily use Python-based tools such as SpaCy and Tensorflow for this kind of work.”
– Thomas Wood, Founder and Director of Fast Data Science
As organizations embrace the opportunities presented by generative AI, certain use cases stand out as popular choices.
5. From code generation to content creation, businesses are game for innovative solutions
We’ve seen how generative AI has permeated software engineering with tools like ChatGPT and Github Copilot. Simform’s survey also confirms that an impressive 61% of organizations prefer using GenAI for tasks like code generation and auto-completion.
However, businesses also recognize the necessity for caution while using generative AI. For example, tech leaders like Joshua Blanchard encourage their software engineers to utilize code generation in ways they find useful while simultaneously addressing any concerns that may arise.
“Our biggest concerns are a) that we might end up with a large amount of code that is a mystery to the engineers who committed it and b) that we might inadvertently include code that has legitimate copyright owned by another party.
We mitigate these by having two primary rules for AI use: Firstly, no code may be committed unless the engineer understands the entirety of the result. This has a minimal impact on time saved in exchange for a tremendous reduction in technical debt. Secondly, prompts should be used either to help implement a generic process or to solve narrow parts of a specific problem. This helps reduce the risk of receiving a code block large or specific enough to be a copyright issue, but it also helps ensure that the engineer doing the prompting has an understanding of the problem they want solved.”
– Joshua Blanchard, CTO at Black Wallet Limited
Meanwhile, our study also highlights that 56.1% of organizations concentrate on using NLP for applications such as chatbots or language translation.
The significance of content generation is also not lost on technology leaders, with 48.8% of organizations now using generative AI for technical documentation and content generation.
With a rising interest in generative AI-powered innovation across code generation, content building and more,
6. Most corporate teams are gradually gearing up for GenAI adoption
Generative AI empowers various corporate teams to explore unique solutions tailored to their specialized needs.
Despite the potential applications, our survey reveals that the adoption of generative AI remains relatively low, as for 61% of respondents, less than half of their team members use generative AI tools. This indicates that teams are gradually opening up to the possibilities these tools offer.
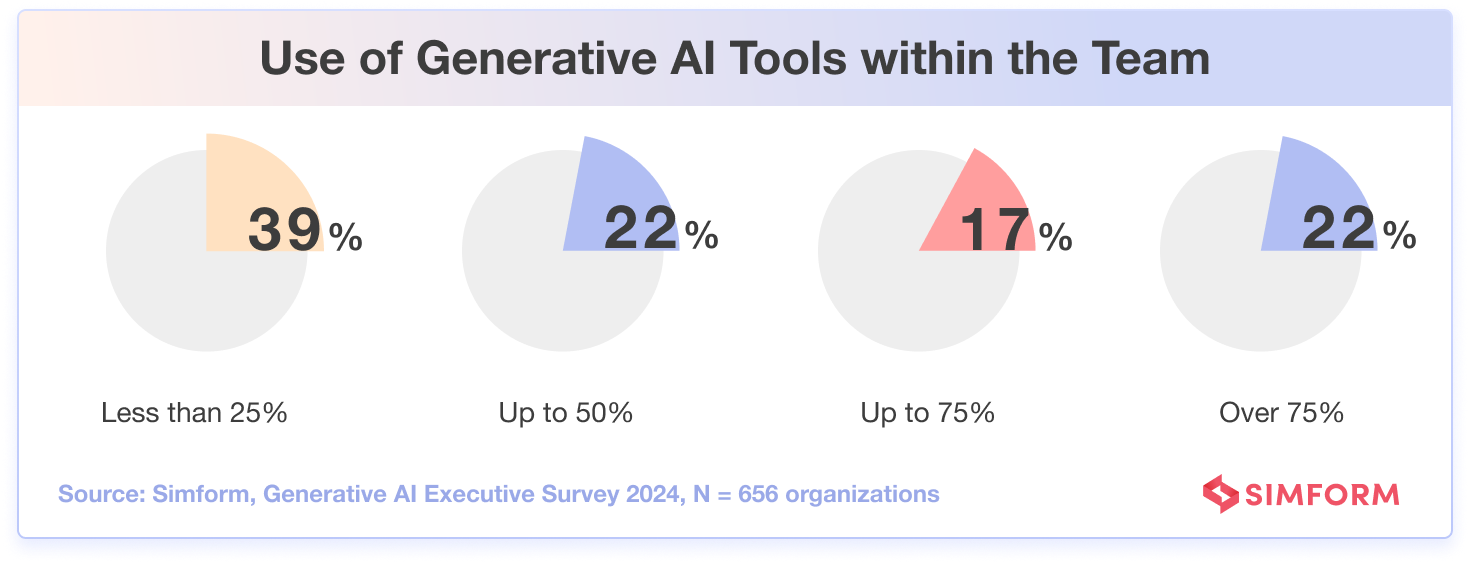
Among the survey participants, in about 39% of the cases, less than 25% of the team members utilize GenAI tools. This signifies a considerable scope for expanding AI usage across corporate teams. However, in 22% of the surveyed organizations, the adoption of generative AI is significantly higher, with over 75% of team members actively utilizing these tools to enhance their workflow and achieve better results.
Marcello Cardoso leads a company where a growing number of team members – approximately 60% – regularly utilize generative AI tools.
“Our team uses them primarily for automating our marketing processes and SEO optimization, thus improving customer engagement and ensuring effective data analytics. Furthermore, real-time adjustments based on AI recommendations allow us to maintain our competitive edge. The remaining 40% are yet to incorporate them into their regular workflow, partly due to varying degrees of technical backgrounds among the team, but we’re developing ways to patch this deficit.”
– Marcello Cardoso, the CEO of Cabana Digital
7. Companies target different areas to drive innovation and create value
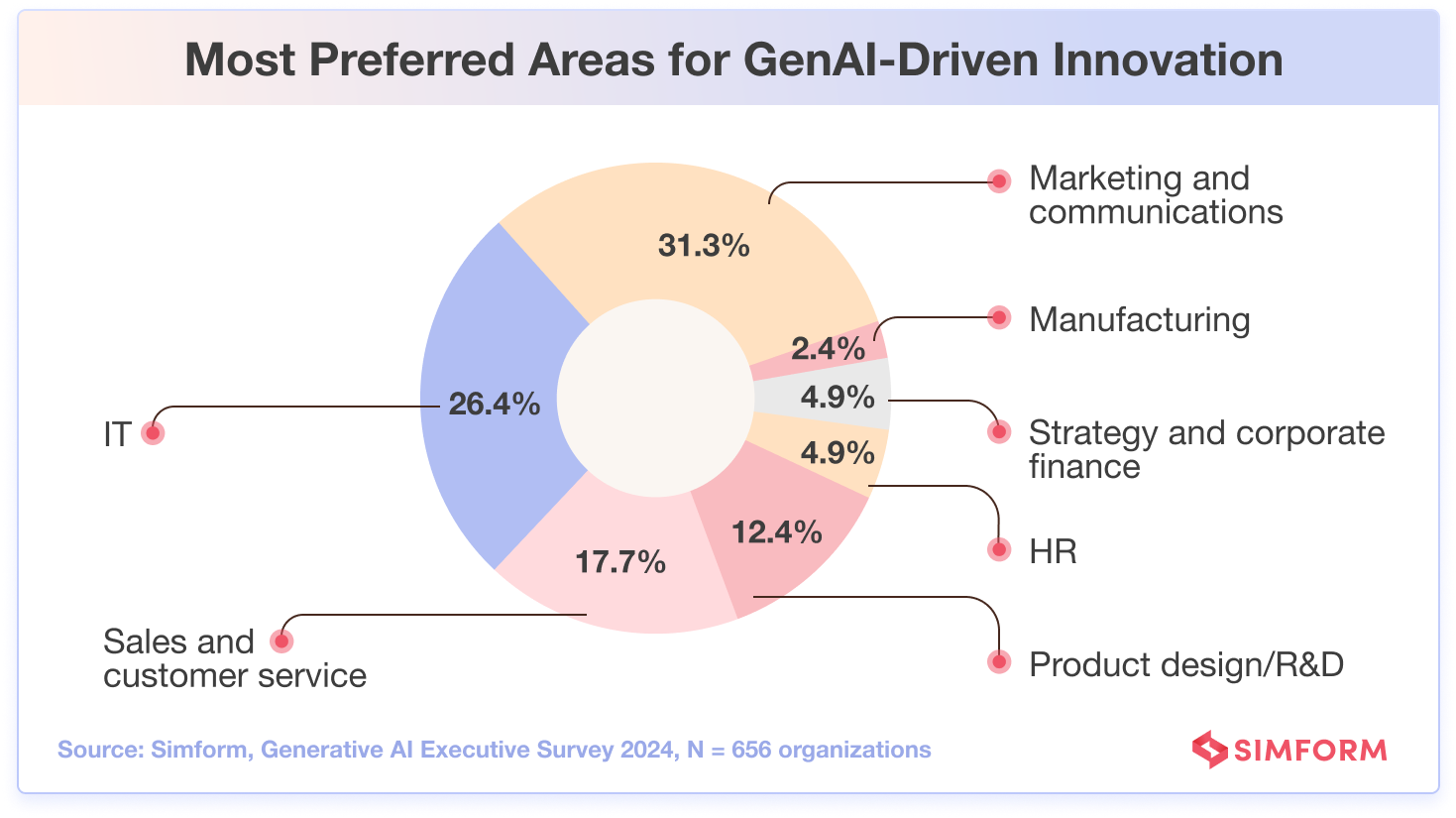
With various impressive capabilities, generative AI provides valuable support to numerous business functions within an organization, particularly marketing and communications, as chosen by nearly 1 in 3 respondents.
As mentioned earlier, Cabana Digital has integrated generative AI into its workflow for content generation.
“We leverage it primarily for automating our marketing processes, which include crafting engaging content, carrying out market and customer analysis, and predicting marketing trends that allow us to stay ahead of the curve. The most challenging aspect has been the initial integration process, which was an investment in terms of both financial resources and time.”
– Marcello Cardoso, the CEO of Cabana Digital
Meanwhile, for over a quarter(26.4%) of survey participants, the game-changing significance of GenAI lies in its ability to optimize IT coding and testing workflows, thanks to automated support for debugging, writing, and validating software.
Ultimately, these statistics show that organizations are increasingly focusing their investments and resources on the successful development and implementation of GenAI-driven innovations across diverse functions.
Find out Exclusive 2024 GenAI Survey Findings
From contemplation to implementation: Businesses are creating plans to address issues
Businesses have already started progressing from cautiously assessing the potential of generative AI to actively piloting and deploying these technologies to solve real-world problems.
However, organizations are thoughtfully implementing generative AI by starting with limited pilots, establishing rigorous testing protocols, and requiring human-in-the-loop approval before deploying algorithmic outputs.
8. Companies are scrambling to add new competencies for generative AI
As generative AI technologies evolve, the need to develop new competencies to handle such advanced projects also rises. Leveraging LLMs and fine-tuning generative AI systems demand a unique blend of skills and expertise.
53.7% of the survey participants identified prompt engineering as the most vital competency to steer generative AI projects effectively. This implies that businesses must prioritize resources to develop skills in designing, testing, and managing complex interactions between users and AI systems.
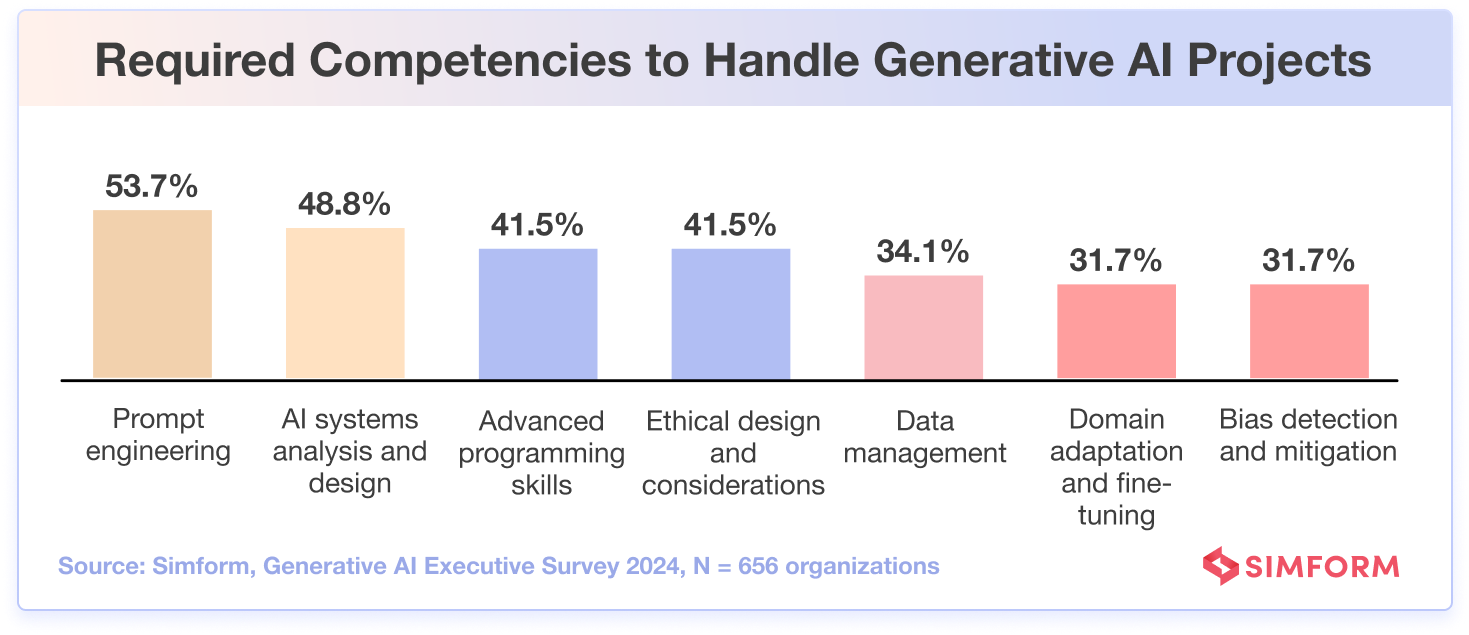
There are differing approaches among tech leaders, with some opting to build specialized teams of prompt engineers while others prefer integrating skills within existing roles.
For example, Spectrum Search’s CTO, Peter Wood, has established a dedicated team of prompt engineers.
“This team plays a crucial role in customizing and optimizing our generative AI and machine learning algorithms. Their expertise is instrumental in refining the interaction between our AI tools and end-users, ensuring that our technology remains intuitive, responsive, and aligned with our business objectives. Expertise in prompt engineering is not just about technical proficiency; it’s about understanding the nuances of AI interaction and user experience and aligning AI outputs with specific business goals.”
– Peter Wood, CTO at Spectrum Search
Additionally, 48.8% of respondents emphasized the value of AI systems analysis and design, underlining the importance of knowing how generative AI models function and creating tailored solutions for specific goals successfully.
Though acknowledging the competencies is a start, businesses need to go further by developing well-rounded generative AI teams to responsibly and effectively integrate generative AI into products, services, and operations. BUT…
9. Finding skilled GenAI professionals isn’t easy!
The necessity for a clear and compelling AI talent strategy is obvious, but the difficulty of tracking down qualified GenAI professionals leaves businesses struggling to fill critical roles and falling behind competitors.
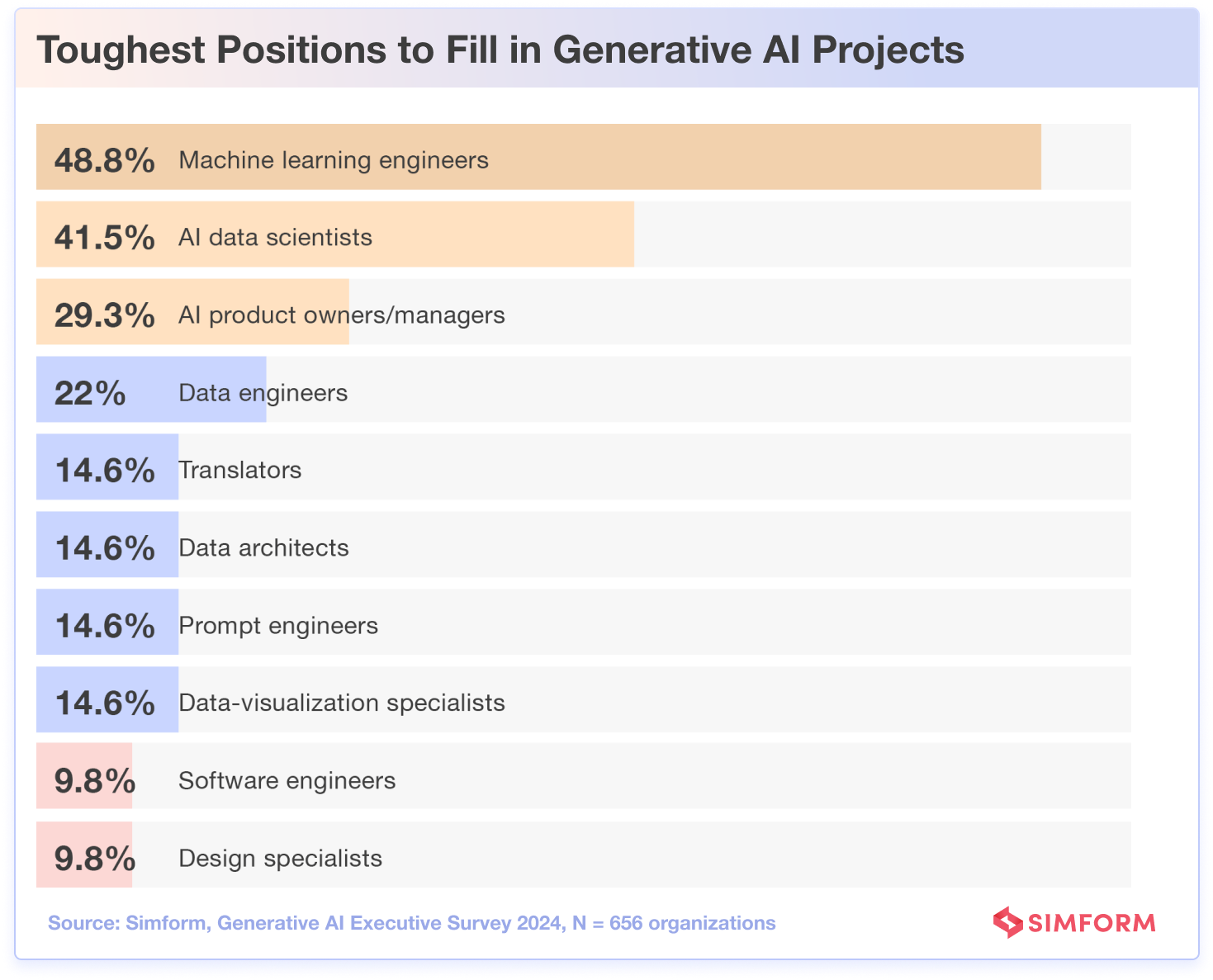
Meanwhile, machine learning engineers often represent the core of AI and ML projects. However, with persistent hiring challenges, 48.8% of organizations cite Machine Learning engineers as the most difficult positions to fill, followed by AI data scientists at 41.5%.
 Jeff Mains, who helps SaaS leaders grow to impressive ARR using a proven methodology, mentors, and CEO connections, has an interesting take on the situation.
Jeff Mains, who helps SaaS leaders grow to impressive ARR using a proven methodology, mentors, and CEO connections, has an interesting take on the situation.
“Due to their unusual mix of mathematics, programming, and domain-specific knowledge, machine-learning jobs attract fewer applicants. Organizations need to utilize strategic recruitment, continuous learning, and come up with new methods to attract and retain top talent in today’s competitive recruiting environment.”
– Jeff Mains, CEO of Champion Leadership Group
Describing Security Compass’s approach to dealing with this problem, Adhiran Thirmal says,
“When hiring AI experts, we prioritize not just technical skills, but also ethical awareness and a healthy skepticism towards AI’s limitations. We need team players who can explain AI’s outputs clearly, collaborate effectively with analysts, and constantly reassess its impact on our processes. Finding these unicorn skills in a talent crunch is definitely a challenge, but investing in training and building a diverse, collaborative AI team is essential.”
– Adhiran Thirmal, Sr Solutions Engineer at Security Compass
However, it’s more than just the technical roles that companies are struggling to fill; there are other challenges, too, of course.
10. Host of GenAI challenges that companies CANNOT neglect
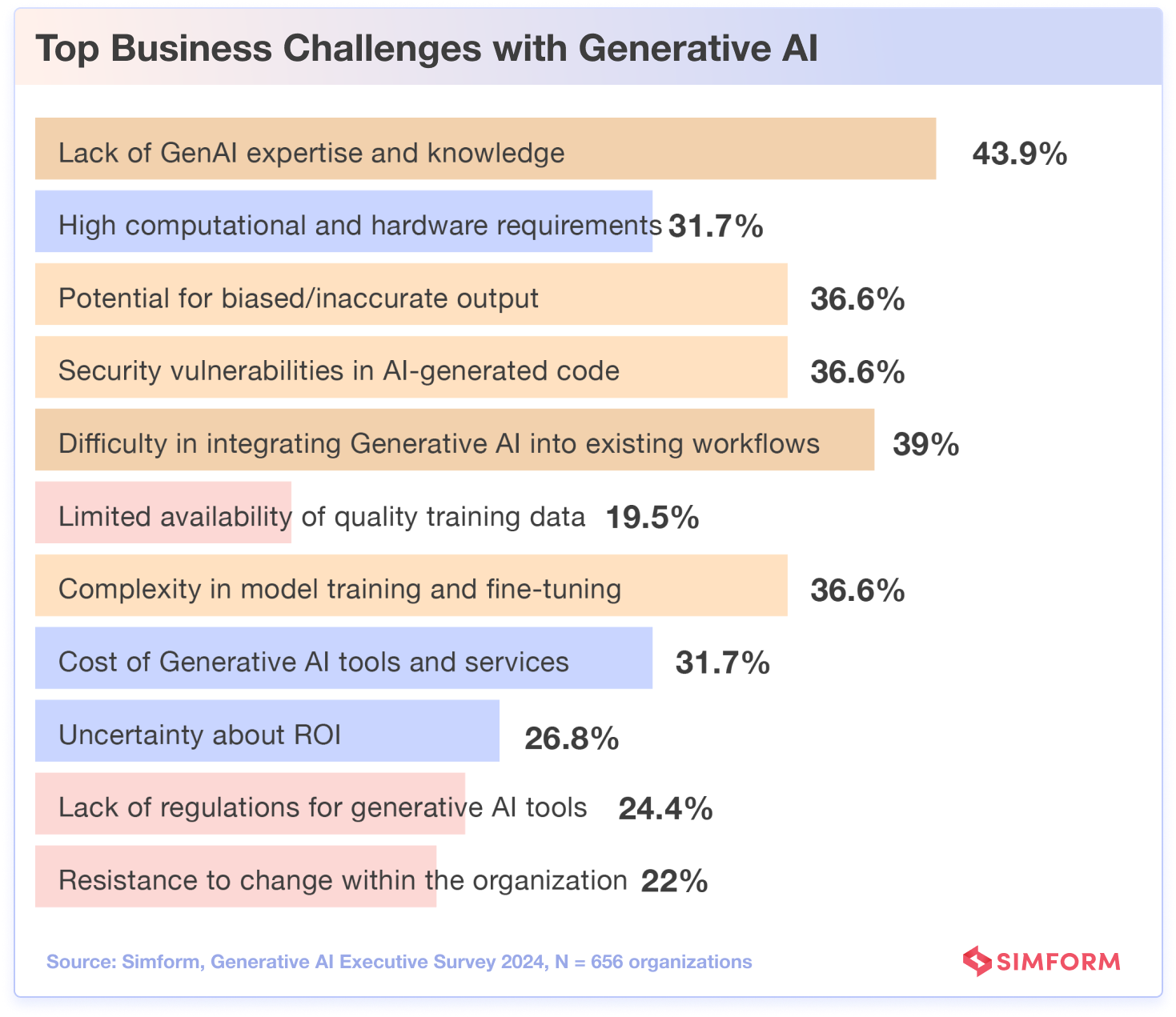
Like other cutting-edge innovations, generative AI poses complications for organizations to address when rolling out initiatives. Simform’s research indicates that 43.9% of organizations struggle with acquiring generative AI expertise, further emphasizing the need for skill development.
 Luciano Colos also emphasizes that one of the biggest issues he faces is locating individuals with the specific expertise required for their industry and the type of generative AI they aim to develop.
Luciano Colos also emphasizes that one of the biggest issues he faces is locating individuals with the specific expertise required for their industry and the type of generative AI they aim to develop.
“It’s not the same to work with text AI generation as image AI generation, and the expertise needed for each domain is distinct. For instance, if we’re crafting an AI system to generate creative and informative text, we seek individuals with a strong grasp of NLP and text generation algorithms. This specialized skillset, combined with the growing demand for AI talent, makes it difficult to secure top-tier AI experts. Companies like ours are competing with other tech giants, startups, and research institutions for a limited pool of skilled individuals.”
– Luciano Colos, Founder & CEO at PitchGrade
Then, difficulty in integrating generative AI into existing workflows accounted for 39% of the responses, indicating that organizations need to invest in modernizing their systems to accommodate this cutting-edge technology.
Concerns about potential biased or inaccurate output were also prevalent amongst 36.6% of respondents. This emphasizes the need for companies to prioritize building responsible, transparent, and well-audited AI systems to mitigate any undesirable consequences.
Additionally, an equal number of participants (36.6%) expressed concern over security vulnerabilities in AI-generated code.
Complexity in model training and fine-tuning was another top challenge reported by 36.6% of respondents again, suggesting that organizations should emphasize refining AI models to optimize their performance. Recognizing the array of potential pitfalls surrounding generative AI, from biased outputs to misinformation risks, businesses can take proactive steps to mitigate them. AND SO…
11. Organizations are laser-focused on addressing generative AI skill gaps
To lead any project to success, organizations must implement comprehensive training efforts.
In fact, Simform’s survey reveals that more than two-thirds(68.3%) of organizations prioritize in-house training as a key strategy for addressing the knowledge and skills gap in generative AI technologies.
Furthermore, over half(51.2%) of the companies rely on webinars and other online resources to develop AI skills. Providing employees with such easily accessible and flexible learning resources showcases an organization’s commitment to fostering an AI-centric culture.
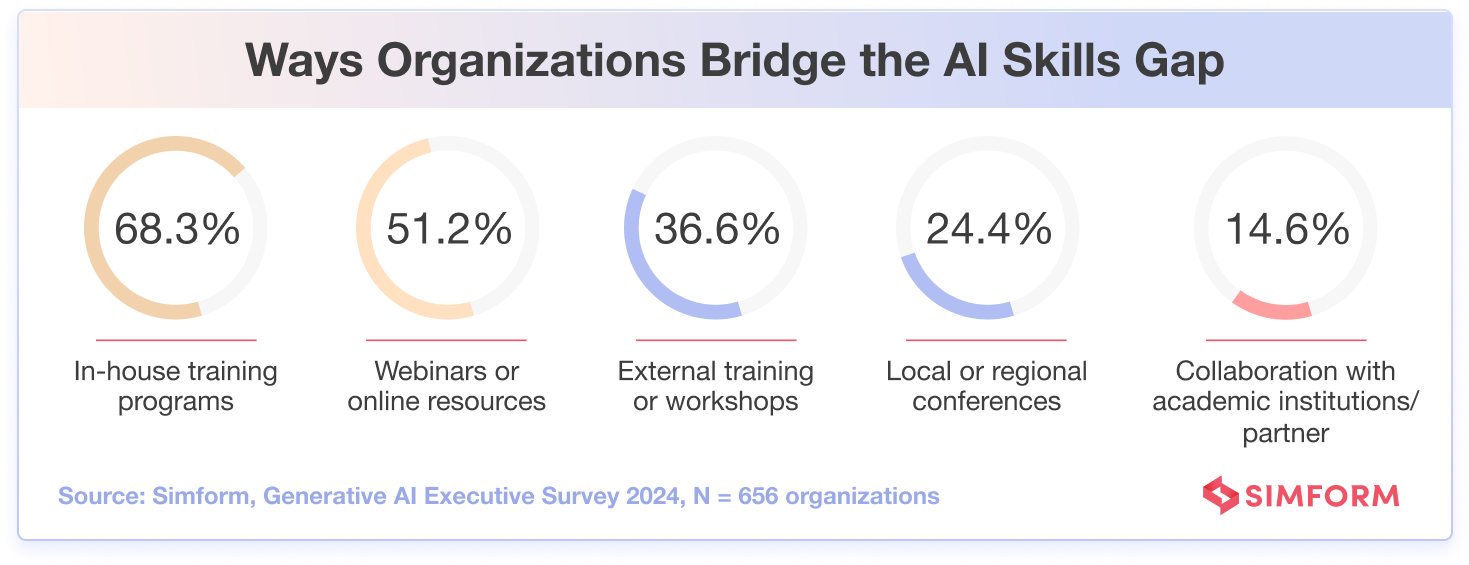
Meanwhile, over one-third(36.6%) of the participants utilize external training or workshops, and nearly a quarter attend local/regional conferences, each highlighting a proactive approach toward professional development in AI.
Similarly, Peter Wood has taken a proactive approach to upskilling employees by implementing in-house training programs, webinars, and selected online resources focused on AI development.
“These initiatives are held quarterly and are tailored to address specific needs identified within our teams. For instance, our recent focus has been on upskilling employees in generative AI and advanced data analytics, pivotal to our AI-led recruitment platform. The benefits of these programs are evident in the enhanced efficiency, creativity, and problem-solving capabilities of our teams. They foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptability, crucial in the fast-paced tech industry.”
– Peter Wood, CTO at Spectrum Search
Notably, the survey results underscore the importance of integrating various AI training methods to facilitate employee growth, adaptation to generative AI technologies, and, eventually, long-term organizational success.
12. Organizations are also diligently working to address ethical concerns and biases
Generative AI implementation could result in various ethical challenges and risks related to data privacy, security, workforces, and policies.
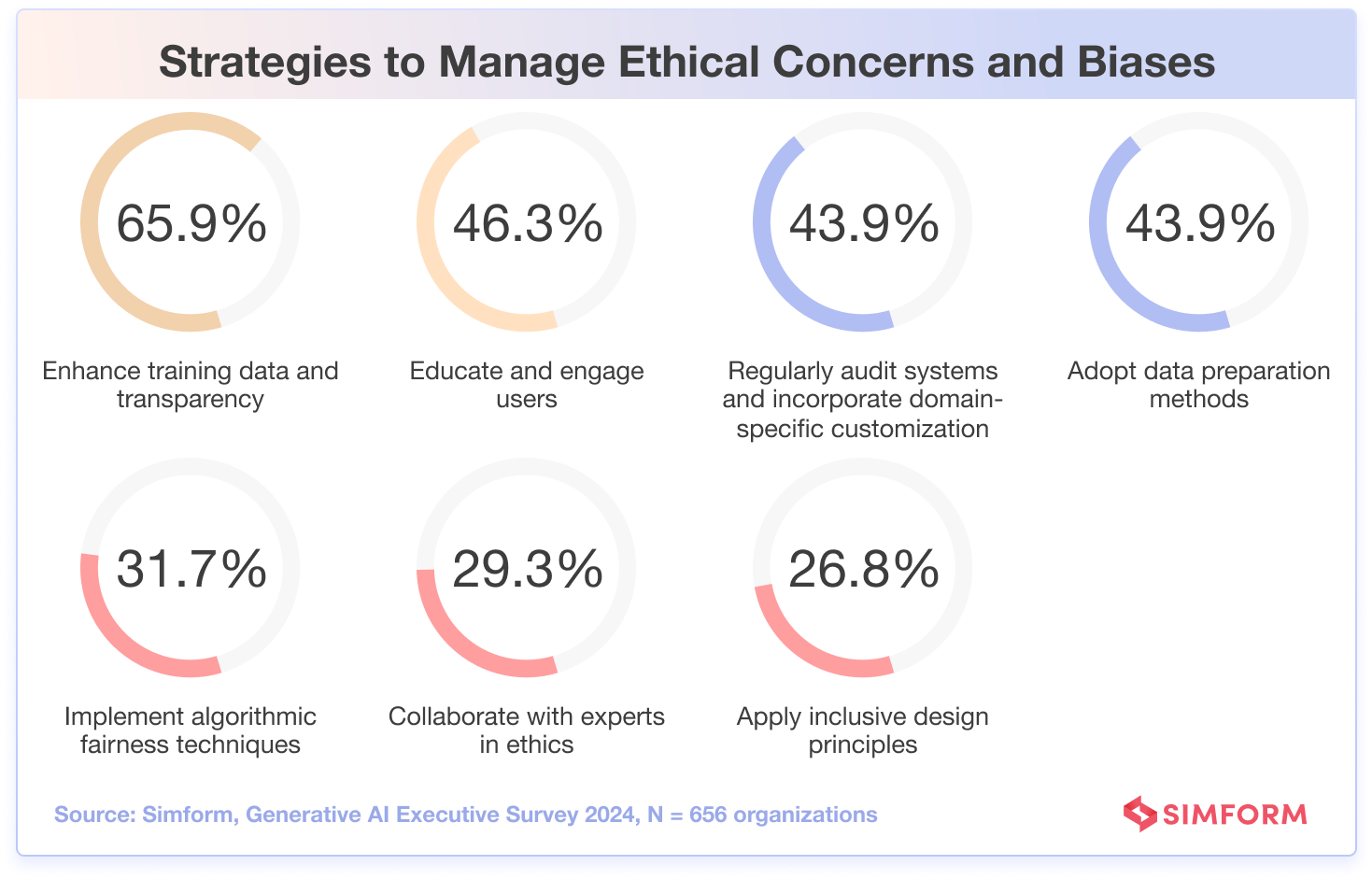
Our survey reveals that nearly 7 out of 10 industry professionals intend to improve training data and transparency to tackle AI ethics issues. This highlights the need for higher quality, unbiased data to train AI systems.
Resonating with this stance, Steve Feiner, Co-Founder & CEO at ABF Group, insists that when training generative AI models, domain-specific data is crucial.
“In specialized domains such as healthcare, finance, or law, it is imperative to source data relevant to those applications. This guarantees that the AI model can produce language that is accurate in context. For instance, a medical research institute may use research papers and journals to build a generative artificial intelligence model that will automatically summarize intricate medical materials.”
– Steve Feiner, Co-Founder & CEO at ABF Group
Ensuring that the data fed into generative AI models comes from diverse and reliable sources is essential for businesses to minimize biases, provide well-rounded insights, and improve overall decision-making.
A prime example of this can be seen in the approach to sourcing training data at Email Tool Tester, which combines years of hands-on experience and trusted resources to develop content that reflects genuine expertise and serves their audience’s needs.
“Our core training data comes from 13+ years of Tooltester’s own testing experiences across thousands of web tools and hundreds of categories. We input the key qualitative and quantitative insights from reviewing website builders, email services, e-commerce platforms, and more into the generative systems. Other training data is sourced from customer interviews, software documentation, case studies, and product release notes. We only extract unbiased, accurate info – no marketing fluff!”
– Robert Brandl, Founder and CEO of Email Tool Tester
Overall, the focus on strategies to improve training data and increase transparency shows organizations recognize the need for unbiased, high-quality foundations to build ethical AI systems. In fact, some popular strategies include educating and engaging users (46.3%), regularly auditing systems (43.9%), and adopting data preparation methods (43.9%).
Combined with initiatives to audit models, collaborate with experts, and educate users, businesses are taking a thoughtful, accountable approach to AI ethics.
13. Businesses proceed with caution when contributing data to LLM training
The prospect of training LLMs on company data has given rise to numerous security concerns among businesses, making them hesitant to implement LLMs on their proprietary information.
As a result, over a third(34.1%) of organizations will only consider using LLMs if comprehensive data privacy measures are implemented to safeguard their sensitive information. This cautious approach demands technologically sound methods to prevent breaches and protect intellectual property.
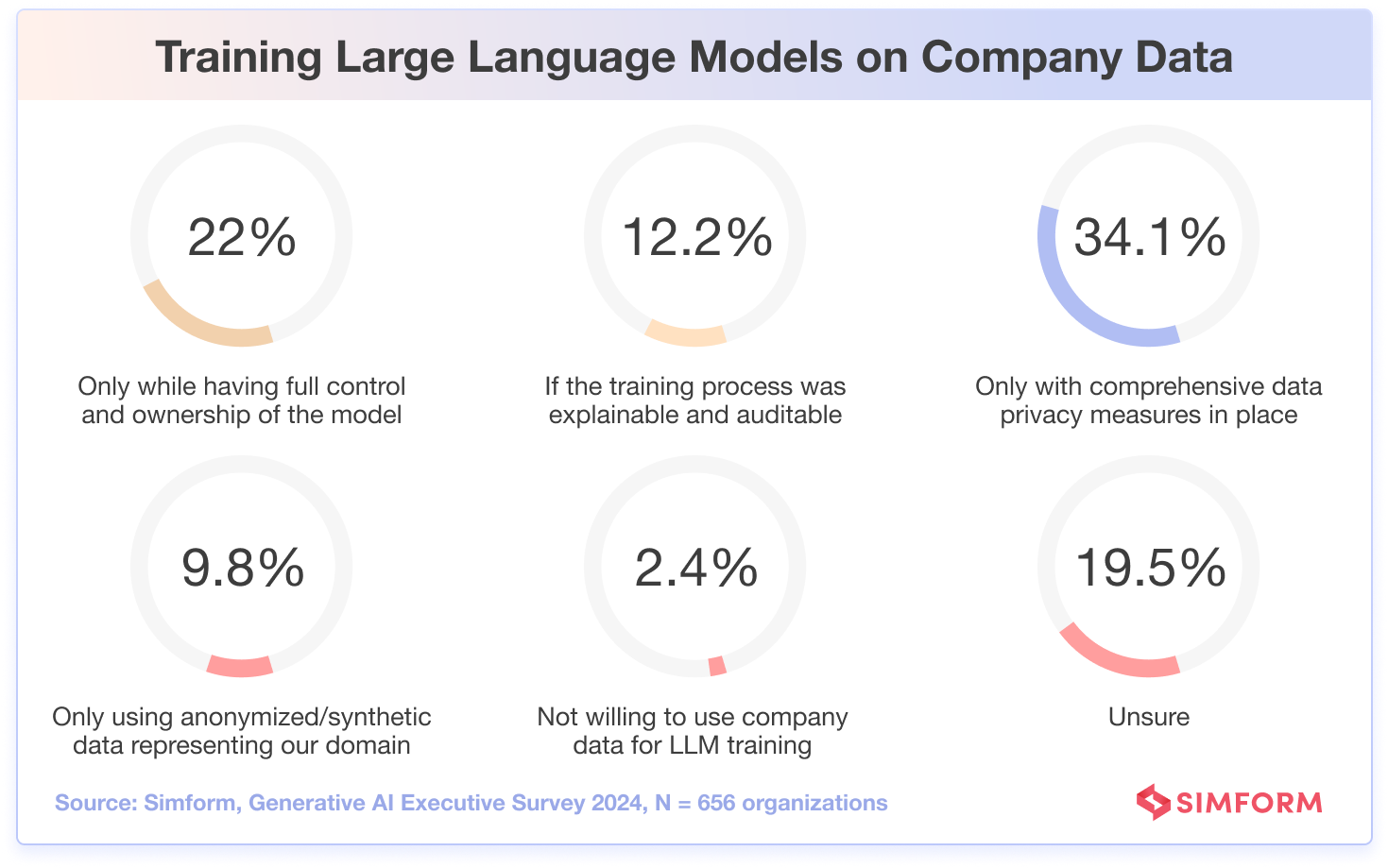
Additionally, 22% of businesses prioritize the ability to govern and regulate their large language models to tailor them better to their internal processes and requirements.
Businesses expressed varying preferences for participating in large language model training with their data. 12.2% of the organizations require explainable, auditable processes, valuing methodology transparency and validation. 9.8% only want to provide anonymized or synthetic domain-relevant data, prioritizing data privacy and protection over using real organizational information.
Incorporating company data into the training of large language models necessitates following a meticulous and well-organized procedure at Survicate, which effectively addresses various concerns raised by businesses.
“Initially, we focus on data preparation, which includes cleaning, anonymizing, and categorizing the data. This step is crucial to ensure the privacy and security of the information. You can’t skip any step of the way either, so it often takes a while to do it properly, with cleaning and anonymizing taking 80% of the time.
The next phase involves the actual training of the LLMs, where the prepared data is fed into the models. During this phase, we closely monitor the models’ performance, making adjustments as needed to improve accuracy and reduce biases. Addressing challenges like data bias involves a combination of using diverse training datasets and applying techniques like algorithmic fairness to ensure the outputs are as unbiased as possible.”
– Kamil Rejent, CEO at Survicate
Interestingly, 19.5% of the organizations expressed uncertainty about participating in LLM training, indicating a need for greater education on the potential benefits and risks. This presents an opportunity for technology providers and clients to engage in open dialogue to build understanding, address concerns, and make informed decisions regarding responsible data contribution versus protection.
Overall, businesses are cautious about contributing their data to LLM training, with preferences centered on process transparency, domain relevance, and data privacy.
Constant evaluation brings generative AI projects to fruition
With advancements in their generative AI projects, businesses recognize the significance of regularly assessing the performance and outcomes of these artificial intelligence systems.
They consider cost an important factor as the costs can range from thousands to millions or even billions of dollars, depending on the scale and complexity of the project. Recognizing the potential impact of these expenses on a company’s bottom line, it becomes even more critical to maintain oversight and optimize the AI’s performance.
14. Gauging the ROI of generative AI is essential for strategic implementation
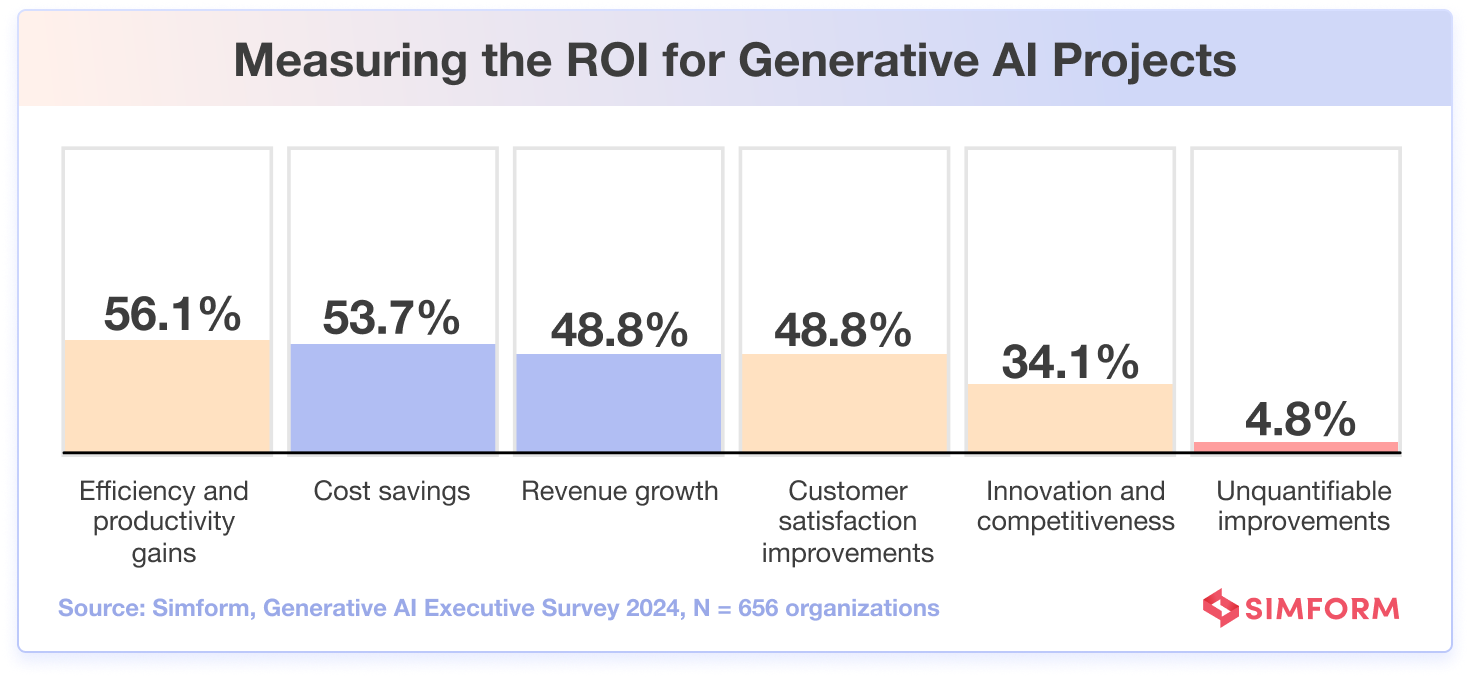
In Simform’s survey of tech leaders, 56.1% of the participants cited efficiency and productivity gains as the primary metric for measuring ROI, indicating the significant role of AI-driven improvements in internal operations.
Understanding the importance of quantifying the ROI of generative AI projects, 53.7% of survey respondents emphasized the value of closely examining cost savings.
Consequently, businesses must thoroughly analyze each project to maximize the potential benefits and justify their AI investments. Marc Martina, Vice President at Cerebral Blue, approves of this meticulous examination, noting that the ROI on many AI use cases is high and very fast.
“Depending on the use case, it can be either easy or difficult to determine the ROI. In Customer Care, it is the easiest to calculate. For example: If you have 100 customer service reps, AI can easily cut this down to 40 reps at the cost of 10 reps. The ROI, in this case, is straightforward – 50% of the cost of the 50 employees. However, there are other factors involved that are harder to gauge. Often, customers prefer AI assistance over human interaction or having to navigate through phone menus by pressing 1 for this option or 2 for that option. As a result, customer satisfaction could also increase.“
– Marc Martina, Vice President at Cerebral Blue
As Marc says, organizations need to take a multifaceted approach considering benefits beyond just financial metrics. Garrett Yamasaki, Founder of We Love Doodles, explains that measuring the ROI for GenAI projects involves assessing both tangible and intangible benefits.
“We evaluate efficiency improvements by tracking the time saved in content generation and customer service responses, which GenAI tools have significantly automated. The increased output in these areas measures productivity improvements.
Cost savings are another crucial factor; we analyze the reduction in operational costs due to the automation provided by GenAI. The overall ROI is considered successful if there’s a noticeable improvement in operational efficiency, decreased expenses, and increased content production without compromising quality.”
– Garrett Yamasaki, Founder of We Love Doodles
However, the revolution doesn’t happen overnight; it’s essential to understand that successful implementation requires time, education, and gradual adaptation. And that’s what Antonio Grasso, Author of “Toward a Post-Digital Society,” technologist, and sustainability advocate asserts,
“It’s crucial to set realistic timelines, recognizing that while generative AI can bring transformative benefits, these are often realized over a period of 6 to 12 months, with more significant impacts becoming evident in the years that follow – but mostly, it depends on the industry and the specific feature we ask of AI.”
– Antonio Grasso, Author “Toward a Post-Digital Society”
Organizations also factor in other metrics like revenue growth (48.8%), improvements in customer satisfaction (48.8%), and advancements in innovation and competitiveness (34.1%) to gauge ROI in their projects.
The fact that only a small percentage (4.8%) of businesses do not assess the ROI of generative AI indicates that most companies are taking a measured approach to adopting generative AI, wanting quantitative data to justify implementation.
Determining the ROI of GenAI also sets the stage for organizations to establish the right KPIs for securing optimal performance and long-term success.
15. Organizations establish the right KPIs to ensure efficient outcomes and justify investments
KPIs play a crucial role in generative AI deployments for several purposes: objectively evaluating performance, syncing with business objectives, allowing data-based fine-tuning, boosting adaptability, and simplifying communication with stakeholders.
63.4% of the surveyed organizations revealed that they focus on how accurate and reliable the AI predictions are. This makes sense, as the significance of AI predictions is entirely on their accuracy and reliability.
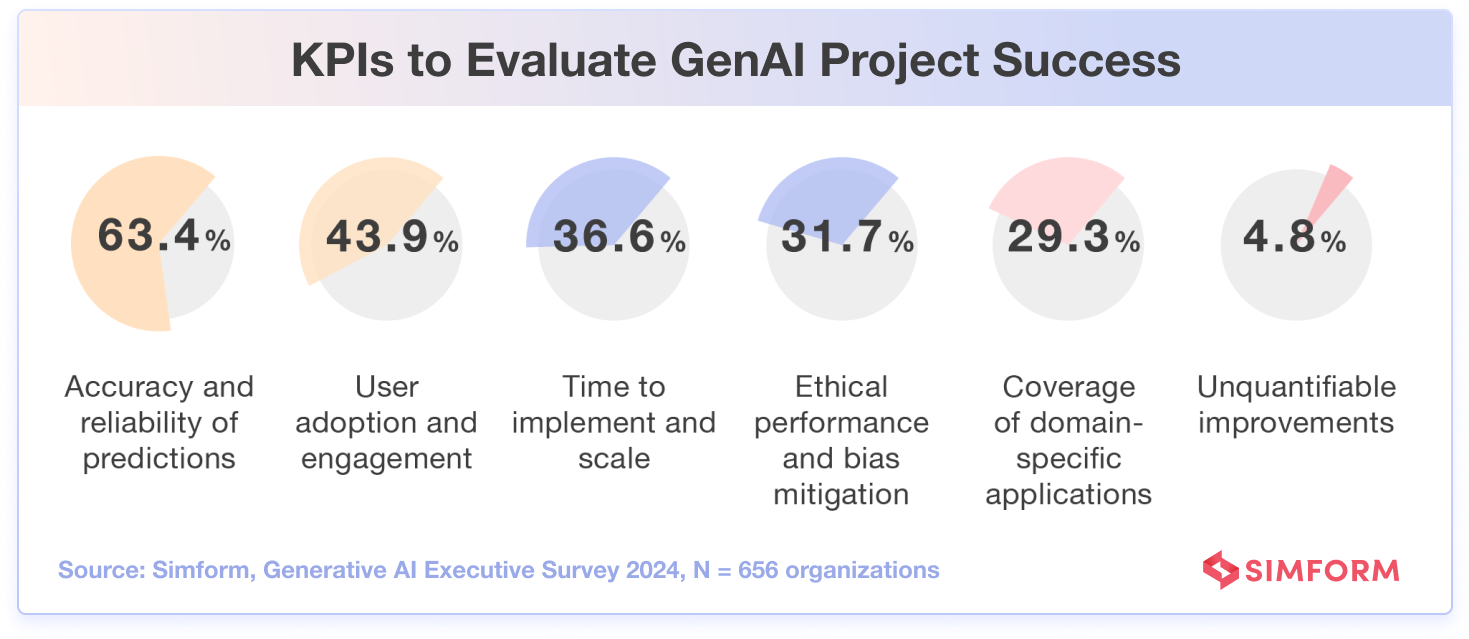
Businesses must have confidence in these insights to make actionable decisions. About 43.9% of participants also mentioned that user adoption and engagement are important, meaning that while accuracy is critical, ensuring employees and customers embrace the technology is nearly as important for success.
Emphasizing the importance of KPIs in AI deployments, Dhanvin Sriram, CTO at Prompt Vibes, states that for him, KPIs play a pivotal role in determining the success of GenAI projects and justifying ongoing investments.
“Accuracy and reliability of predictions serve as primary KPIs, with a constant focus on aligning technical metrics with real-world outcomes. User satisfaction and the project’s contribution to overarching organizational objectives are integral components, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation that extends beyond traditional benchmarks.”
– Dhanvin Sriram, CTO at Prompt Vibes
Other factors that businesses consider when evaluating AI projects include how quickly the project can be implemented and scaled up (36.6%), how well the project takes into account ethical issues like mitigating biases (31.7%), and how well the AI system can be applied to specific areas or industries (29.3%).
This well-rounded approach helps businesses ensure a comprehensive project evaluation, laying the groundwork for sustainable success.
16. The key to generative model success? Never stop evaluating!
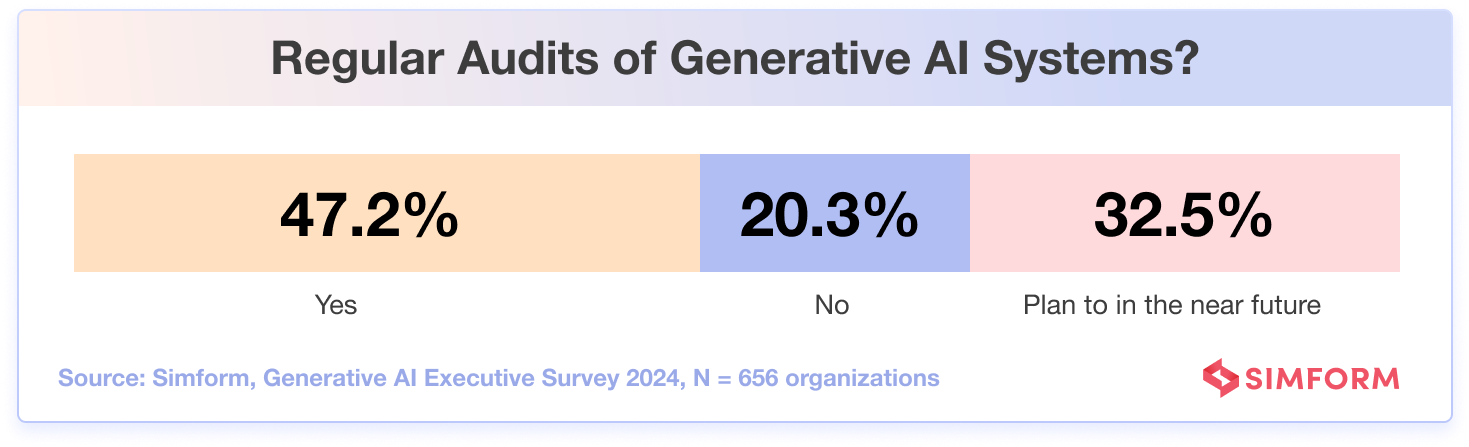
Regular audits of generative AI systems are crucial in ensuring that these technologies continue to function effectively and provide valuable results for businesses. According to Simform’s survey, an encouraging 47.2% of the organizations conduct regular audits of their generative AI projects.
Such commitment to regular audits and upholding excellence is exemplified by organizations like First Aid at Work Course, as highlighted by Operations Director Derek Bruce:
“We fervently uphold excellence and innovation—our core values—and thus continually audit our AI projects in accordance with these principles; such audits fulfill multiple objectives: primarily, they ascertain that the AI meets our stringent educational standards. In performing these evaluations, we both assess the AI’s impact on enhancing learning outcomes and verify its compliance with our stern ethical codes; by scrutinizing the decision-making of the AI and interactions with students extensively, we identify areas for improvement—reinforcing client trust in our cutting-edge educational solutions.”
– Derek Bruce, Operations Director at First Aid at Work Course
Yet, it’s worth noting that a significant number of businesses, 20.3%, do not currently conduct regular audits of their generative AI projects. This appears to be a missed opportunity, as these organizations may face issues related to output reliability, accuracy, and even potential ethical concerns that could have been resolved through consistent monitoring and evaluation.
Fortunately, 32.5% of respondents plan to implement regular audits in the near future, indicating a growing awareness of the importance of maintaining AI system performance.
By instituting recurring checks through both automated and human review, businesses can feel confident their generative AI projects are progressing successfully from conception to implementation to completion.
Organizations are jazzed about what generative AI has in store!
As advancements in multimodal AI models, small language models, and autonomous agents promise to revolutionize various aspects of business operations, the future of generative AI holds immense potential for enterprises.
The democratization of generative AI through open-source models will also enable small and medium-sized enterprises to access AI solutions comparable to proprietary models, fostering greater innovation and competitiveness across industries.
17. GenAI combined with emerging techs open up a world of new possibilities
The convergence of new technologies can create great advantages for companies as the combined power of these innovations has much more impact than each one alone. By incorporating multiple technologies into one solution, businesses can utilize new data streams and unlock immense value.
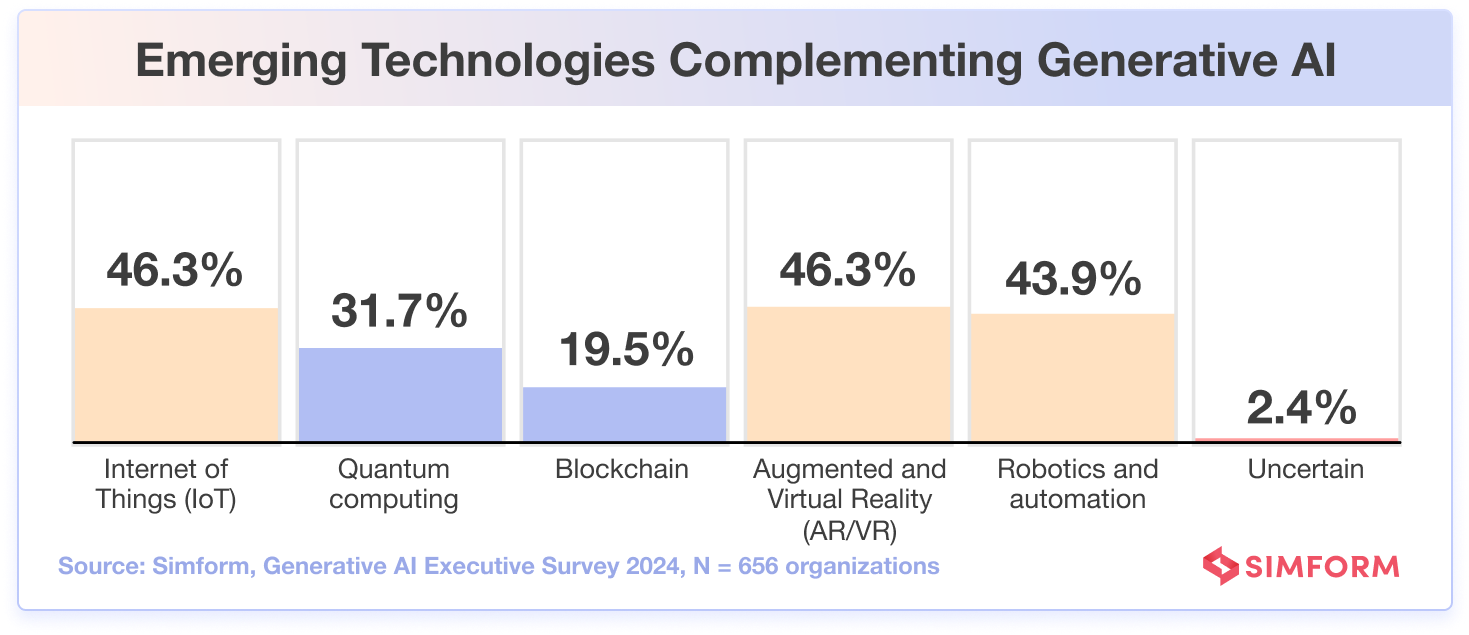
According to our survey, 46.3% of respondents believe that the Internet of Things (IoT) could significantly complement and enhance the capabilities of generative AI in their organizations.
When combined with generative AI, IoT enables businesses to benefit from interconnected devices while leveraging advanced algorithms that create dynamic solutions and insights. IoT devices can collect vast amounts of real-time data from various sources, which, when processed by generative AI, can help uncover patterns and relationships that may have gone unnoticed otherwise.
Additionally, 46.3% of the organizations believe that integrating augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) with generative AI shows great potential, opening new doors for industries like entertainment, gaming, and education and creating immersive, interactive, and adaptive experiences.
Recognizing the immense possibilities that arise from this integration, firms like Fifth & Cor are stepping up to cater to the unique needs of a wide array of industries, from Aesthetic Medicine to Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG).
“These businesses have the opportunity to leverage the power of AI combined with Spatial Computing (AR/VR) to enhance the experiences of both their internal team members and end-users.
For instance, in collaboration with a safety company, we crafted an innovative Augmented Reality training solution. This tool enables users to comprehend common safety issues on a job site, complemented by an AI-driven quiz to ensure a thorough understanding of potential challenges and their prevention. Such solutions are rapidly multiplying for both internal employees and customers, marking a significant shift in how organizations approach training and engagement.”
– Kira Green, Marketing Manager at Fifth & Cor
As AR/VR technology expands into different sectors like healthcare and engineering, legal experts like Jonathan Rosenfeld, Founder of Rosenfeld Injury Lawyers, are examining the possibilities for incorporating the technology and have also started seeing the benefits.
“The use of AR/VR in courtroom simulations has improved our trial preparation, providing a more immersive and realistic experience for both attorneys and clients. This integration has not only increased the effectiveness of our legal strategies but has also contributed to a more engaging and informative client-attorney relationship.”
– Jonathan Rosenfeld, Founder of Rosenfeld Injury Lawyers
Meanwhile, 43.9% of surveyed businesses see Robotics and Automation as a significant complement to generative AI, envisioning smarter automation systems. Additionally, 31.7% show promise in Quantum Computing, and 19.5% recognize Blockchain potential, acknowledging the need for further technology maturation and exploration of specific use cases.
Innovate at scale with generative AI, with Simform
Nowadays, a key aspect of staying competitive in respective industries is, of course, by utilizing generative AI. Many organizations have started incorporating generative AI for diverse applications, such as marketing, code generation, and overall process optimization and improving employee productivity.
However, they are concerned about certain issues, such as acquiring skilled talent, ensuring ethical implementation, and maintaining data security. To tackle these challenges, companies are prioritizing in-house training programs, emphasizing data quality and transparency, and adhering to responsible guidelines while implementing generative AI technologies.
Brenton Thomas, Founder at Twibi, states, “Decision-makers should focus on integrating generative AI in a way that complements human talent, automates repetitive tasks, and ultimately drives business growth. This strategic alignment ensures that AI is not just an innovation but a pivotal component in achieving business objectives.”
However, considering the complexities surrounding the adoption of generative AI, companies require a dependable partner with the necessary expertise to navigate the intricate process of implementing generative AI solutions. Simform provides a comprehensive suite of generative AI, machine learning, and big data services spanning various domains.
As an AWS Premier Consulting Partner, our team of specialists is continually enhancing their knowledge and skills in generative AI, ensuring that we can accommodate the need for talent in the latest AI/ML technologies.
Get a free consultation to find out how we can help create intelligent solutions to drive your business growth by designing, training, and integrating customizable generative AI models. Download the detailed survey, here.