Do you love binge shopping? If you are like Bart(The Simpsons), trapped in the Springfield mall, overprovisioning may not be an issue for you! However, it can be for your Homer, who is bound to pay in the end.
Long story short, higher costs become inevitable if you stuff more than you can chew. This happens with every organization that spends high on instances for peak loads and ends up paying for idle instances when the load declines.
A report from Wall Street Journal indicates that Netflix is also struggling to cope with cloud computing costs. It is reducing the data copies hosted on AWS and is finding more ways to cut cloud costs.
This blog post will look at the prominent factors causing a surge in expenses. And then, we’ll also consider the tips on cloud cost optimization.
What is cloud cost optimization?
Cloud cost optimization is a process of identifying critical areas of unused and wasted resources to optimize expenses. It involves resource analysis, identification, monitoring, and management instances for optimized cloud costs.
The process of cloud optimization continues beyond resource monitoring and management. You need to see the holistic view of cloud costs for each phase of the software development lifecycle(SDLC). Optimizing the costs at each stage involves data monitoring and visualization.
Why does cloud cost optimization matters?
Effective cloud cost estimation is crucial for sustainability and growth. Optimizing cloud costs ensures that companies aren’t just pouring money into the cloud but are instead investing wisely. It’s a practice that balances expenditure against performance, helping businesses in reducing cloud costs, capitalizing on cloud computing’s full potential, and allocating resources towards innovation and growth.
All in all, cloud spend optimization is the bedrock of maximizing efficiency and competitiveness in an increasingly cloud-centric economy.
Top reasons for higher cloud costs
Like every other solution, cloud-based solutions can overwhelm your organization’s budget if not optimized. A Gartner report estimates the cloud costs to reach $364,062 million by the end of 2022.
#1. Poor visibility
Cloud monitoring is key to business success because poor visibility can lead to high costs. According to a survey, 82% of IT and cloud decision-makers said they incurred unnecessary cloud costs, and 71% of respondents mentioned the lack of visibility as one of the top reasons.
There are several reasons for poor visibility on the cloud, such as lack of governance, problems with opaque containers, and blind spots. In addition, with rapid cloud adoption and changing customer demands, the predictability of cloud costs is disrupted.
Earlier, monitoring – what was easy to predict and offered the benefit of single pricing, is now complex. The fluctuation of cloud spending based on customer needs and agility requirements make it challenging to manage. In addition, a further lack of governance and visibility makes cloud resources opaque, causing unnecessary costs.
#2. Overprovisioning
If you have watched ‘Fight Club,’ Edward Norton in the movie has an obsession with fancy furniture and stuff more than he needs in the house. Overprovisioning is where organizations spend more on cloud resources than what’s needed. So, when the load is low, instances run idle, leading to higher costs.

The best way to reduce overprovisioning costs is by identifying underutilized resources, terminating idle instances, and checking for memory leaks. Many organizations choose a cloud-first approach and overprovision resources.
However, overprovisioning is not the only issue when you go for a cloud-first approach, data gravity is a major challenge to overcome.
#3. Data gravity
It is often easier for businesses to store and transmit large amounts of data on the cloud than on the premises. This can lead to a ‘data gravity’ phenomenon, in which more data moves to the cloud at first. Still, as organizations become more efficient with their resources, they move back towards using on-premises systems.
So, businesses end up paying for migrating data to the cloud and back to an on-premise setup. It is a highly inefficient and costly approach. One way to avoid data gravity is to have a project infrastructure management plan.
#4. Pricing issues
Cloud pricing can be a complex and opaque process. This can lead businesses to spend more time researching the best deals or negotiating directly with providers. Take an example of cloud calculators provided by different service providers.
Some of these cloud cost calculators require knowledge of computing resources like what should be the cache size, ram, type of instances, and details of workloads. As a result, it becomes overwhelming for a CEO or CFO with limited technical knowledge to use such calculators.
Another key challenge is keeping yourself updated with cloud services’ price fluctuations. Unfortunately, many organizations need to be aware of price hikes and spend more on the instances, increasing cloud costs.
#5. Complexity of cloud contracts
Cloud contracts are complex and need thorough analysis before signing them. In addition, most businesses don’t know the hidden costs of cloud contracts and pay more. So, you need a cloud assessment expert to help you figure out contracts and pricing structures.
Further, you need to analyze the terms of cloud contracts, data ownership, and data compliance requirements.
Cloud contracts need to explain the exit strategies for a business that wants to opt out of the services. It should also include add-on details like connectivity and data transmission costs.
Cloud cost optimization best practices
Cloud cost optimization process is dynamic and requires continuous assessment of cloud resources, pricing, and changing business requirements.
#1. Optimize the cost at each SDLC stage
Optimizing cost at each stage is key to reducing cloud expenses. Optimizing cloud costs at each SDLC stage requires continuous assessment, data tracking, and system monitoring throughout the lifecycle. Here is how you can apply cloud cost optimization to different phases of SDLC.
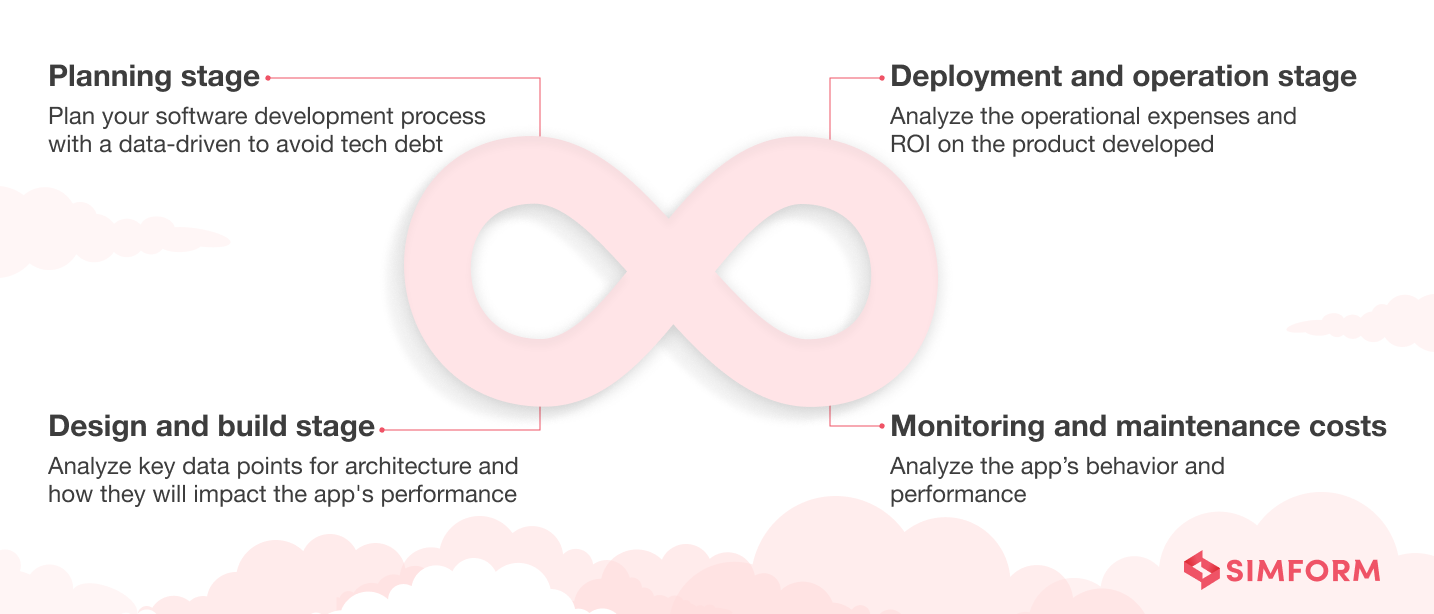
Planning stage: Plan your software development process and use a data-driven approach for critical decisions to avoid tech debts. The planning stage involves the assessment of systems requirements, cost analysis, and creation of a framework for the development process.
Design and build stage: The designing process for cloud-based applications requires data analysis. So, you should analyze key data points, like what they should be, the architecture, and how they will impact the app’s performance. Further, you also need to analyze the costs of app architecture and cloud computing resources required.
Deployment and operation stage: At the development stage, you need to analyze the operational expenses and ROI on the product developed. Further, you should consider the cost of cloud deployment and plan automation to improve efficiency.
Monitoring the performance and maintenance costs: Monitoring the application and performance costs is key to ensuring better ROI. So, you need to define metrics and analyze the app’s behavior and performance. It will help you reduce expenses on error rectification and maintenance costs.
#2. Use cloud cost as a metric
Keeping cloud costs a priority allows businesses to create a culture of optimizing cloud-based expenses. Cloud costs as a metric require defining key areas where organizations can monitor, measure and optimize costs.
Some key areas are
- “Accountability and enablement” is one of the foundational pillars for implementing cloud costs as a metric culture. It focuses on streamlining the financial processes to accelerate financial accountability and business value. Cloud enablement is a crucial metric for this pillar, and you can measure it in percentage.
- “Measurement of cloud costs and realization” is the second pillar involving defining resource hierarchy, tagging data architecture, and identifying IT-driven designators.This pillar focuses on cloud resource attributions through consistent tagging, which enables organizations to identify cloud cost centers. Companies can measure cloud allocation metrics for this pillar in percentage.
- “Planning and forecasting” is one of the most important cloud cost optimization best practices that focuses on planning the resource requirements and budgeting cloud costs annually. Here you can use annual forecast accuracy percentage as a lead metric, which is calculated by assessing workload forecasting models, trend-based models for steady-state workloads, and monthly budget variances.
- “Tools and accelerators” is a pillar that focuses on detailed analytics reports of resource tagging and identifying the accelerators of cloud costs. It helps you measure the automation percentage implemented from the analytics tool’s recommendations after analyzing the tagged resources.
#3. Identify the cost anomalies
Identifying the cloud costs needs monitoring tools and predefined metrics. Some of the critical cloud cost metrics that you need to focus on are,
- Uptime is a metric that helps in measuring the time for which a system is available to serve user requests.
- CPU utilization helps measure the computed percentage used for completing a specific task or processing a user request.
- Memory usage helps measure the memory used in public, private, and hybrid cloud environments.
- Requests per minute is the number of user requests a cloud-based app will receive every minute.
- Disk usage is a metric that allows you to track the amount of disk volume used on a node and helps determine whether the storage cavity is enough for workloads.
- Average time to acknowledge is the metric that helps measure your system’s time to respond to a user request.
- Latency is the measurement of time between a request time and a response time. In other words, it is the time between a request sent by the user and a response received.
- Mean time between failure (MTBF) is the average time a system or application takes from one failure to another. In other words, MTBF helps determine when a cloud component will work before failing.
- Mean time to repair(MTTR) is the metric that helps you find the time needed for a system to restore services after failure. A shorter MTTR is desirable for cloud cost optimizations as it reduces downtime costs.
Top cloud monitoring tools
Mitigating the complexities of cloud expenses requires best cloud cost optimization tools like CastAI, Harness, Kubecost, etc. These sophisticated tools demystify cloud spending, offering insights and control over your cloud investments. Here are a few of the leading cloud monitoring tools:
- CastAI is a platform that helps in monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing Kubernetes apps. It allows you to automate cloud cost optimization through rightsizing, instance selection, autoscaling of resources, and more.
- Harness is a CI/CD platform with a pre-built cloud cost management module. It focuses on enhancing transparency, governance, and resource efficiency.
- Cloudability is a cloud monitoring and optimization tool that collects key data on resource usage from the last 10-30 days. Further, it leverages algorithms to provide rightsizing recommendations.
- Cloudcheckr is a cloud cost monitoring tool that helps track, monitor, and report key expenses for your applications. Further, it leverages the recorded data to create policy-based automation.
- Kubecost is a cloud cost management tool that allows you to monitor resource allocation and generate accurate reports to find cost anomalies.
Some of these tools provide data analytics and insights in a visual format, which makes cloud cost optimization efficient. For example, you can use heat maps to find high resource demand or idle instances for scaling up and down the cloud infrastructure.
Heat maps help you determine the intensive use of computing resources and optimize it for cloud costs. Cloud monitoring tools help you rightsize the resources for enhanced cloud cost optimization. However, let’s first understand rightsizing.
#4. Rightsize the resources
Rightsizing, one of the most effective cloud cost optimization techniques, is a process that comprises identifying idle resources, and switching off such instances to optimize cloud costs. Further, it also involves matching the cloud resources with the workload and rightsizing the overprovisioned instances.
If you know how to rightsize instances, savings on the cloud costs can go as high as 70%. Cloud providers have pre-built features to facilitate cloud infrastructure optimization and rightsize instances.
For example, AWS offers spot and reserved instances that you can use for cloud cost optimizations. Spot instances are like a backup that allows you to utilize idle EC2 capacity rather than spending high on on-demand resources.
Take the example of Webbeds, which is a leading travel accommodation provider worldwide. During the pandemic, it saw a decline in operations. So, Webbeds migrated its infrastructure to spot instances in 2020 to save 64% of cloud costs and improve CPU performance by 40%.
Another approach that you can take to optimize your cloud costs and rightsize instances is to use reserved resources. For example, you can leverage reserved instances provided by AWS to reduce cloud costs.
Similarly, Google Cloud Platform delivers Google Committed Use Discounts for cloud cost optimization. Rightsizing is also crucial for optimizing resource provisioning.
#5. Optimize resource provisioning
Rightsizing instances and resource provisioning require analysis of the system. You need to analyze the workloads to create a resource requirement plan. Here are some key questions you need to ask for resource provisioning and creating a requirement plan.
| Type of costs | Questions to ask for optimized provisioning |
| Feature cost |
|
| Customer acquisition
and engagement |
|
| Operational costs |
|
| Deployment costs |
|
Answering these questions will provide two critical data,
- Types of workloads you need to provision
- Resources required for the workloads
You can provide the resources and improve cloud cost optimization based on these data.
#6. Leverage a hybrid strategy
Vendor lock-in can be a challenge to your cloud cost optimizations. When you use a single cloud service provider for all your resource requirements, chances are that there will be specific restrictions. For example, many cloud service providers offer services that are not compatible with external services.
Another significant issue is cloud costs that surge due to changes in pricing. Due to interoperability issues and dependency on a single vendor, cloud costs increase. So, the best way is to leverage a hybrid cloud strategy.
A hybrid cloud approach is where organizations leverage multiple environments to run apps. For example, you can use public cloud infrastructure for specific services and private cloud services for others.
Take the example of British Petroleum’s (BP)’s hybrid cloud approach. The oil giant had a vast network of data centers across 73 countries. As a part of the cloud-first approach, it migrated many applications to Microsoft Azure.
However, there were remote locations for which complete lift and shift of the applications were not economically feasible. So, it leveraged a hybrid approach for cloud cost optimization.
#7. Choose the exemplary cloud service
Choosing the right cloud service provider helps optimize cloud costs. You may leverage different cloud service providers through a hybrid approach for optimized cloud costs.
| Comparators | AWS | GCP | Microsoft Azure |
| Maximum processors in virtual machines | 128 | 128 | 96 |
| Maximum memory | 3904 | 3800 | 1433 |
| SLA availability | Annual uptime of the EC2 instances is up to 99.95%, and 99.9% monthly uptime for S3 | 99.9% annual uptime | 99.9% monthly uptime |
| Pricing for on-demand compute instances | $0.166/hour | $0.238/hour | $0.149/hour |
| OS compatibility | Windows, SLES, CoreOS, CentOS, Cloud Linux, and more | Windows, SLES, CoreOS, CentOS, OpenSuse, and more | Windows, SLES, CoreOS, CentOS, Cloud Linux, OpenSuse, and more |
#8. Simplify cloud contracts
Simplifying cloud contracts is key to reducing costs, as there are several clauses and hidden expenses which can go unnoticed. Cloud contracts need proper assessments and breakdowns by consultants to avoid overhead costs.
Here are some of the essential things to consider when you sign a cloud contract,
- Analyze the cloud cost breakdown and, if not provided, ask for it
- Research the contract for any hidden expenses, add-ons, and capacity information
- Understand the data ownership clauses and migration policies
- Ensure there are security measures employed by cloud service providers are mentioned in the contract
- Look for SLA availability and service-based clauses
Questions to ask yourself about optimizing cloud costs
When addressing the topic of cloud cost reduction, it’s essential to consider several pivotal questions that could lead to significant savings, such as:
How can we systematically assess and manage cloud costs across the organization?
Utilize cost management tools to create a structured framework, providing clear visibility and precise budget allocation. Ensure regular reporting and enforce accountability measures to monitor and control cloud usage across all teams.
What cloud cost optimization strategies should we adopt for provisioning cloud resources and controlling spending over time?
Adopt dynamic provisioning and automated scaling to effectively match resource usage with demand. Implement continuous cost analysis and set budget alerts to maintain strict control over spending, avoiding over-provisioning.
How can we prevent over provisioning and unnecessary costs?
Conduct regular audits of your cloud resources, right-size infrastructure for demand forecasting and capacity planning, and foster a culture of cost awareness among your developers and IT teams.
What metrics beyond the cloud service bill should we monitor?
Beyond the cloud bill, tracking metrics such as per-service costs, resource utilization, and performance against capacity can offer deeper insights. This also includes availability metrics to ensure that cost-saving measures do not compromise service quality.
How can we optimize multiple-cloud environments?
For multi-cloud cost optimization, it’s beneficial to utilize cross-platform cost management tools that provide visibility into all cloud environments. This approach enables you to compare costs and usage patterns across different providers and optimize accordingly.
How do we align cloud investments with business value?
Measure the return on investment for your cloud expenditures. Monitor the impact on business performance and agility, and adjust your cloud strategy to support key business outcomes.
By addressing these critical questions, businesses like yours can pave the way for significant cost savings and optimized cloud efficiency. This introspective approach to cloud cost management is a strategic step toward a more cost-effective and resource-efficient cloud infrastructure.
Simform redesigned BI and data analytics platform with WAR
A leading data analytics provider wanted to build BI platform from the ground up and approached Simform. We leveraged a re-architecting approach to modernize the existing application without disrupting the operations.
Our team of engineers used AWS services to create reliable cloud architecture and provide advanced filters for users to process data. Simform leveraged a well-architectured framework to build a new system that replaced the outdated application with massive tech debt. We optimized cloud costs for data analytics providers.
Optimizing the cloud costs requires engineering excellence, an understanding of cloud services, pricing, and the right scaling of instances.
Being a WAR partner and experienced in building cost-effective cloud-native apps, we can help you optimize cloud costs by tackling business challenges. Get in touch with our cloud experts now and reap the benefits of cloud cost optimizations.
vibin augustin
Thanks for this article. Cloud Cost optimization is really a mandated thing for an organization those who have opted for the service for cloud service for their organization. There are different kinds of Cloud Service providers Google Cloud Providers, Amazon Web Service, Microsoft Azure-based on the service the cost varies.