When it comes to developing websites or apps, organizations seek two principal skill sets, as pointed out in this tweet.
8/ Thus if you want to become a software developer, do yourself a favour and do not *start* in smart contract development.
Learn frontend and database backend development first. These are easier to learn, and you can be productive faster. pic.twitter.com/4aHwzuOoKC
— Mikko Ohtamaa (@moo9000) December 31, 2020
Frontend deals with the client-side activities, while backend takes charge of server-side interactions. Whenever a user fills a form or enters a web address, the browser sends a request to the server-side, sending a code to the client-side. Your browser will interpret the frontend code and display the information.
Editor’s note: Hiren briefly explains all the aspects such as performance, support, and development that you can consider while choosing between Django and PHP for a new project. If you’re looking for an experienced team to start your project, consider turning to Simform’s custom web application development offerings.
Django and PHP are the two most preferred frameworks that stand out from their counterparts. By the end of this comparison – performance, scalability, architecture support, and ease of development – between Django and PHP, you will have maximized the understanding of these backend technologies.
Overview of Frameworks – Django vs. PHP
What is Django?— An overview
Django is a popular web framework written in Python. This free, open-source framework was first introduced by two web programmers, Adrian Holovaty and Simon Willison, working at Lawrence Journal-World newspaper to develop applications. Named after the famous guitarist Django Reinhardt, its development began in 2003 while the first milestone release came out in September 2008.
Django facilitates faster and secure builds and frees the developer from mundane web development tasks, negating the need to create solutions from scratch. With multiple out-of-the-box features, it lets you create complete applications. It goes well with all kinds of websites and supports multiple formats (HTML, RSS feeds, JSON, XML, etc.). Additionally, Django comes with various security features and is ridiculously easy to scale.
Here are some cool usage stats for Django:
- It is a popular Python-based web framework with more than 27k watchers and 63.8k stars on Github.
- It powers 88,892 websites used across 55,742 unique domains.
- With 6.86% of projects coming from the domain, Science and Education is the most popular industry vertical using this framework.
Use cases of Django
- Web applications with ORM support
- API backend
- Scalable apps
- ML integration
- Data-driven apps
What popular apps are built using Django?
- Disqus, a blog comment hosting service, handles 50 million monthly comments and 17-billion monthly pageviews from 2-billion monthly unique visitors hailing from 191 countries. The entire project was built on Django from scratch and has scaled with ease ever since its inception.
- Spotify shares its vast music library with millions of users across the globe while rocking a swift backend and machine learning features simultaneously.
- Mozilla switched to Python and Django for all its newer components to better handle the daily increase in traffic and API.
- Dropbox added an array of features such as user history, synchronization accounts across different devices, add various file-sharing options, and so on.
- Instagram leverages Django to scale with its continuously growing traffic and usage while retaining the simplicity of its UI/UX.
What is PHP?- An Overview
PHP(Personal Home Page) or Hypertext Preprocessor is a scripting language used for automating various tasks on the server-side web development. It is a general-purpose programming language that easily embeds with the HTML codes. PHP enables the creation of dynamic web pages, eCommerce web apps, and even database-driven applications. It is an open-source scripting language compatible with MySQL, Oracle, and other such database services.
Here are some stats on Market usage of PHP:
- PHP is one of the top 10 scripting languages with a 26.2% share, according to the StackOverflow Developer Survey 2020.
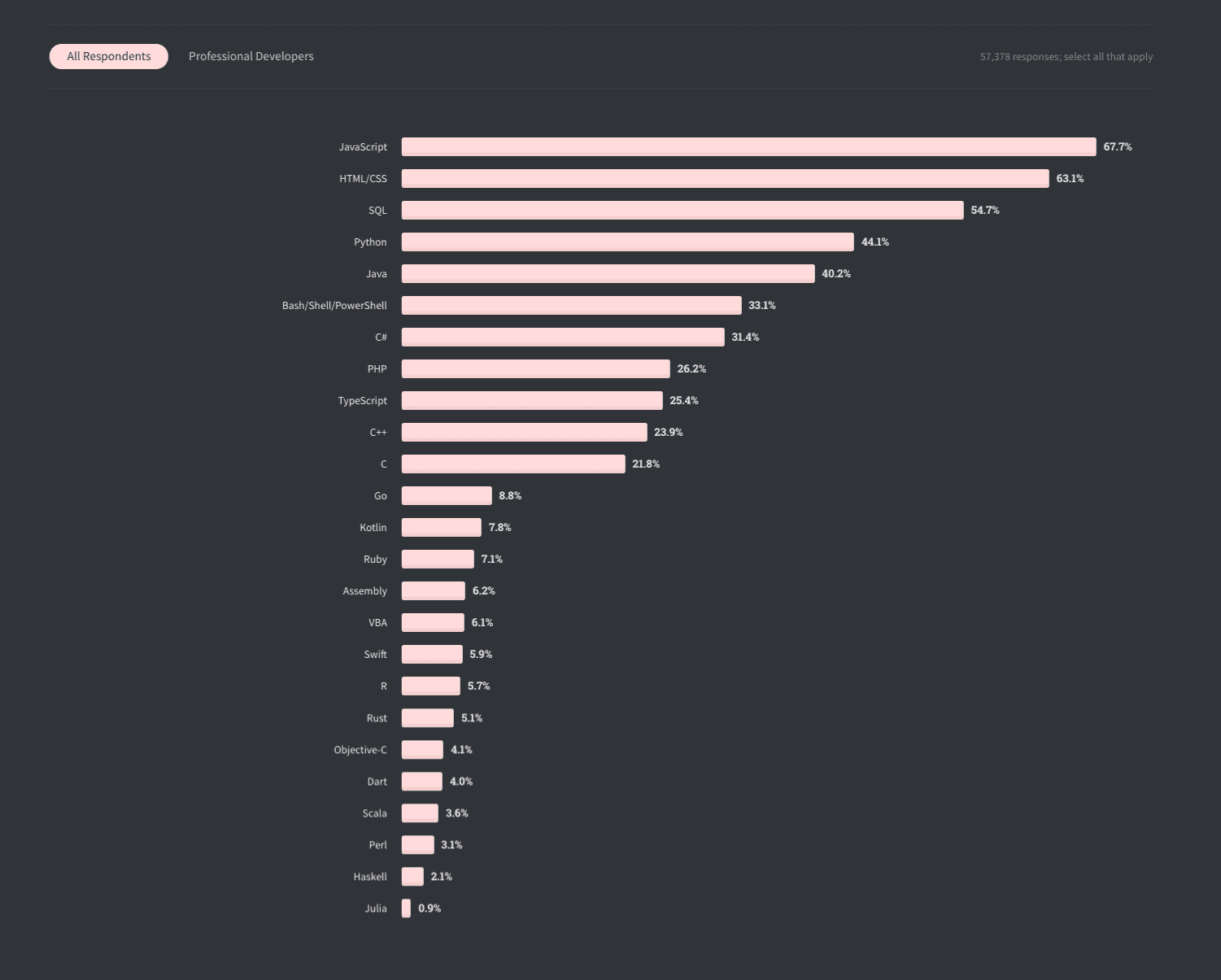
- About 77.5% of the total websites on the internet use PHP as a scripting language for server-side programming language.
- WordPress fuels 34% of websites on the world wide web, inevitably making PHP a choice for 8 out of 10 sites.
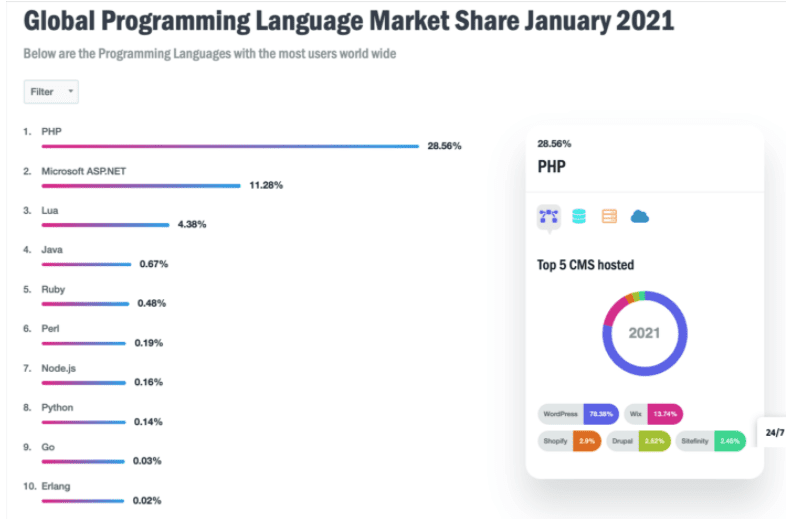
- With a market share of 28.56%, PHP has the highest number of users across the globe.
Use cases of PHP
- Websites with custom scripting of codes
- Sites with non-scaling server deployment with Linux, Apache, and MySQL
- Websites that need extensive image processing
- Websites and web applications (server-side scripting)
- Desktop (GUI) applications
What are popular apps made with PHP?
- Facebook- Created a new PHP-driven language known as Hack as a part of HipHop Virtual Machine (HHVM), an open-source JIT compilation virtual machine.
- WordPress- Offers a host of themes, plugins, and template customizations with HTML+CSS connection to the database through their software.
- Flickr- Used PHP base to offer image processing for photographers to upload high-quality pictures in a limited bandwidth.
- Wikipedia- Enabled web access to a massive database of information on diverse topics through UI with database services like MySQL.
- Slack- Improved workflow efficiency and boosted web request time by reducing the program defects.
- Etsy- Created an analyzer called Phan for PHP to identify false positives and reduce errors in the server-side scripting.
Django vs. PHP— Pros and Cons
Pros of Django
- Faster development: Developers can use the batteries-included framework to add functionalities to reduce the development time and shorten the time-to-market.
- Scalability: Presents a lot of opportunities to scale seamlessly and keep up with the growing needs. Additionally, it supports a plethora of websites with millions of users and huge traffic.
- Secure: Facilitates the creation of secure websites and applications and protects them against common attacks such as cross-site request forgery, SQL injections, clickjacking, etc.
- Flexibility: Supports rapid changes during development, thanks to explicit programming and a host of libraries and packages. You can quickly pivot according to market trends while working on Django.
- Machine learning-friendly: Preferred for machine learning algorithms because of its computational and statistical capabilities. You can easily add advanced features to your application and woo customers.
- Rich talent pool: Written in Python, one of the most popular programming languages, its popularity translates into the availability of competent developers and an active community to fast track the development process.
Cons of Django
- Not suitable for smaller projects: Django is a coding-intensive framework occupying a lot of bandwidth and server processing time. So if you are not planning to scale up the project in the future, you may want to think long and hard before going through all the hassle.
- One request at a time: Unlike other popular frameworks, Django can’t handle multiple requests simultaneously, making it harder for developers to work on the underlying code.
- Slow evolution: Django is also considered to be monolithic. All the modules developed need to be backward compatible, thus slowing down the framework evolution.
Pros of PHP
- Pre-written Scripts- Comes with pre-written, ready-to-use codes that save time for development.
- Cross-Platform- Supported by major operating systems including Linux, Solaris, UNIX, macOS, and Windows.
- Learning Curve- An easy-to-learn language with a consistent and logical syntax that shares similarities with C.
- Database Connection- Compatible with popular database services like MySQL or MariaDB and offers clutter-free data exchange, minimizing the time taken for building web applications.
- Speed- Boosts user engagement and SEO rankings by loading web pages faster without disruptions.
Cons of PHP
- Need for Interpreter- You will need an additional interpreter program to allow the interpretation of codes in computer-friendly language, which slows the speed of websites.
- Lack of Uniformity– Lack of uniformity in structural patterns of frameworks can increase the cost of hiring new human resources.
- Speed Issues- Developers need to add-ons for a better user experience which slows the website down.
Django vs. PHP— Performance Comparison
How does Django stand out in terms of performance?
Django isn’t the fastest framework out there. But then the following question should be— how fast do you want it to be? You might run into a few bottlenecks if you happen to employ Django for the wrong use case. In fact, you may experience a slow down when serializing and deserializing JSON strings, converting database queries into Python objects, and running requests through middleware.
However, you can easily bypass all these possible performance issues by sticking to the best development practices, deploying optimum hardware, and identifying the best areas of applications.
Stack Overflow, and 23,000+ watchers on Github. As a matter of fact, the community is only growing with time, and we can expect to see a healthy amount of activity around this framework in the future. You can easily find various Django enthusiasts on other platforms as well– Discord server with 3,400 members, Telegram group with 6.08k participants, and various thriving Slack channels among others.
How does PHP stand out in terms of performance?
PHP offers better performance on higher concurrency as compared to its counterparts. The concurrency relates to the number of machines or devices that a language can handle for user request execution. Early versions of the language lacked the ability to handle concurrency, which is rectified in the latest iterations.
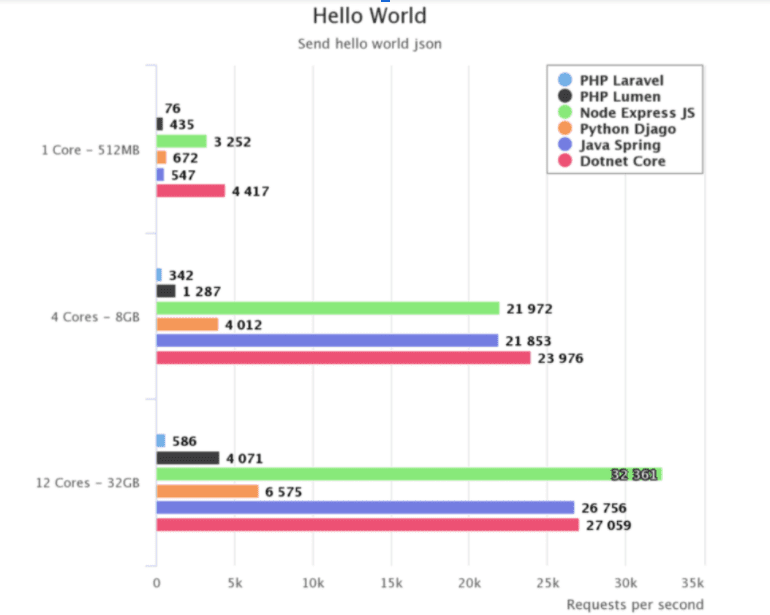
According to a benchmark test, PHP’s 8.0 version generates 1617 requests per second for single concurrency, whereas, for higher concurrency, say 20, it initiates 9352 requests per second. The REST API test contains 500 routes, 15,000 translations, and returns about 100 objects serialized in JSON.
Simultaneously, if you are to render a big template with about 93,700 lines of code, the score will be 53.3ms at 18.7 requests per second for a single concurrency. But, as the concurrency increases, it renders more requests per second that are 86.
Django vs. PHP— Application Architecture
What kind of architecture does Django support?
It follows the MVT (Model View Template) architecture, which is a slight variation of the widely used MVC (Model View Controller) architecture. A significant difference between the two architectures is that the template file containing HTML and Django Template Language does the controller’s job of facilitating the creation of dynamic websites. Consequently, it gets convenient to manage scenarios where each user is supposed to have a personalized feed, such as on Instagram.
What kind of architecture does PHP support?
PHP offers a wide range of frameworks such as Ubiquity, Zend, Laravel, Codeigniter, CakePHP, and others that mostly provide MVC architectures, which differentiates the business logic with the representation layer. While the model part helps with the data side of the application, the view part extracts data from the model when it receives requests from its users. The trigger for the execution of requests is handled by the controller part. In fact, frameworks like CakePHP offer ORM (Object Relational Mapping) to reduce SQL reliance for the database connection.
Django vs. PHP— Scalability
Is Django scalable?
The range of high-traffic Django applications such as The Washington Post, Instagram, Spotify, etc., speaks volumes of the framework’s scaling capabilities. It works flawlessly with various technologies while maintaining optimal performance and loading times. When it comes to scaling, it becomes crucial to optimizing elements like DB, images, CSS, etc., and balancing the load with other resources. On top of that, you also need to make space for scaling by implementations such as CDN and cloud solutions. If anything, Django facilitates all these operations. It is among the best frameworks to deploy if your long-term plan is to scale up your web application.
How Scalable is PHP?
PHP is a highly scalable scripting language, and it can be great for small businesses or enterprises. For example, it scales through opcode cache and autoloader by interpreting the code, for each request, to a machine-friendly language.
With opcode cache, it saves the interpretation from the first request that is automatically applied to further requests. So, PHP does not have to recompile the entire code on each interpretation. As recompilation slows the performance on each request it becomes an obstacle for scalability. Similarly, autoloader removes required to include statements and improves the performance on various requests.
Love PHP? Here is a detailed comparison between PHP and Laravel for you
Django vs. PHP— Ease of Testing
How easier is it to test a Django app?
Testing is not much of an issue on Django with the array of tools provided to simplify the test-writing process. Moreover, its comprehensive documentation allows you to roll out efficient websites and applications free of anomalies. You can effortlessly test all the layers of logic and come up with a bug-free end product.
How easier is it to test PHP applications?
Testing PHP apps becomes easy through scalar-type hinting and return-type declaration. With scalar-type hinting, the code’s intent becomes more explicit, and PHP can easily track all the data types returning from a function in the app.
When you validate the assertion, only one string of data is necessary as PHP ensures that the function can only accept the same data. Furthermore, it makes the tests shorter and more comfortable to write, verify, and maintain. Return type declarations, at the same time, warrants precision of the return datatype from the function. What’s more, it allows you to create an error-free testing environment.
Django vs. PHP— Microservices compatibility
Is Django compatible with microservices architecture?
In a word, yes! Features like rapid development, built-in security features, and versatility make Django a fine backend technology for microservices architecture. While Django projects can usually be scaled exponentially, breaking it down into smaller microservices functionalities is a good idea and simpler with this framework. One of the reasons you may want to include Django in one of the microservices is to introduce ML features into your project.
Is the PHP compatible with microservices architecture?
PHP is compatible with SOA (Service Oriented Architecture), which predates microservice architecture. However, there are many similarities between SOA and microservices. For starters, both the architectures work on the same principle of breaking down the application into smaller individual units. You can leverage SOA and create microservices that encapsulate large-scale services or systems in comparison to modern architectures. Additionally, it offers microservices that scale independently and are resilient to failures. With service-oriented architecture, there is no limit to message queues for asynchronous calls.
Django vs. PHP— Database support
How good is the database support for Django?
Django provides official support for PostgreSQL, MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, and SQLite. While it runs seamlessly with these five databases, it also works well with other database backends by third parties. Additionally, Django gives you the liberty of using multiple databases at a time if the project demands. It’s safe to say that the framework won’t disappoint you while setting up databases for your website or application.
How good is the database-support for PHP?
PHP supports primary database services like MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, IBM-DB2, Sybase, and MariaDB. Most importantly, it offers a PDO (PHP Data Objects) layer that constantly interacts with your app and database services.
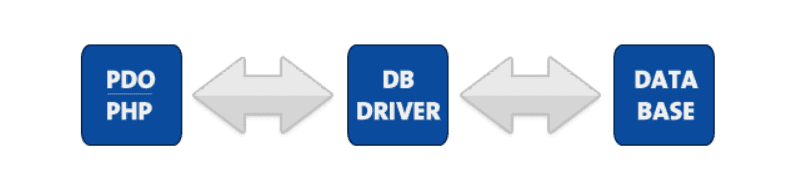
So, even if you are switching from MySQL to MariaDB or PostgreSQL, you won’t need extensive coding. It offers other features like,
- Abstraction layer
- Object-oriented syntax
- Prepared statement support
- Efficient exception handling
- API security and reusability
Django vs. PHP— Community
How big is the community around Django?
Django enjoys the perks of a large community around Python. When it comes to raw figures, the Django community has more than 101k members on Reddit, 289,000+ questions tagged in Stack Overflow, and 27,000+ watchers on Github. As a matter of fact, the community is only growing with time, and we can expect to see a healthy amount of activity around this framework in the future. You can easily find various Django enthusiasts on other platforms as well– Discord server with 3,400 members, Telegram group with 12.57k participants, and various thriving Slack channels among others.
How big is the community around PHP?
PHP has a vast community of developers that spans over different frameworks built on this scripting language. The open-source programming language has more than 5.5 million developers with different levels of experience.
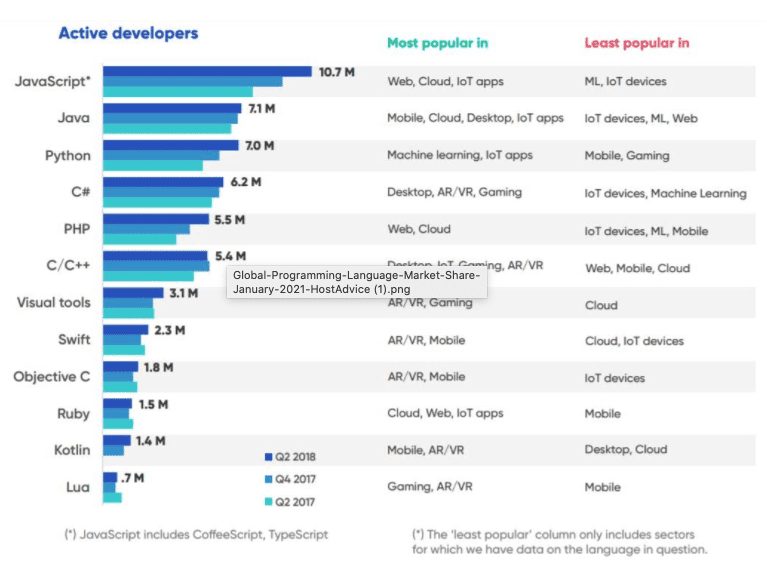
Django vs. PHP— Hiring developers
How convenient is it to hire Django developers?
The large community of developers around Django and an increasing number of skilled Python developers make it easier to hire Django developers. The average hourly rate for Django developers is $61-$80, so you should not find it challenging to find one or some for your projects. With only a few things in mind, such as the portfolio and experience, you should be able to decide upon the right developers for you.
How convenient is it to hire PHP developers?
Many factors affect the cost when you hire a PHP developer like hourly rates, total hours of operations, total coding needs, and others. You could choose to engage freelance developers through online communities or simply hire a PHP development company. While the average cost for freelancers is around $61-80/ hour, the hourly range of hiring a development company ranges between $25 and $49.
You may end up bearing more costs than expected on freelancers, for the different frameworks employed by them may lack uniformity of structural patterns. However, when you hire a development company, you have the potential to minimize costs as the team comes with a diverse skillset that enables quick problem solving and faster development.
Conclusion
Django is a great web application framework with support for advanced technologies like machine learning. At the same time, PHP is an easy to understand scripting language that can help create robust web apps. But if you are to pick one from these two back-end technologies, it will depend on the projects you will be working on.
Choose Django if:
- Your project needs more features at reduced development time.
- You want to develop a web app based on AI-based technologies.
- You need to develop new features on the fly.
- You want to create an app that can work across platforms.
- You are building a geographic-based application with extensive use of maps.
- You are creating custom software or an online application for business analytics.
Choose PHP if:
- Your project is of small scale and does not require too much scaling in the future.
- You need a web app without the need for real-time changes in features.
- You want to create an image processing app or a marketplace for stock images.
- You need a desktop application for your online business tools.
- You are building a website with cloud integration for scalability.
- You want to build an interactive website from scratch through hand-written codes.