In today’s fast-paced digital era, businesses rely on different applications for operations like supply chain management (SCM), customer relationship management (CRM), business intelligence, and enterprise resource planning (ERP). But managing multiple applications and their data is a complex and challenging task. Eventually, they may end up with a cluster of applications operating in silos, unable to communicate and share data properly.
For example, in June 2020, DHL Supply Chain, a contract logistics global leader, recognized the need to ease the process of adding new automation devices to their warehouse management solutions.
To address this, it introduced a “plug and play” robotics platform, which helps its clients in implementing new robotic solutions in warehouses per their needs. The first implementation of this solution at a company site in Madrid resulted in a massive 60% cost reduction while integrating different systems and ensuring seamless data sharing.
Integrating applications across the organization has significant benefits in terms of cost reductions and operational efficiency. If your business involves using multiple systems for a range of activities, enterprise application integration is the best way to optimize operations.
In this blog post, we dive deeper into what enterprise application integration means, its benefits, challenges, models, and tools.
Let’s get started!
What is enterprise application integration (EAI)?
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) is an ongoing process of implementing tools and technologies that enable all business applications to share data and workflows with each other.

It ensures a free flow of data among different applications within the enterprise. Such data exchange is useful for making well-informed decisions.
Specifically, integration enables enterprises to:
- Find valuable data, applications, and services
- Access application functions via APIs
- Monitor application life cycles
- Combine multiple enterprise services
Overall, enterprise application integration ensures that changes in the data are correctly reflected among all the applications and can be used consistently.
Why is enterprise application integration important?
Although it offers several benefits, the main goals of enterprise application integration are:
- Database integration is the biggest goal of enterprise application integration. EAI removes data duplication and reduces potential mistakes through synchronization tools and data warehouse designs. As a result, your organization gets access to more comprehensive, accurate and consistent data for enhanced business intelligence.
- Another significant goal of EAI is to achieve efficient workflow integration across the organization. With enterprise application integration, your teams can complete related tasks by getting various tools to work with each other in a single workflow. Workflow integration increases productivity and ensures data consistency across different programs.
- Lastly, enterprise application integration also facilitates interface integration across all the connected applications. That means the components of all the applications present the same UI/UX to users, regardless of where they access those applications from.
Apart from these broader goals, here are the most important benefits of integrating enterprise applications:
1. Simplified and aligned processes
An enterprise application integration strategy strives to combine different processes to create a unified system for operations. If implemented well, EAI can streamline the IT processes and connect the infrastructure in a way that optimizes every process in the organization. This reduces waste, makes data easily accessible, and enables employees to collaborate effectively.
Moreover, when the applications are effectively integrated, customers have an easy access to personnel from various departments of the company. Integrated databases and workflows automatically direct customer inquiries to the corresponding department, helping customers reach the right person easily.
2. Eliminate data silos
Without the use of the right technology, communication between different applications can be complex and sometimes, ineffective. For instance, a company with 60 applications can have 60 disparate but similar data sets. So, if employees from different departments choose different data sets to process the information they need, the data variances can multiply greatly.
Enterprise application integration ensures optimum data usage by efficiently eliminating data silos. It centralizes all the crucial data in a single place, and users can easily review such data in real time. As a result, businesses and employees can easily access and share them without wasting time searching the multi-region databases.
3. Data-informed decision making
Information and data are generated at every level and department of an organization. Therefore, decision-makers rely on effective data reporting programs to use this information for making strategic business decisions.
Enterprise application integration provides a unified single source of truth for the decision-makers to extract the information they need, in their desired format. Also, EAI ensures that data is synchronized across different applications. This enables business leaders to access the most up-to-date data, reducing the risk of making decisions based on outdated or inaccurate information.
Ultimately, EAI-powered data-informed decision-making enables a business to achieve operational efficiency, identify opportunities and prepare for unforeseen challenges.
4. A surge in overall productivity
Juggling multiple software tools is time-consuming which eventually reduces your team’s productivity. Instead, having a single interface connecting these software solutions can save a lot of time.
Application integration brings everything under a single umbrella and streamlines the overall workflow. It lets users create a seamless series of events and automate data transfer by using information from one tool to feed the process of another. This eliminates the need for entering data manually into different tools, eventually reducing errors and input time.
Challenges of enterprise application integration
When apps are customized per an enterprise’s specific needs, they are quickly adopted and integrated into daily operations. But, developing robust and secure enterprise applications is not easy; it necessitates precision, vision, and expertise. The challenges can be numerous, but it is critical to be aware of them to obtain the best product:
1. Obsolete software
Software gets outdated with time. Outdated products have problems integrating with other systems and become non-compliant with companies’ requirements. They often crash and have bugs, and it is rather tricky to implement new functionality.
2. Skill shortages
Finding skilled experts has always been troublesome for enterprises. On top of that, third parties lack the motivation to meet your business requirements in full. Such shortage in skills can make it challenging for enterprises to implement applications, eventually leading to delays, suboptimal performance, and high costs.
3. Fewer capabilities
Inadequately integrated applications directly impact customer interactions. Furthermore, customer response time lags when employees work across poorly integrated applications. When an organization lags in response time, it risks Service Level Agreement violations and poor customer service ratings.
Examples of commonly integrated applications
Various software integration methods use different infrastructures to meet the needs of a business. For example, some solutions transfer data between specific subsystems, while others use an interconnected network to create a robust database.
Thus, companies should educate themselves on each system integration method to determine which option is best for their organization. Here are some common application integration examples:
1. On-premise
On-premise software requires an enterprise to purchase a license or a copy of the software. As the software is licensed and the entire instance resides within an organization’s premises, it offers better protection than a cloud infrastructure.
Traditional techniques for internal application integration include specialized coding. However, an enterprise service bus (ESB), a middleware platform that uses a rules engine to convert and route messages and enable communication across applications, is also a viable option.
2. SaaS
Nowadays, enterprises use different SaaS applications across their entire ecosystem. SaaS app integration includes connecting a SaaS application with cloud-based or on-premise solutions via various APIs. Thanks to SaaS applications, enterprises can seamlessly transfer their essential data to the cloud and access it from anywhere, anytime.
3. Application-to-application
Application-to-application integration is the process of enabling different programs to communicate and collaborate separately. It helps businesses to seek comprehensive visibility into essential business operations and end-to-end processing. It also allows for automation and boosts productivity by removing the need for manual data entry.
Enterprise application integration levels
Business organizations employ various enterprise application integration strategies. In general, there are four levels of enterprise application integration- business process integration, communications-level integration, data integration, and presentation-level integration, etc. Let’s look at them one by one:
1. Business process integration
In business process integration, organizations make strategies to improve their performance and achieve desired enterprise goals by automating their processes.
Business process integration can be done in three ways – Pull, Push, and Process Trigger.
- Pull: In this type of integration approach, the data is automatically transferred from any system to Business Process Management (BPM) software.
- Push: Here, the data gets transferred from BPM to a separate system. Transferring a successful candidate’s data to the HRM is the best example of this type of business process integration.
- Process Trigger: An event happening in a specific system triggers a process in an enterprise’s BPM. Also, process triggering takes care of the automated process execution based on an event.
2. Data integration
This level of implementing enterprise apps allows users to share information between applications with complete transparency. Without it, integration is unclear and incomplete.
Most application integration solutions rely on either specialized code or translation to convert each application’s output to data. These concepts are the backbone of any successful enterprise application integration solution.
3. Communications-level integration
Communications-level integration is a method to achieve data and business process integration. While data integration ensures that applications can communicate with one another, communications-level integration specifies how communication takes place. APIs are used to accomplish these tasks.
4. Presentation-level integration
Presentation-level integration or screen scraping amalgamates multiple applications into a single one with a standard interface. This can be achieved via middleware solutions and technology.
Presentation-level integration creates a virtual intermediary for data collection. Then the data gets distributed to each of the separate applications. Overall, this method provides a suboptimal way for data integration and access.
How does enterprise application integration model work?
Various EAI models are available to businesses, similar to any other integration solution. Each type contains a distinct methodology and framework to improve data management and overall communication. The top five models for enterprise application integration are:
1. Point-to-Point Model
In the Point-to-Point model, developers create unique connector programs for each integration. Here, every connection requires a separate script to process, translate, and send the data to the receiving app.
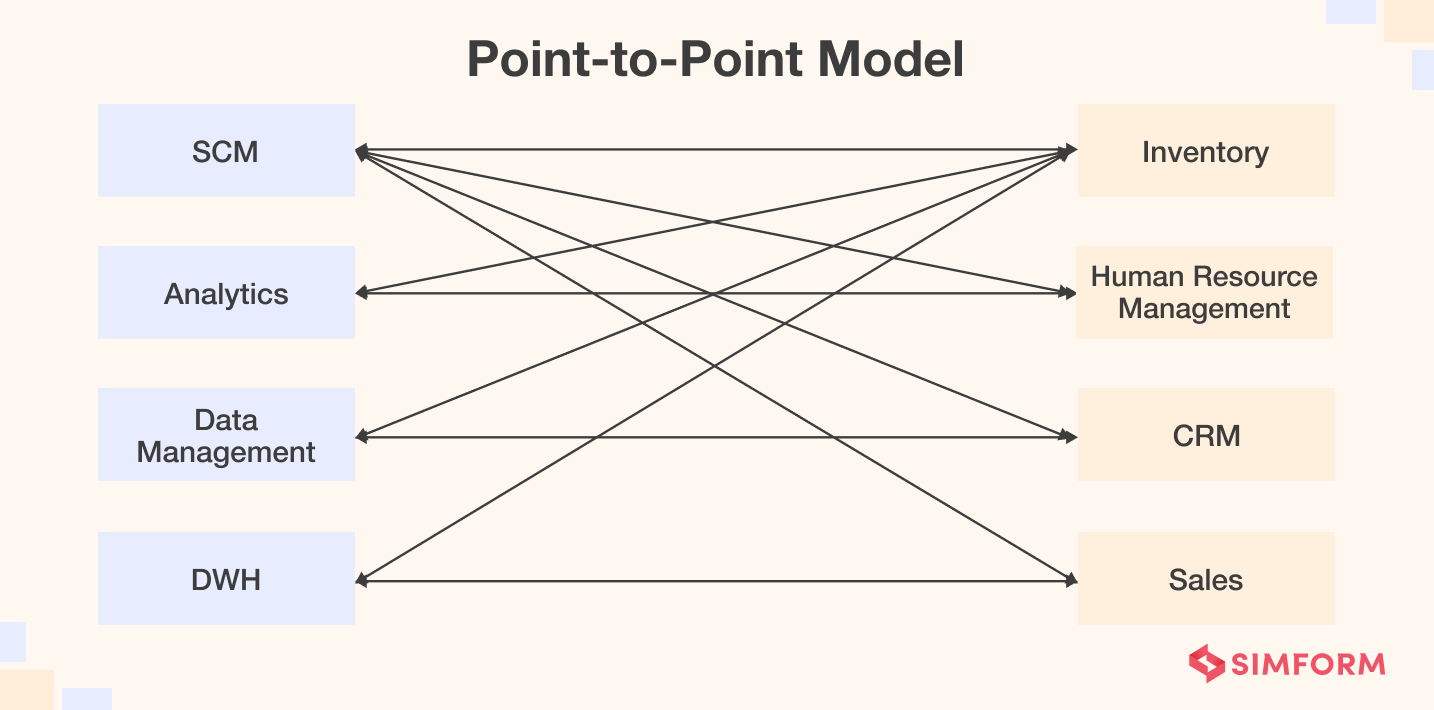
The Point-to-Point system suits enterprises that just have minimal services. It offers greater flexibility by letting the users add an abstraction level. Overall, the point-to-point model is fast, reliable, and inexpensive for coordinating minimal components.
2. Hub-and-Spoke Model
The Hub-and-Spoke model has a central component solely responsible for integrating different features and facilitating the connections of every single element. In other words, this model works like a central hub, responsible for receiving, reformatting, and sending data to the specified destinations.
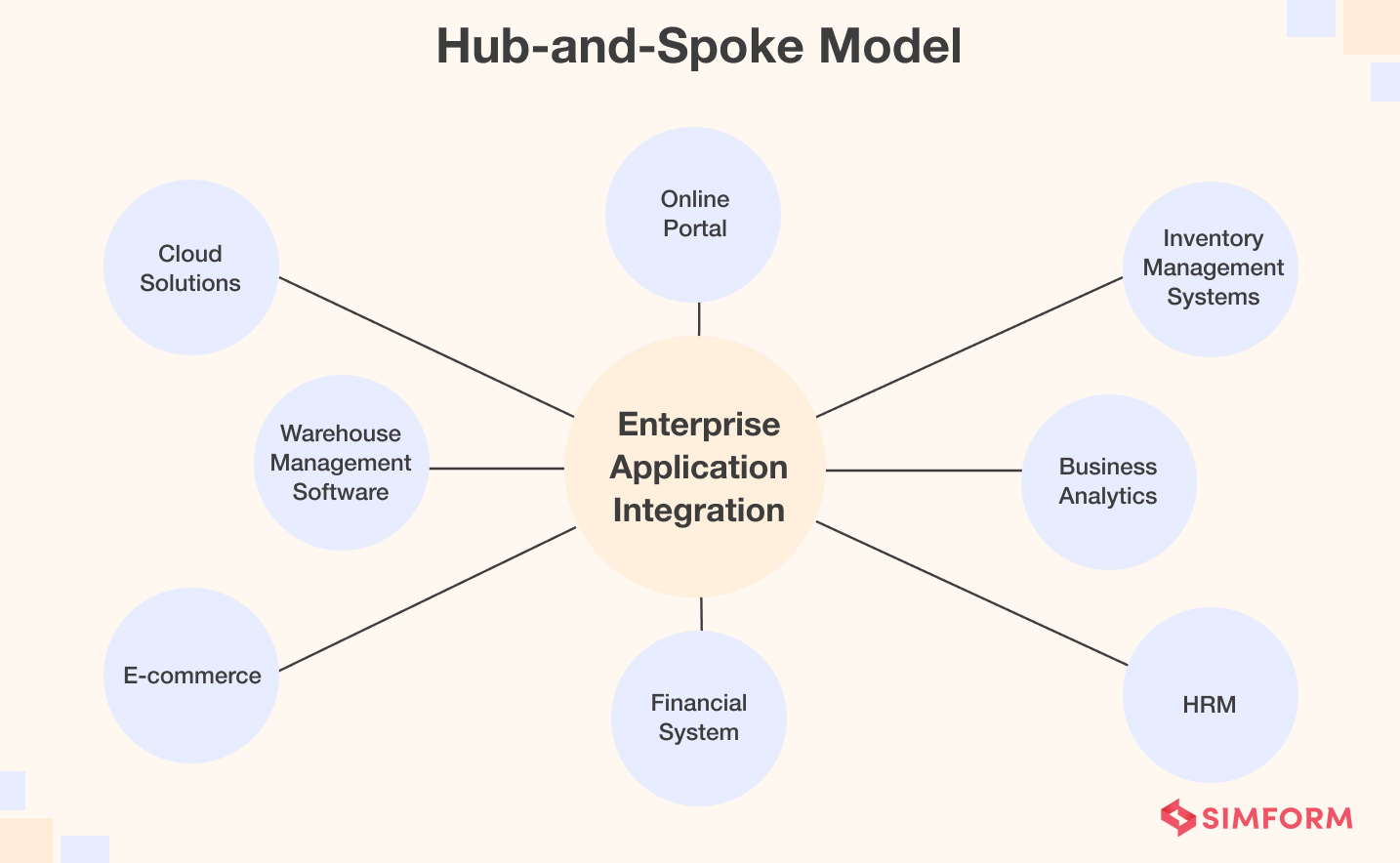
Hub-and-Spoke integrates several organizational services. What’s more, it lets businesses add and remove particular components as per their needs.
3. Enterprise Service Bus Model
The Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) model relies upon Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA). It offers excellent interconnectivity to facilitate communication between network applications. Furthermore, the ESB model creates an indirect connection between systems that enables the development of simple applications.
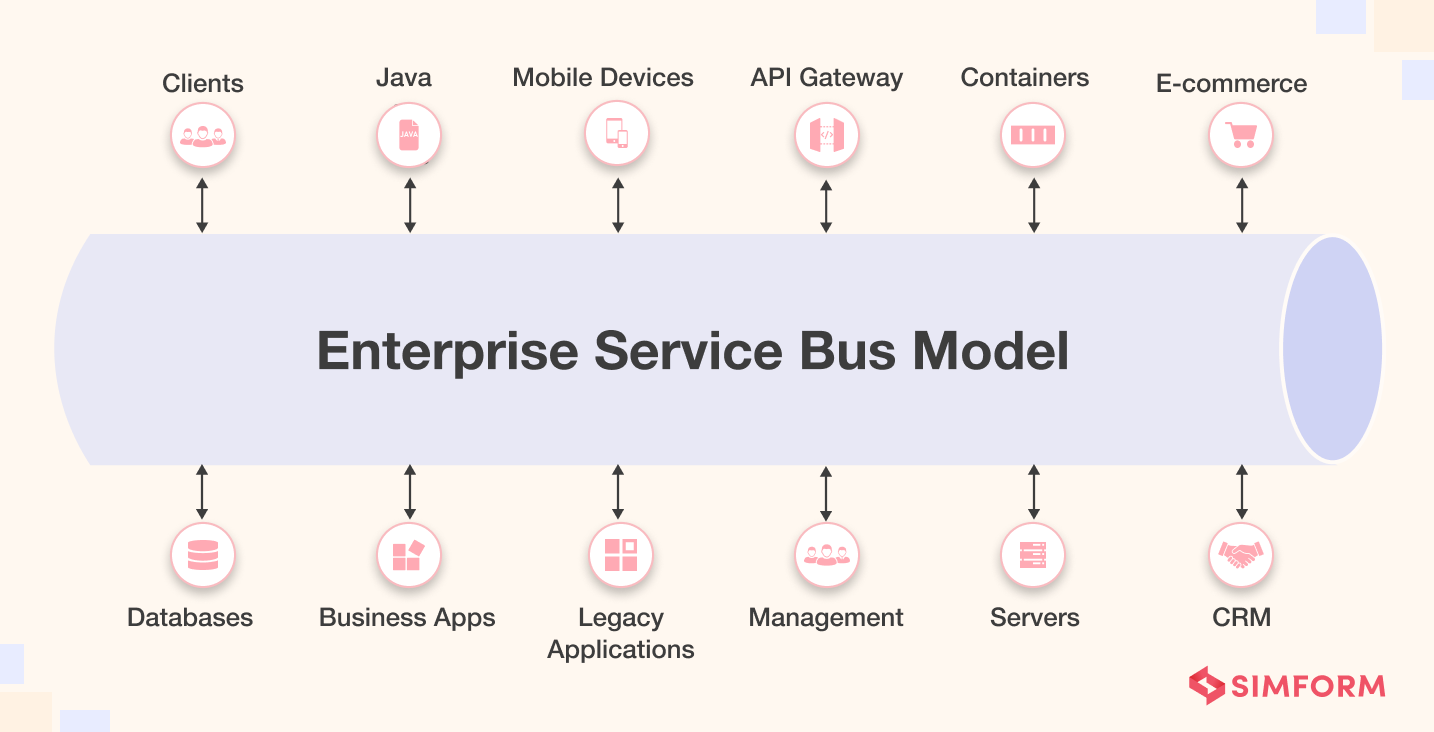
The enterprise service bus model is easy to implement for large, complex systems, avoiding the bottleneck issues of a single hub. It’s the most scalable EAI model, allowing new apps to be added and removed with minimal changes to the EAI software. Additionally, the ESB model doesn’t need constant attendance by developers.
4. Middleware
Middleware is a solution that acts like the connective tissue between applications, users, and data. Besides, middleware helps developers build and deploy applications effectively.
There are many types of middleware, like message brokers, transaction processing monitors, database middleware, message-oriented middleware, application-server middleware, mobile device middleware, etc. Notably, middleware creates a connection pool to offer faster access to back-end databases.
5. Microservices
Microservices is an architectural design approach for building applications. Under this approach, developers break down an extensive program into smaller, independent components, each with its own responsibilities.
Microservices support integration by breaking down a monolithic application into smaller, independent components that communicate via APIs. They are independent, so even when some services of enterprise apps fail or need some modifications, other services still continue absolutely uninterrupted.
Moreover, if enterprises operate their apps across several platforms and devices, they can implement microservices best practices to upsize or downsize them. This can be possible thanks to the modular components of microservices.
Enterprise integration tools
EAI vs. SOA vs. ESB
Now that we have covered all the basics of enterprise application integration, let’s briefly explore some other approaches for app integration, like Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Enterprise Service Bus (ESB).
Service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an approach to having software resources in an enterprise discoverable on different networks and services. Each service achieves a predefined business objective and performs discrete work units. They work within distributed systems architecture.
Although an enterprise service bus (ESB) is an integration model, it provides an API to develop services and makes them interact reliably. Technically, it is a messaging backbone that does routing, message format transformation, and delivering messages from various services and applications linked to ESB.
Although all three aim to integrate different organizational applications, EAI, SOA, and ESB differ in their underlying architecture. EAI is good for point-to-point integration, while SOA advocates for the use of reusable services. But when it comes to building a messaging infrastructure to connect loosely decoupled services, ESB is the right choice.
Ensure the effectiveness of EAI with Simform!
Enterprise application integration (EAI) connects various software applications and systems within an organization to streamline business processes.
It offers ample benefits like improved collaboration, enhanced operational efficiency, and better customer experiences. However, it poses several challenges, including skill shortages, lack of data security, complexity, and high costs.
However, working with an expert technology partner can help your organization achieve EAI efficiently. Recently, we helped one of our esteemed clients, who is a leading manufacturer of utility transmission structures and small cell towers, to digitize its legacy enterprise applications.
Our engineers assisted them with automating their sales and quotation process. Consequently, they have reduced turnaround time, achieved consistency, and seamlessly migrated their legacy system to the cloud.
If you are looking for an experienced team to work with your company and ensure the effectiveness of EAI for your business, let’s join hands and take your organizational efficiency to the next level.