Catching up with the latest technology trends in software development is difficult and implementing it even more difficult. The story is not so different for serverless. Leaving the misnomer debate aside, cloud architects find it challenging to change their old VMs and container ways to adopt serverless technology.
But the technology which snowballs into popularity is often the result of the tremendous community feedback and experiments.
Thus an understanding of practical use cases is essential to bring clarity, consensus, and commitment towards the adoption of serverless.
In the previous article, we discussed simple use cases of AWS Lambda and their applications for cloud architects who want to get started with serverless. In this blog, I would be explaining a few more AWS Lambda examples which are a bit complex.
#1. AWS Lambda Example showing Media Transformation
Cross-device development is a huge concern when it comes to application development. Facilitating this comes at a high cost and manual tasks which hinders the efficiency of development teams.
However, with AWS Lambda you can solve and automate this problem by developing a multi-platform media and content delivery pipeline.
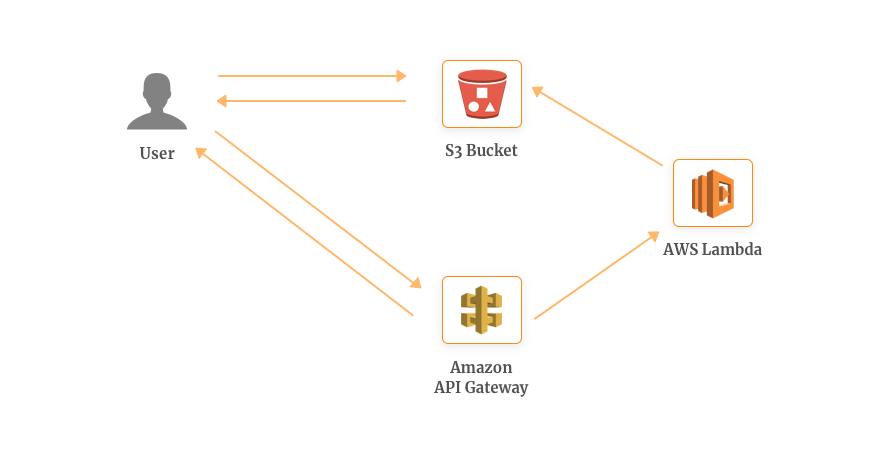
For example, whenever a user requests for an image which isn’t available in the Amazon S3 bucket, the user’s browser follows the redirect and request the image resize through Amazon API Gateway.
This triggers the Lambda function which fetches the original image from the S3 bucket, resizes it and uploads it back along with the corresponding requested key.
The best example is Netflix with its 70 billion hours of content in a quarter to nearly 60 million customer uses AWS Lambda examples of media transform to facilitate their media files in more than 50 formats.
They are also leveraging it to build a self-sufficient automated infrastructure to replace inefficient processes to reduce the error rates and valuable time.
The major areas where AWS Lambda helps are
- When you’re redesigning your website or app, you don’t need to resize your entire image archive. Transformation on the go gives you high agility.
- With on-demand image resizing, you’re not required to store your archive in every possible format. Along with this, you can also delete the expired and older images.
- With Lambda, each request is initiated if the required image is not available. This means each request is not affected in any way with the previous failover.
#2. Deriving Multiple Data Format from Single Source
Many times there comes a requirement when a single object is required in multiple formats. AWS Lambda along with S3 & SNS helps in building a general purpose event-driven system which processes the data in parallel.
To facilitate this, a pub-sub (SNS & Lambda) model is used to create a layer where data can be processed in the required format before sending it to the storage layer (S3).
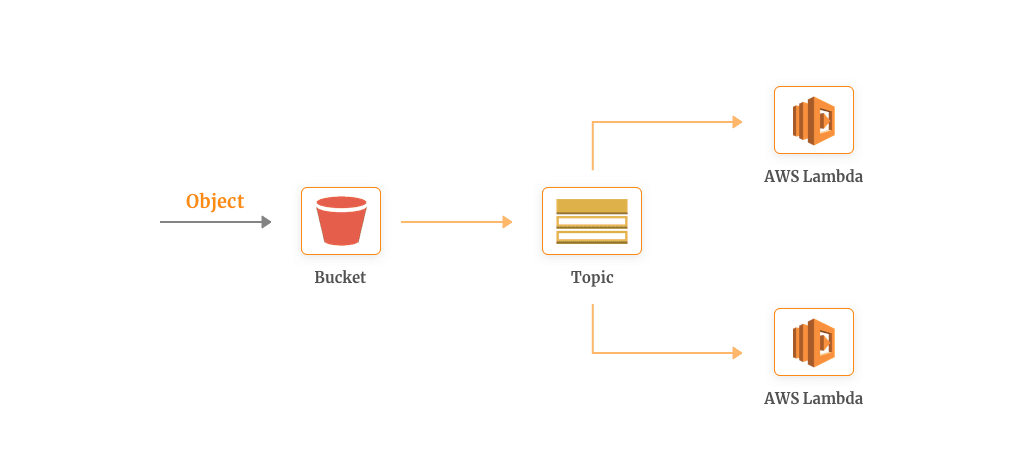
In the above architecture, SNS works as a publisher of message delivery while AWS Lambda as a subscriber. Here, the event notification from the Amazon S3 goes to the Lambda functions which will process the multiple derivatives of the given data object.
The main part of our architecture is the “SNS topic”. It is notified when the object enters into the S3, transforms it into the message and distributes it to the subscribers (AWS Lambda). This architecture is not only fast (due to its serverless nature) but is scalable without much hassle of maintenance.
Here are some of the use cases of the above architecture:
- Processing the data logs to produce multiple result derivatives which can be used for operations, marketing, sales, etc.
- Transforming the content from one format to another, for example, Microsoft Word to PDF.
- A master media file which needs to be converted into multiple formats.
#3. Real-Time Data Processing Example using AWS Lambda
Processing data in real time and responding to them is highly imperative for modern business requirements. To enable this, analyzing the metrics data in real time is critical. But Amazon Kinesis Stream and AWS Lambda have made it possible!
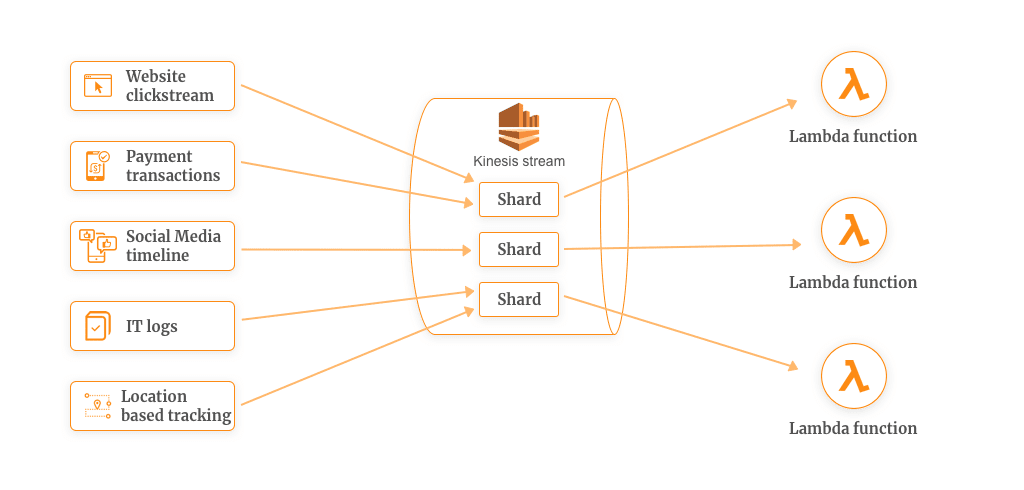
Create a Kinesis Stream and configure it to capture data from your website. Kinesis facilitates the data volume processing on 1 shard: 1 function basis to limit the parallelism as soon as you hit a certain data limit per shard. The number of Lambda function instances scales automatically as the stream is scaled.
Once your application writes the records to the stream, AWS Lambda polls the stream from the shard and process them whenever a new record is found.
For example, you can have your Lambda function polling the Kinesis stream 5 times a second on a per shard basis. That means one Lambda function is invoked every 200ms per shard.
Here are a few examples of data sources:
- Website clickstream
- Payment transactions
- Social Media timeline
- IT logs
- Location-based tracking
You can integrate Kinesis and AWS Lambda in 3 different formats:
- Stream-based model (event source mapping) where you map out your data sources across your app/website. These sources write data to the stream and whenever a new record is found, a Lambda function is invoked to execute your custom logic.
- Synchronous invocation model where you invoke your Lambda function manually using RequestResponse invocation type (synchronous invocation by manually monitoring the Kinesis stream.
- Event structure model where your Lambda function receives data as a collection of records to process. The batch size of these records needs to be specified at the time of event source mapping.
For example, there are thousands of IoT devices sending data logs. In some cases, you need to execute an operation when a condition is matched, Lambda & Kinesis works best for you! Also, check out how Dubsmash used Kinesis + Lambda while they were scaling for 200 million users.
Bustle processes high volume of site metric data in real time. This allows them to capture more data quickly. Which in turn helps them in analyzing how new features are affecting the website audience. Not only that, they have been able to monitor user engagement which has empowered marketing to make decisions driven by data.
Check how we improved the online web experience for International Hockey Federation (FIH) on the AWS stack
#4. Custom Logic Workflows using AWS Lambda
We have often come across complex applications (e-commerce, analytics software, ERP, etc) which consists of complex repeatable scenarios that need to be executed in a response to some event. In other words, workflows.
Earlier, it was not possible to include Lambdas in such workflows. Coordinating these functions, chaining them and checking conditions for deciding what to do was a responsibility of a developer.
However, with Step Functions, coordinating AWS Lambda is possible. These functions will be short, easy to test and will accommodate a single responsibility.
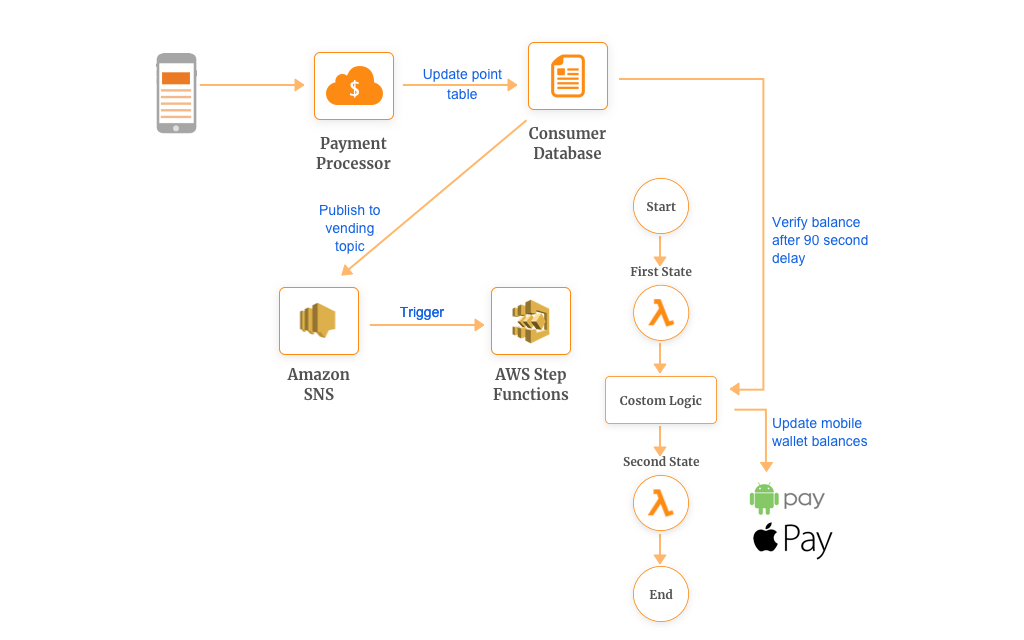
As shown in the image, you can apply custom logic before you invoke your subsequent functions, for example, delay of 10 seconds. Some of the potential scenarios where you can use Step Functions and Lambda are:
- Customer onboarding
- Shopping Cart Management
- Drip Marketing
- Loyalty programmes
For Coke Vending Pass Program, developers used a combination of SNS and Lambda. But eventually, it was slow to react and prolonged timing dependencies. This lead to confusing updates to the vending machine. As a potential solution, 90 seconds of time delay would work fine and hence they added a delay to the first Lambda function.
As you might have guessed it, this increased the execution time of the function which resulted in an increased bill. In order to make this solution more cost-effective, they turned to Step Functions to coordinate their components of microservice at scale.
Similarly, FoodPanda, the popular food delivery giant uses Step Functions along with AWS Lambda to improve their food delivery application workflow and continually improve their delivery times.
Here’s another interesting example by Alex Casalboni where he developed a state machine which estimates the best power configuration to minimize the cost for any given Lambda function.
Check How We Helped Our Client, Swift Shopper, To Build E-commerce Solutions On the AWS Stack
#5. Change Data Capture with AWS Lambda
Many times it is required to analyze and keep track of the changes made in the database. Or maybe you want to process data before it is stored in the database. With AWS Lambda & DynamoDB Streams this is possible.
Amazon DynamoDB, when integrated with AWS Lambda, can help you trigger a piece of code that automatically responds to the events in the DynamoDB Streams. These triggers can help you build an application that reacts to the data modification in DynamoDB tables.
Once you enable DynamoDB Streams for your database, it keeps records of changes such as puts, updates & deletes. Whenever an item is modified in the table, a new record has appeared in the DynamoDB Stream. AWS Lambda polls the stream and executes your function which can be used for custom requirements.
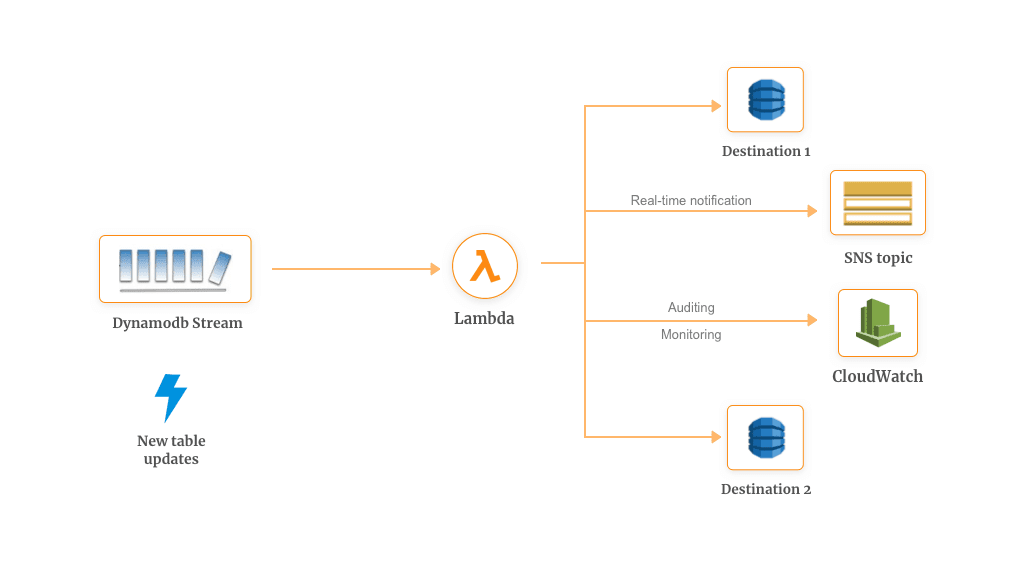
DynamoDB streams with AWS Lambda can also be used for enabling multiple workflows. Some of them are:
- Cross Region Replication
- Filtering
- Monitoring
- Auditing
- Notifications
For example, cross-region replication is highly useful when you want to run real-time applications in parallel. Mapbox serves maps to almost 100 million unique users every month across the world. To reduce the speed at which the maps are delivered and rendered, they turned to cross-region replication using DynamoDB and AWS Lambda. More information can be found here.
Similarly, Netflix also uses AWS Lambda to update its offshore databases whenever new files are uploaded. This way, all their databases are kept updated.
Apart from this, you can also use AWS Lambda examples to create backups of the data from DynamoDB Stream on S3 which will capture every version of a document. This will help you recover from multiple types of failure quickly.
Another example, you can use AWS Lambda to notify SNS for multiple use cases. Suppose you want to send out an email whenever new books are added to the library.
For this, whenever new books are added to the database, an AWS Lambda function will trigger which will notify SNS. This, in turn, will send mass emails to the students.
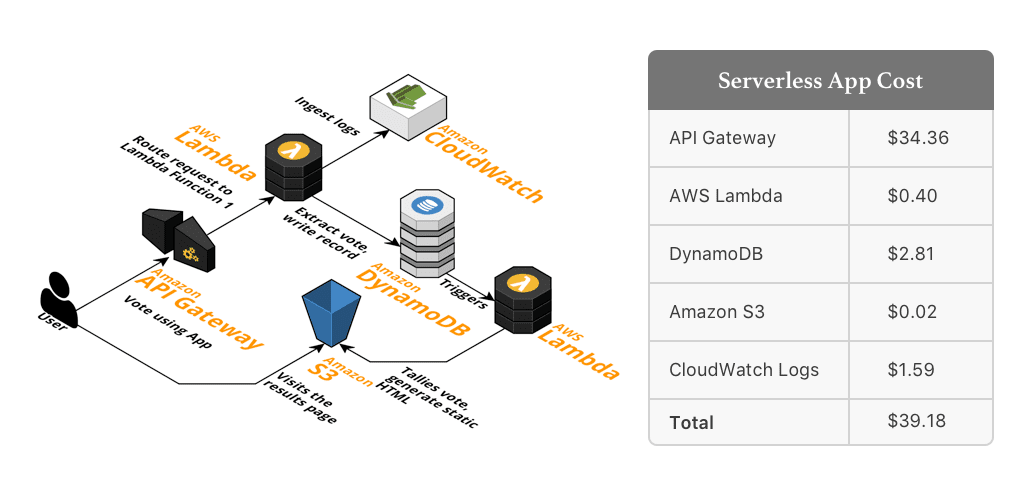
Is running a serverless application cost effective. Let find out!!
I recently wrote this blog – ‘AWS Lambda Pricing: How much does it cost to run a serverless application?‘ which covers the price structure of AWS Lambda, how to monitor lambda functions, strategies to optimize the cost and case studies.
#6. AWS Lambda Example showing Custom Alexa Skills
Most of us are familiar with Alexa, popularized with Amazon’s multiple lines of Echo smart speakers and devices.
We are accustomed to using voice-enabled searches and interacting with voice assistants in-built in our smartphones.
One such AWS Lambda example is Alexa. This comes with a predefined set of functionalities (called skills) which are used for the voice interface. For voice interaction, Alexa processes the natural language into a programmatic action.
For example, you can create a straightforward and basic functionality which will call a Lambda function in response to the given voice command.
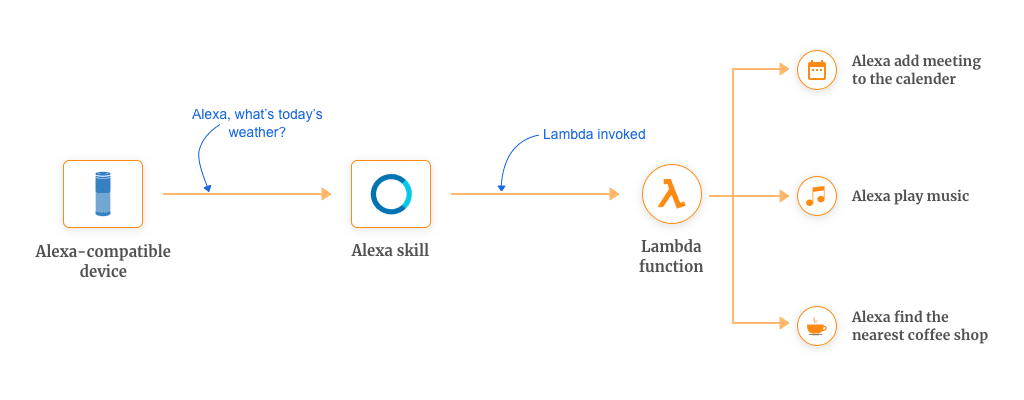
- Custom Alexa Skill Set: This is an object embedded inside AWS Console which invokes your handler function in response to the voice command from the Alexa enabled devices.
- Alexa Skill Handler Function: This is an AWS Lambda function which provides us with the custom logic that we want our command to execute. This handles the task of fulfilling the user’s request.
- Third Party Functions: These functions are hosted outside of the Alexa skill. These provide us with the functionality of interfacing with the 3rd party services like interacting with a Database, call to a 3rd party services, etc.
Some of the Alexa skills that you can write for yourself are:
- Adding a meeting to the calendar
- Finding out the nearest coffee shop
- Create a reminder
- Playing the music
Need some more inspiration? Check out this list of 50 most useful Alexa Skills.
#7. Automated Stored Procedures using AWS Lambda
To derive multiple formats of data, sometimes users need to do compute work. This compute work is based on the data which is being inserted, updated or deleted to the database. However, oftentimes they do not want the compute work to be done on the compute resources but on the database itself.
Amazon Aurora MySQL has the ability to invoke Lambda as a “storage/stored procedure”. This functionality triggers the function before/after some operations of interest are performed on the particular database table.
This ability of Lambda has reinvented the old methods of stored procedures to new methods which are higher and greater in the velocity.
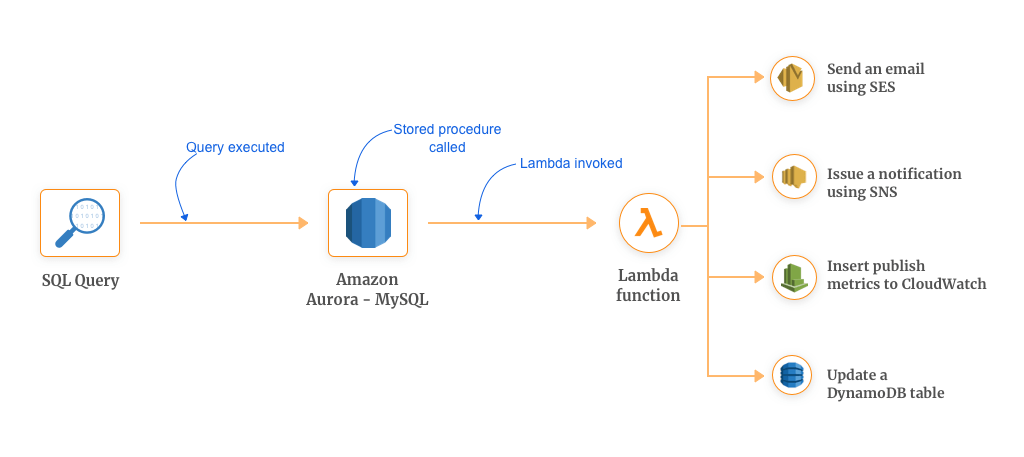
This could be very useful for databases having high velocities or high traffic where traditional stored procedures have become a pain point in terms of consuming CPU resources from the other capabilities of the database. You can take this use case to invoke Lambda for whatever your requirements be.
This mechanism helps you wire other services of AWS with your Aurora database. Here are some of the things you can do:
- Send an email using SES
- Issue a notification using SNS
- Insert publish metrics to CloudWatch
- Update a DynamoDB table
On the application level, you can now do the following things:
- Implement complex ETL & workflows
- Track & audit actions on database tables
- Perform advance performance monitoring & analysis
Combining AWS Lambda example with Amazon RedShift (Data Warehouse)
Amazon RedShift has the number of different ways for which it creates events along with AWS Lambda, for example, when you want to create replicas, do snapshots, backups or create an event to which SNS topic is subscribed to.
This SNS topic subsequently invokes Lambda which can be useful for things like:
- Single region multiple copies
- Creating multiple copies of redshift clusters
- Responding to failures/incidents
- Number of automotive capabilities
#8. Serverless Image Recognition Engine
Imagine you have a website where people can upload images. As soon as the images are uploaded, you want the images to go through a set of workflow actions.
For example, a workflow where a user uploads an image which is stored in the S3 bucket triggers a Lambda function 1. This function invokes the state function workflow, as shown in the image.
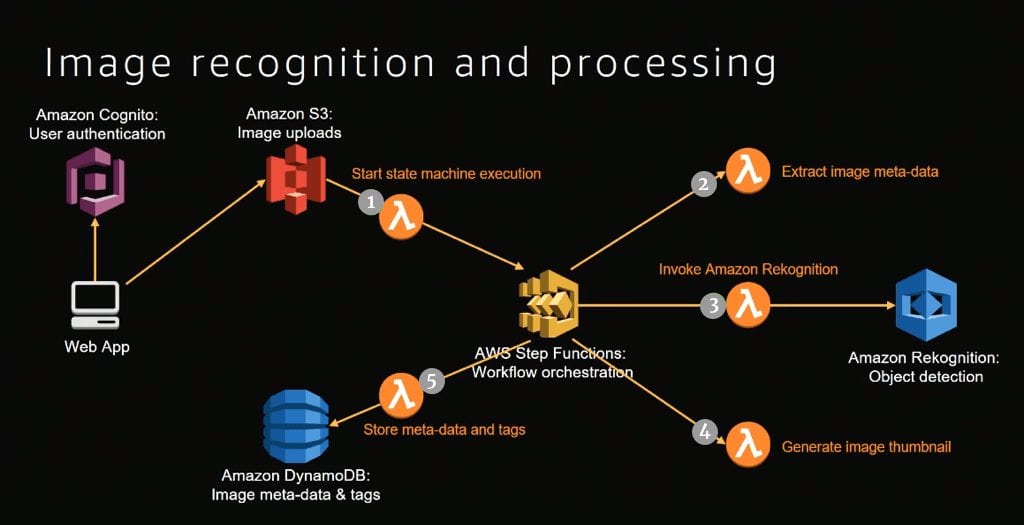
Source: AWS re:Invent 2017
This step function workflow orchestrates the job of multiple Lambda functions. The first thing it does it to extract the metadata from the image, for example, image type information. Meanwhile, another three lambda functions are invoked in parallel.
- Lambda function 2 is invoked to extract the image metadata
- Lambda function 3 invokes the Rekognition which finds out the object in the image
- Lambda function 4 is invoked to generate an image thumbnail
- Lambda function 5 writes all this information back into the DynamoDB
End result: Whenever the page refreshes after the user has uploaded the image, they see all the metadata, thumbnail and the object tagged that are evident in the image. This is an example of an image processing pattern and can extend it as per your custom requirements.
NatGeo Example: As they were moving towards a larger platform, they found out that they have a lot of metadata about the text content but the images didn’t really have a lot of metadata and that was affecting how they were surfacing content which isn’t tied to the text.
This was important since they were trying to showcase images and videos and not just magazines articles.
Using AWS Lambda example and Rekognition helped them in two ways:
- Personalizing not just the content but images as well
- Cropping mechanism where the system identifies the focal point and crops automatically
#9 Serverless Text-to-Speech Example
With the advent of AI enabled devices, text-to-speech has become imperative for modern applications. Medium being the latest one in facilitating TTS functionality. More to that, speech synthesis is a tricky subject and the list of interpretation challenges is endless.
With AWS Lambda & Amazon Polly, you can harness the power of lifelike speech synthesis application. Amazon Polly uses advance deep learning technologies to synthesize speech that resembles the human voice.
AWS Lambda here enables Polly to work with faster response times which is critical for real-time and interactive dialogue.
Here’s an application architecture of our sample application which converts a text module into an MP3 file. To run the application asynchronously, SNS is used to receive information and convert the files simultaneously.
This uses two methods where AWS Lambda along with API Gateway as a RESTful web service:
- Lambda 1: Initially for sending out the notification about a new post which is to be converted into an MP3 file.
- Lambda 2: For retrieving information about the post which includes a URL of the MP3 file stored in the S3 bucket.
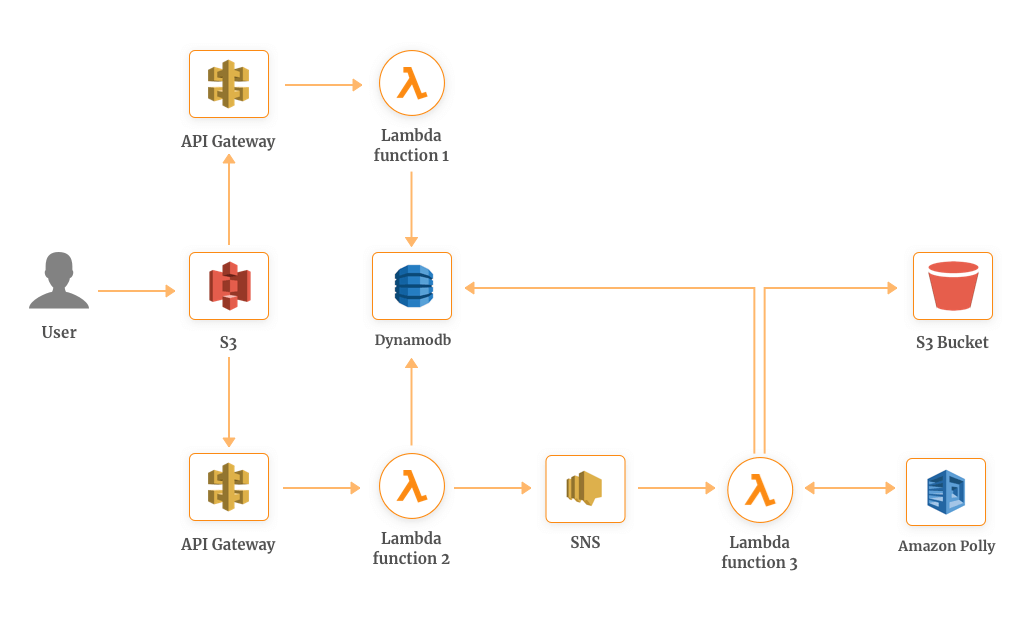
How does it work?
- Whenever a new post is added to the S3 bucket, a dedicated API Gateway triggers a Lambda function 1 which initializes the process of MP3 file generation.
- Lambda function 1 stores the copy of the information in DynamoDB where information about all posts is stored.
- Meanwhile, Lambda function 1 is publishing a message to SNS which trigger Lambda function 2. This function along with Amazon Polly converts the text into the audio in the same language as the text.
- After that, an MP3 file is stored in the S3 bucket with the reference URL and the information about the same will be stored in the DynamoDB.
#10 Personalized Content Delivery through AWS Lambda
Today most of the application facilitates the personalized content and news feed. This is possible because the personalized user experience is becoming an inevitable feature and accessing & monitoring of user touch points is becoming easy.
However, setting up and managing a complex architecture isn’t a requirement. AWS Lambda has made it possible to get started easily with a personalized content platform with the possibility to make changes on the go. Let’s take an example of our reference architecture.
Here all the information extracted from users touch points is stored in the DynamoDB. With the help of Lambda function processed in the backend, it creates the user’s profile and a custom feed based upon various parameters.
This personalised feed aggregates the content from multiple places
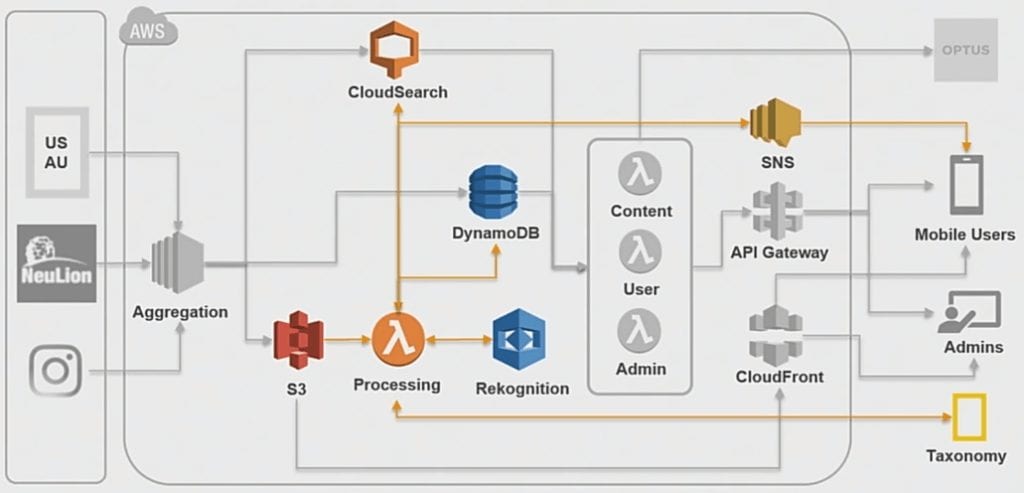
Source: AWS re:Invent 2017
Aggregate the content, normalize it and then prepares it for the delivery. Lambda function 1 is used to communicate with Rekognition where it classifies the image, gives the proper meta tags, resizes it according to the device and so on.
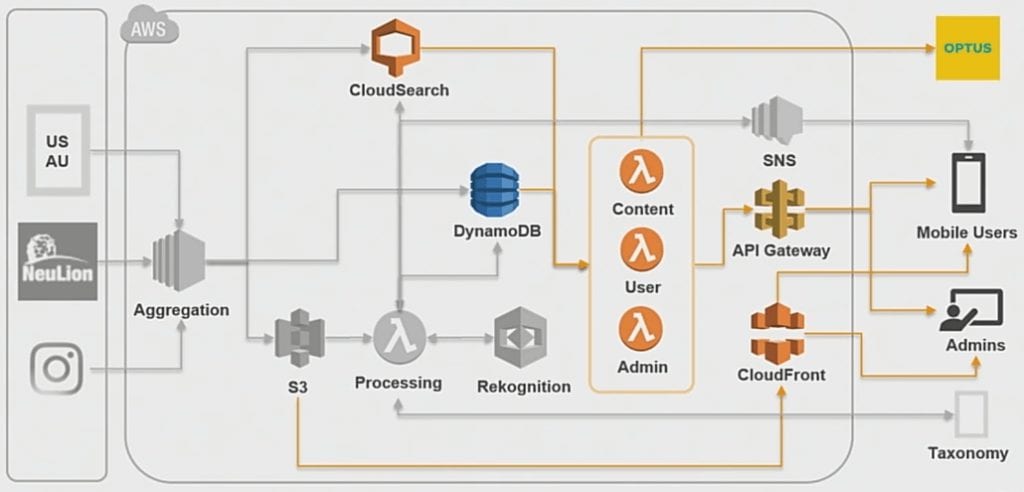
Source: AWS re:Invent 2017
This second part which facilitates the content personalization is mostly powered by the API Gateway and Lambda functions.
- Content API: The primary source of the feed is CloudSearch where the aggregated content is stored for the Content API to communicate.
- User API: This keeps track of what users are browsing in the application, monitors their activity with respect to time.
- Read/Write API: This is mostly pushing back and forth the data gathered into the DynamoDB
- Admin API: This is for the editors to manage things manually from the backend, for example, change the tagging, turn off if it’s unsuitable for the students, etc.
For understanding some simple use cases of serverless technology read my previous blog ‘10 AWS Lambda use cases to start your Serverless Journey‘
I recently wrote this blog – ‘AWS Lambda Pricing: How much does it cost to run a serverless application?‘ which covers the price structure of AWS Lambda, how to monitor lambda functions, strategies to optimize the cost and case studies.
Thinking to migrate your application to Serverless?
Conclusion
As it must have been evident that AWS Lambda has highly specific use cases with a bunch of prerequisites. Figuring out where to start can be a bit confusing! Connect with me on Twitter @RohitAkiwatkar or send me an email on rohit@simform.com to talk more about AWS Lambda examples.
Figuring out what fits best in your picture comes with experimentation and iterations. One must note that AWS Lambda isn’t a new technology although its potential is being realized soon. Can we say the future is serverless technology?
Only time will tell.