When it comes to combining the growing availability of mobile technology with the essential need for good health, it’s no surprise to see a rapid increase in mHealth app development. The mHealth apps market size was valued at USD 56.26 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow to USD 861.40 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 40.2% during 2023-2030.
There’s a growing interest in enabling remote patient monitoring and telemedicine consultations for individuals in need of continuous care, living in remote areas, and those with mobility challenges. To effectively utilize these advanced services, patients need access to personalized health information and educational resources tailored to their specific needs and conditions.
This personalized approach empowers patients to actively participate in their health management and also allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions and deliver optimal care. Many more such innovative mobile health solutions are transforming today’s healthcare landscape by putting patients at the center of their care.
Read on to learn more about mobile health application development, from the types and benefits to challenges and implementation.
What is mHealth?
mHealth, short for mobile health, refers to the practice of medicine and healthcare supported by wireless technology and mobile devices like smartphones, tablets, wearable devices, and other electronic systems. This subset of eHealth allows medical practitioners, patients, and healthcare organizations to connect and share data.
The main goal here is to enhance the delivery, accessibility, and efficiency of healthcare services for all involved parties. To achieve this, we need mHealth apps that can offer various features for healthcare providers, medical professionals, and patients, of course.
And with the rise in the demand of mHealth services, the development of robust, user-friendly, and secure mHealth apps becomes even more important. An expert mHealth app development company like Simform ensures the navigation of the unique challenges of developing healthcare-focused apps.
Different types of mHealth applications and their features
mHealth applications are designed to cater to different users within the healthcare ecosystem, such as patients, medical staff, and organizations. These applications offer a wide variety of tools, making healthcare services more accessible, efficient, and patient-centric.
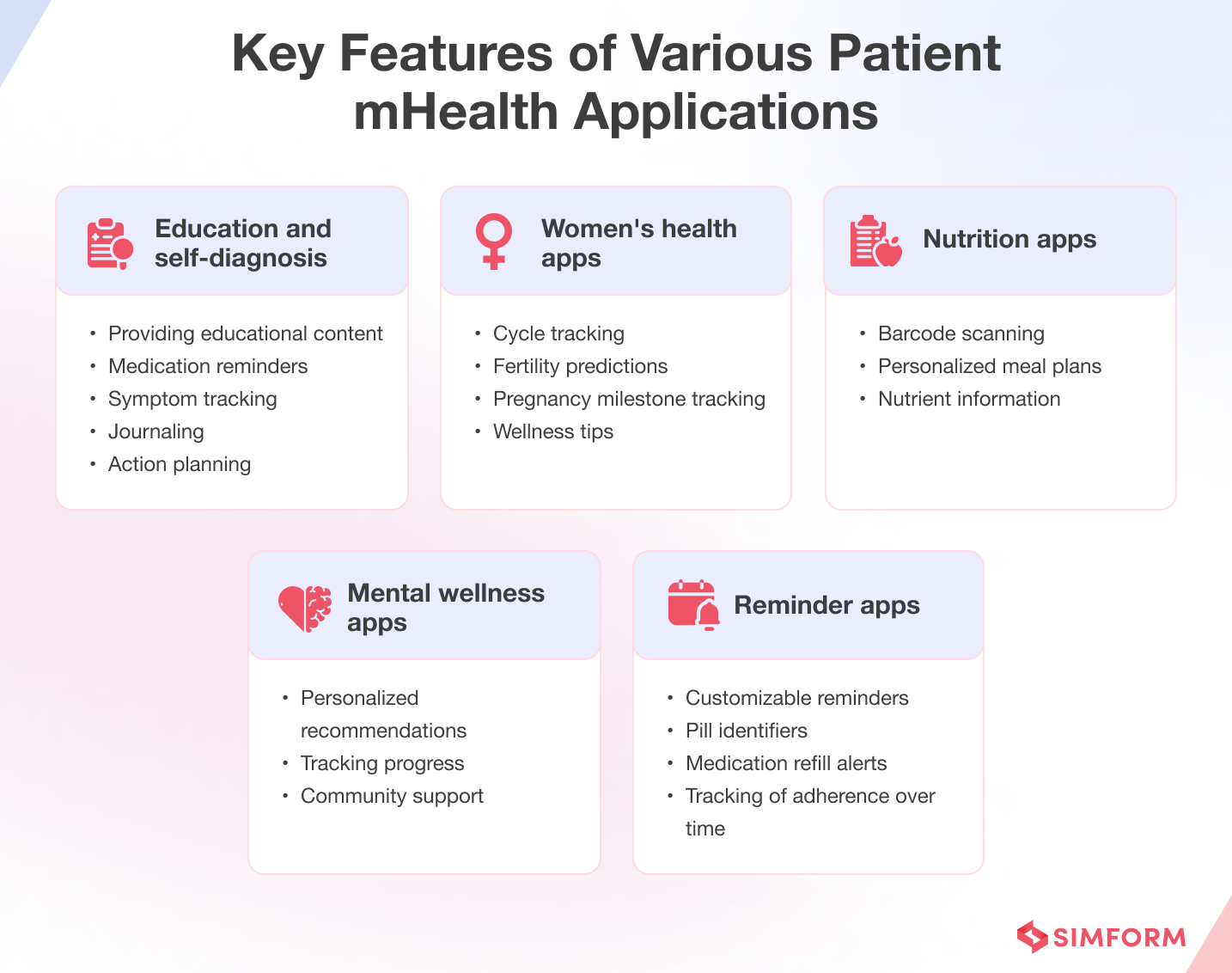
1. mHealth applications for patients
Healthcare apps empower patients to take control of their health, improve communication with healthcare providers, and enhance overall well-being.
Education and self-diagnosis apps – These applications provide patients with information about their condition, allowing them to better understand their symptoms and treatment options.
Nutrition apps also come under this category as they help users monitor their food intake, provide meal planning assistance, and offer suggestions for healthier food options.
Health monitoring apps – These apps track various health parameters such as blood pressure, glucose, kidney and lung function, heart rate, brain activity, and sleep patterns. They often integrate with wearable devices, add-ons, and offer data visualization, trending, and deeper insights into one’s health condition.
Women’s health apps can be tailored to address women-specific health concerns such as menstrual cycles, fertility, pregnancy, and menopause.
Mental wellness apps – Mental health apps support the mental well-being of users by offering tools such as meditation exercises, mood-tracking, stress-reduction techniques, and even cognitive behavioral therapy.
Reminder apps – These apps help patients adhere to their medication schedules and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
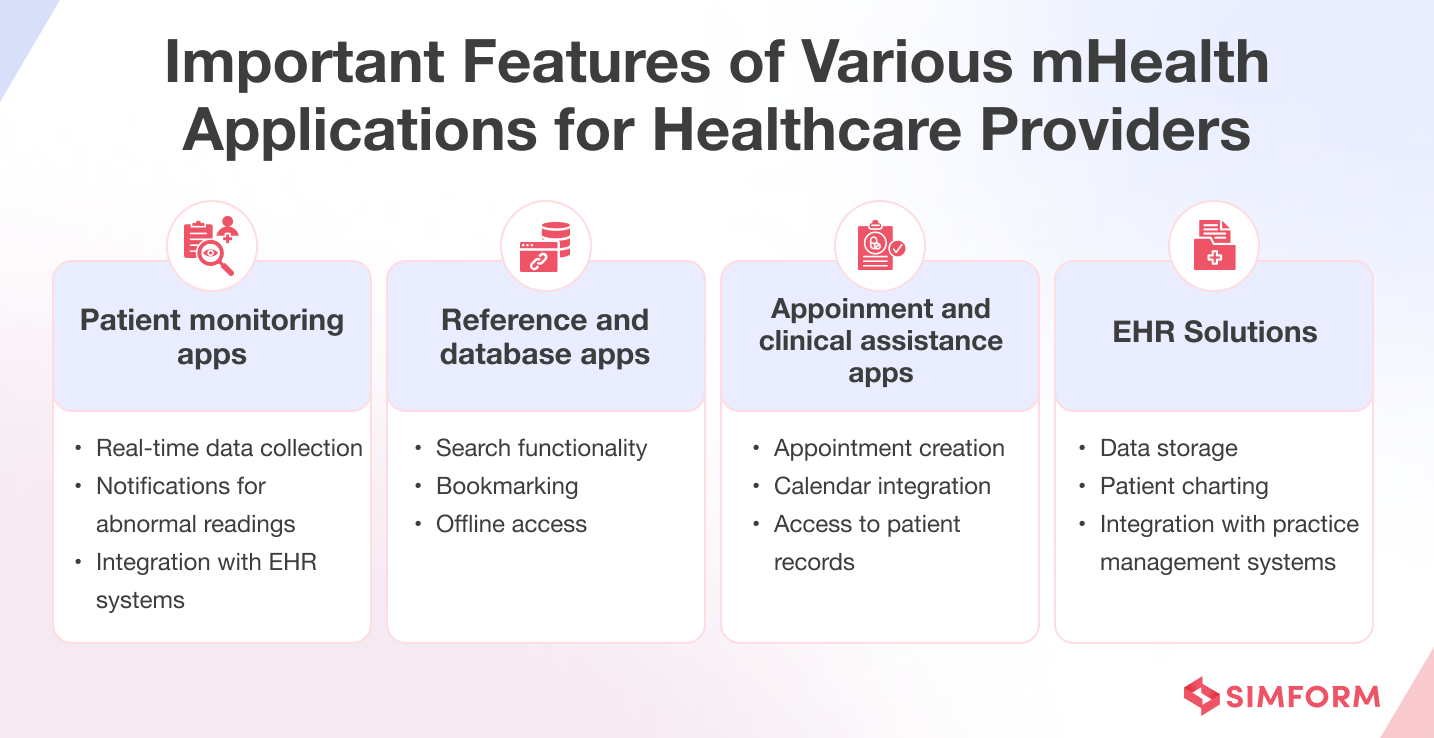
2. mHealth applications for healthcare providers
Healthcare apps enable healthcare providers streamline patient care, improve communication among medical teams, access medical records securely, and stay updated on the latest medical research and guidelines.
Patient monitoring apps – These applications allow medical staff to monitor patients’ conditions remotely, enabling timely intervention and improved health outcomes.
Reference and database apps – These apps provide healthcare professionals with up-to-date clinical information, such as drug interactions, dosages, and treatment guidelines.
Appointment and clinical assistance apps – Medical staff use these apps to manage their schedules, set appointment reminders, and access essential patient information.
EHR solutions – Electronic health record (EHR) applications streamline data management, allowing healthcare providers to access patient information securely and efficiently.
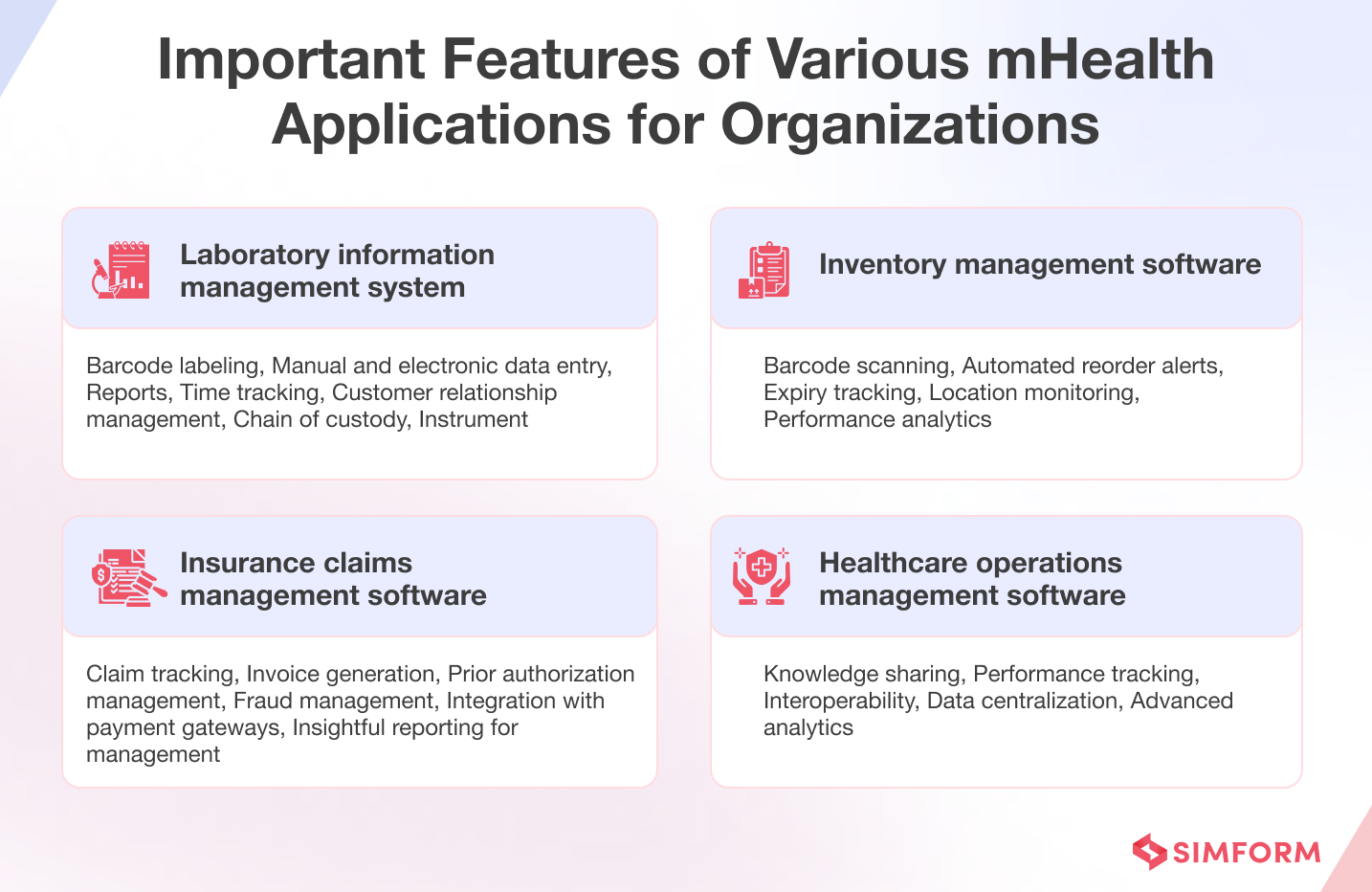
3. mHealth applications for organizations
mHealth applications are crucial for organizations not only for improving healthcare accessibility and patient management but also for enhancing internal operational efficiency by streamlining workflows, reducing errors, and automating routine tasks.
Laboratory information management system – A huge amount of data present in the modern lab cannot be managed with paper-based LIMS or spreadsheets. A Laboratory Information Management System addresses the data management, automation, and regulatory challenges of laboratories, and ultimately helps standardize operations by maintaining workflows, tests, and reporting procedures.
Inventory management software – Healthcare organizations need inventory management software to efficiently monitor stock levels, track medical supplies and equipment, automate workflows, reduce errors, ensure compliance, optimize inventory control, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Insurance claims management software – These applications streamline the billing process for healthcare organizations, tracking insurance claims and invoicing patients.
Healthcare operations management software – Organizations use these apps to improve internal processes, such as task management, staff training, communication, scheduling shifts, and integration of different hospital systems, such as EHR, laboratory, and imaging systems, for a more efficient and interconnected healthcare environment.
Benefits of mHealth apps
Before mHealth apps, health organizations relied heavily on traditional methods of communication and data collection, often resulting in inefficiencies and limited access to care for remote or underserved populations. These organizations also faced challenges in providing timely health information, monitoring patient progress, and promoting preventive measures to reduce the burden on healthcare systems.
Let’s see how the introduction of mHealth apps has revolutionized the healthcare industry.
1. Improved accessibility and convenience
Mobile devices come with high-resolution cameras these days, making it quite convenient for patients and physicians to have real-time communication. Telehealth services and patient portals enable physicians to assess patients’ symptoms, monitor their conditions, and provide preventative care without the need for in-person appointments. The importance of telehealth services became evident during crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Applications like MyChart provide patients and caregivers with instant access to necessary healthcare information, including personal medical records, medications, and physician contact information. These types of mHealth applications are particularly advantageous for patients with chronic conditions, mobility issues, those living in remote areas with limited healthcare facilities, and individuals seeking quick medical advice or follow-ups.
2. Better decision-making
Mobile apps in healthcare offer a wealth of information at the fingertips of both patients and medical professionals. With access to digital medical textbooks, up-to-date treatment guidelines, and a patient’s medical history, physicians can make informed decisions quickly. Additionally, pharmacists can use apps like Lexicomp to access drug information, ensuring patients receive the most appropriate medications. Enhanced decision-making also promotes patient safety, strengthens patient-provider relationships, and aids in the consideration of ethical and legal implications.
3. Enhanced accuracy and data security
The use of mobile apps in healthcare streamlines the process of data collection, storage, and analysis. With all essential medical information stored digitally in a single location, physicians can diagnose and treat patients more accurately. Furthermore, digital healthcare data reduces the risk of medical errors and miscommunications, while offering secure storage of sensitive patient information, ensuring privacy and confidentiality.
4. Increased efficiency and time-saving
Mobile apps in healthcare, such as cloud-based electronic health record (EHR) platforms, drastically reduce paperwork and manual administrative tasks. Using integrated machine learning algorithms, mHealth apps can analyze large amounts of information, allowing physicians to focus on patient care. This increased efficiency results in time-saving for both patients and medical professionals.
How to build a mHealth app?
There are many use cases for mHealth apps, such as building patient charts, sharing images, making e-prescriptions, sharing educational materials, identifying pills, and more.
Let’s understand how to build a mobile health application that successfully combines all necessary functionalities, creating an interactive platform for users and healthcare providers alike.
1. Ideation, design, and prototyping
During this phase, the focus is on understanding the key idea of the healthcare mobile app project and defining the set of tasks and goals for the application. Here’s what typically happens during this phase:
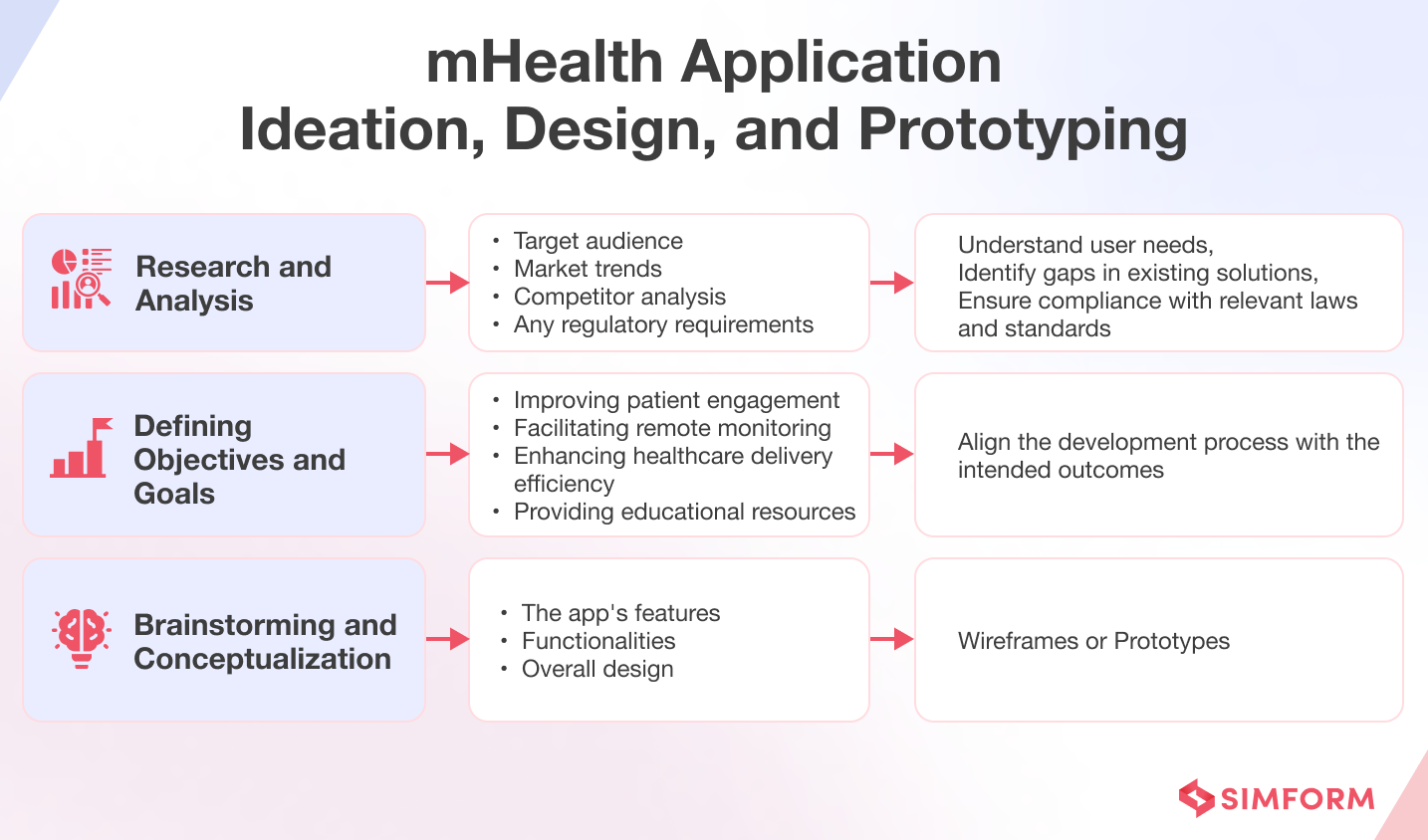
By the end of this phase, the development team should have a clear understanding of the application’s purpose. For example, they should know whether the app is focused on aiding emergency response efforts, promoting prenatal care for expecting mothers, or gamifying meditation and relaxation techniques.
There should also be clarity about who the mHealth app is for, its key features, and the overall design direction. For instance, knowing whether the app is targeted towards elderly patients managing their health, busy professionals seeking stress relief, or individuals with physical disabilities or limitations; the key features may include telemedicine capabilities, integration with wearables, or AI-powered personalized recommendations; and the overall design direction may prioritize accessibility, user engagement, or data visualization.
2. Development and testing
This is the phase where the application is created in several sprints, with specific features being built incrementally. Quality assurance is integrated at each stage of development, ensuring that the app meets required standards and specifications. Developers begin coding the app based on the finalized designs and specifications.
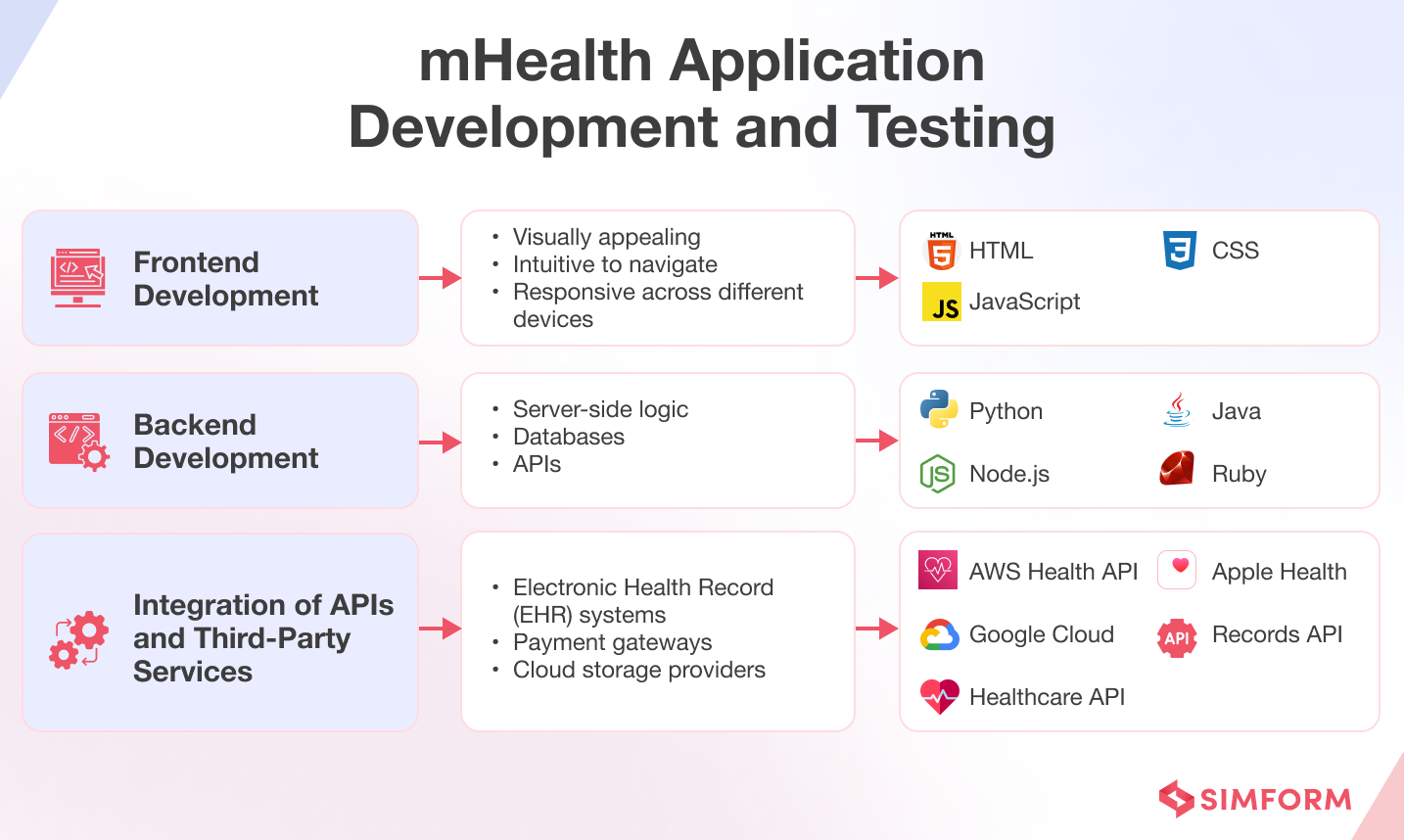
By the end of the development and testing phase, the development team should have built a functional and stable version of the application. They should have tested the application thoroughly to identify and fix any bugs or issues. When it comes to healthcare applications, for instance, the team would need to ensure that
- A medication management app can correctly identify drug interactions and provide accurate dosage reminders.
- A mental health app that offers cognitive-behavioral therapy exercises has been tested for usability, effectiveness, and data security.
- A telemedicine app allowing users to have video consultations with healthcare professionals maintains a strong connection and has proper encryption to protect patient data.
3. Deployment and maintenance
Now is the time to release the application to users. Ongoing support and updates are provided to ensure its optimal performance and continued relevance. Here’s what typically happens during this phase:
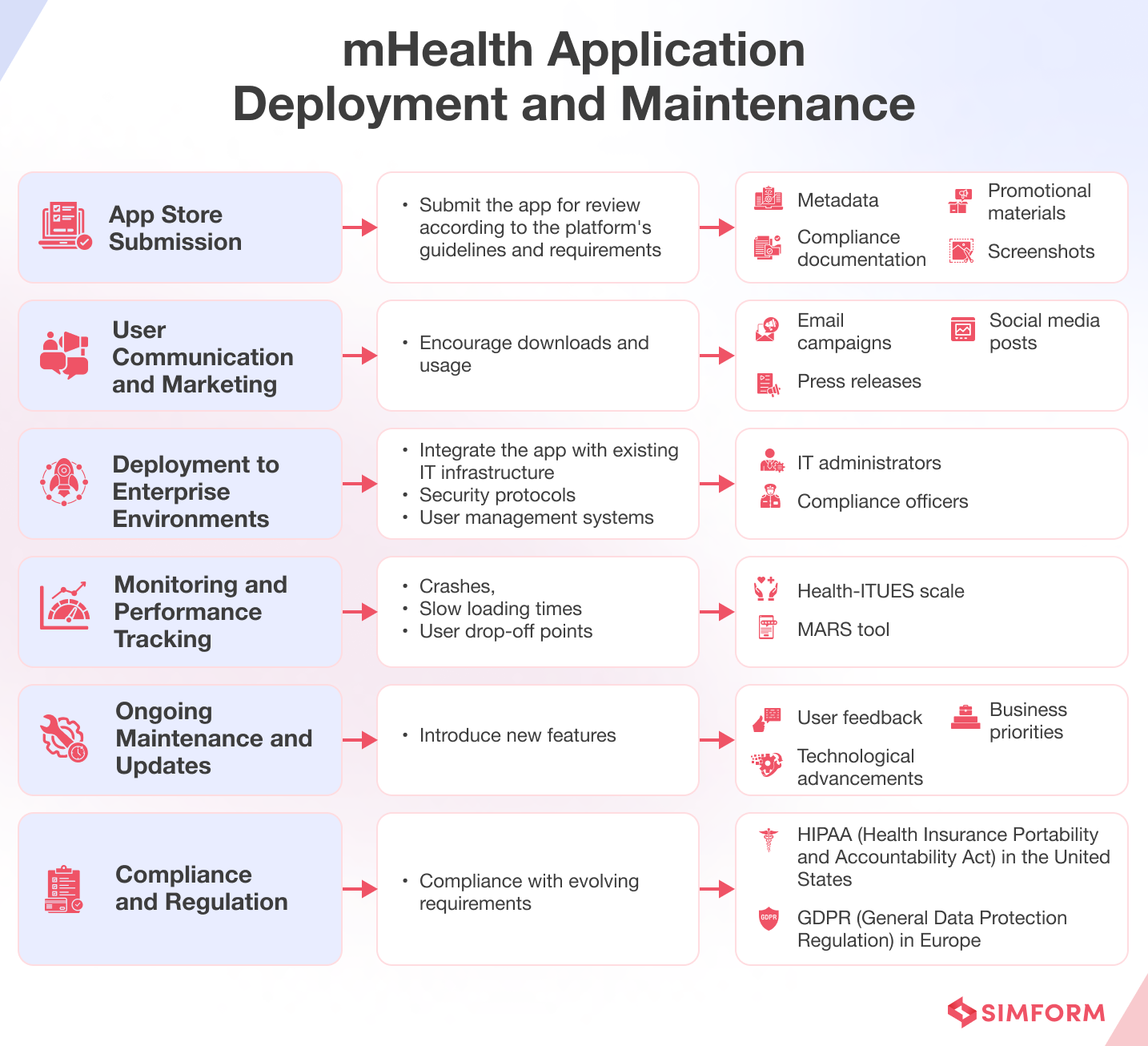
Now, as the mHealth application would be available for users to download and use, the development team should continue monitoring the app’s performance, ensuring it operates smoothly and fixing any issues that may arise. In the healthcare sector, this could involve:
- Regularly updating a fitness app with new exercises, dietary tips, and other wellness resources.
- Ensuring a hospital-centric app remains compatible with the healthcare facility’s patient record system, even as the system evolves and updates.
- Monitoring and maintaining the accuracy and relevance of a symptom checker app by incorporating the latest medical research and guidelines.
4. User feedback and updates
This phase focuses on gathering feedback from users, analyzing their input, and implementing updates and improvements to enhance the app’s functionality, usability, and overall user experience.
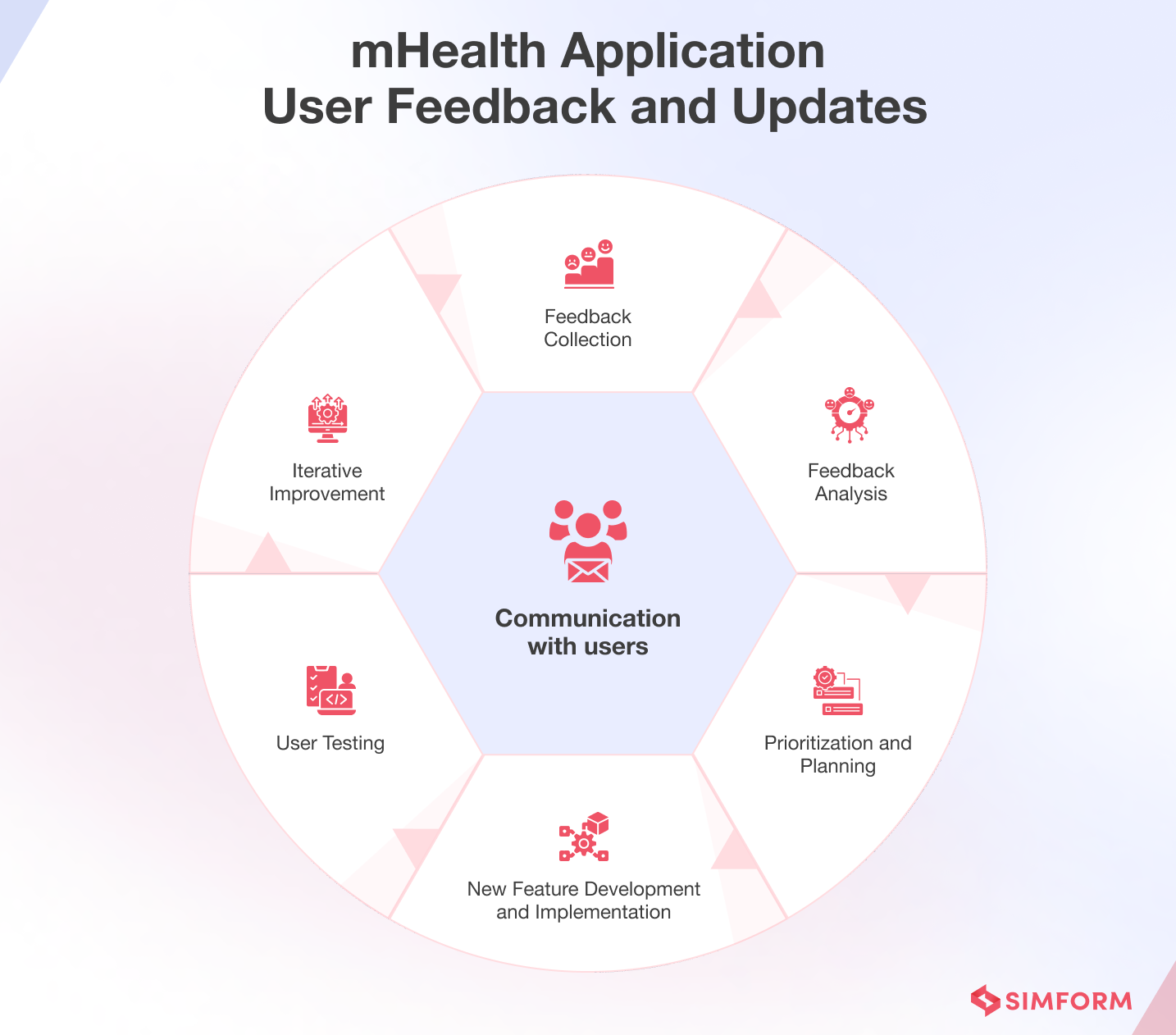
Examples of the development team utilizing the users’ feedback to refine the application, may include:
- Updating a diabetes management app’s user interface based on feedback from users with visual impairments to ensure maximum accessibility.
- Enhancing a mental health support app with new features, such as mood tracking or guided meditation, based on user requests.
- Improving the predictive algorithms in a fertility tracking app to better forecast users’ ovulation dates by incorporating feedback on real-world accuracy and effectiveness.
By embracing user feedback and continuously iterating on the app based on user needs and preferences, developers can create a more user-centric mHealth app that delivers value and fosters long-term engagement and loyalty among its users. However, there are various
Challenges in developing mHealth applications?
In addition to the inherent complexity of healthcare apps, poor project management, communication gaps, or a lack of domain knowledge can result in misaligned requirements, delays, and suboptimal solutions.
Here are the main challenges of mHealth app development:
1. Data privacy and security
Healthcare data can be highly sensitive, and unauthorized access to it can lead to severe consequences for both patients and healthcare providers. Having robust security protocols in place and meeting standards such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is important for compliance purposes.
Failures to protect user data can result in legal, financial, and reputational damages. For example, if a mental health counseling app leaks sensitive information about a patient’s psychiatric condition, this may cause social stigma, discrimination, or other negative impacts on the affected individual’s li
2. Integration with existing healthcare systems
Hospitals and clinics have established healthcare systems, including electronic medical records, billing systems, medical devices, and more. Without seamless integration, mHealth apps may face issues such as incomplete patient records, inefficient care coordination, delays in communication, and billing errors, which can ultimately compromise patient care and provider productivity.
However, healthcare systems often have proprietary or legacy technologies requiring customization and API development. This integration challenge could lead to increased costs, time-consuming workarounds, and numerous incompatibility issues. For instance, a prescription management app that can’t efficiently communicate with the hospital’s medical record system may cause delays and inaccuracies in medication dispensing or billing.
3. User experience and accessibility
A well-designed user interface is especially crucial for health apps where users may have cognitive, physical, or sensory impairments. Creating user-friendly, accessible, and intuitive mHealth applications can be challenging, given the variety of users with different medical conditions, age, education levels, and tech-savviness.
Failure to provide a good UX may lead to errors while using the app, resulting in patients abandoning the app, not adhering to prescribed treatments, or even putting their health at risk. For example, a poorly designed patient monitoring app might lead to incorrect data inputs, causing wrong medication dosage or misinterpretation by healthcare professionals.
4. Regulatory compliance and approval
Developers must navigate complex regulatory frameworks such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) when creating mHealth applications. These regulatory bodies are responsible for ensuring patient safety, and they require mHealth applications to undergo a thorough review for efficacy, accuracy, and security.
Non-compliance with these regulations can result in penalties, delays in approval processes, or withdrawal from the market. For instance, a medical device control app, such as one that controls insulin pumps, that cannot show efficacy in clinical trials or is vulnerable to security breaches may fail to receive regulatory approval or face recalls.
5. Scalability and sustainability
mHealth applications need to accommodate an increasing number of patients, devices, and data points as their use becomes more widespread. Developers must ensure their applications are scalable, with the capacity to handle large volumes of users and data seamlessly. Additionally, it is essential to have a sustainable business model that generates revenue, allowing the app to maintain its functionality, support its development, and remain viable in the long run.
An unsustainable or poorly scaled telemedicine app might suffer from reduced performance, frequent downtime, or potential discontinuation, negatively impacting access to healthcare services for patients in remote or underserved areas.
Emerging trends in mHealth technology
A patient-centered healthcare culture proves to be more than just a ‘nice to have’; it is truly a ‘need to have.’ Below are the trends in healthcare designed to prioritize individual needs and preferences, creating a more connected and engaging environment for both patients and medical professionals.
1. Enhanced medical imaging through machine learning
In addition to detecting diseases in early stages, performing robot-assisted surgery, assisting in clinical research and trials, ML algorithms can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical imaging analysis in mobile health applications. This can lead to faster, more accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment recommendations.
For example, machine learning algorithms can be applied to mobile applications designed to detect conditions like skin cancer or diabetic retinopathy. In this context, users can upload images taken with their smartphones, and the app can analyze the images to determine if further medical consultation is needed. Machine learning can increase the accuracy of these assessments over time, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
2. Using generative AI for drug discovery and personalized medicine
Generative AI can help design new drug compounds and predict their effectiveness for specific patients. In mobile healthcare applications that focus on personalized medicine, generative AI models can analyze a patient’s genetic makeup and create tailored drug recommendations.
A potential application for generative AI is a mobile app that collects genetic information from users through DNA testing. With this information, the app can generate personalized treatment recommendations based on the predicted responses to different medications. This can lead to more effective treatments tailored to individual patients’ needs.
AI in Healthcare Examples
3. Engaging health goals through chatbots and gamification
Gamification and chatbots can be integrated into mobile healthcare applications to improve user engagement and encourage adherence to healthy habits. These applications create an interactive and rewarding experience that motivates users to stay on track with their health goals.
A potential application could include a fitness or nutrition tracking app that uses chatbots to maintain user engagement. The chatbot could provide personalized advice, reminders, and support while incorporating gamification elements like points, badges, and leaderboards to enhance motivation.
4. Ensuring secure patient data sharing using blockchain technology
Blockchain technology can enhance security and privacy in mobile healthcare applications by enabling secure data sharing between patients, providers, and research institutions. By eliminating the need for a centralized authority, blockchain technology reduces the risk of data breaches.
One potential application could be a blockchain-based EHR system in a mobile app. Patients could securely store their medical history, manage their health data, and share it with healthcare providers as needed, ensuring confidentiality and consent throughout the process.
5. IoT-based wearables for continuous remote patient monitoring
IoT-based wearables can be integrated with mobile health applications to provide continuous remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs and other health data. This allows healthcare professionals to track patients’ conditions in real-time and intervene promptly when necessary.
An application of this technology might involve a heart health management app that connects with wearable devices like heart rate monitors or blood pressure cuffs. By continuously gathering and analyzing data from these devices, the app can notify healthcare providers of any irregularities and help patients maintain their cardiovascular health.
What to consider when starting mHealth application development?
Developing a healthcare application that provides a proper solution for a particular issue can be a complex process. When you want to create an impeccable mHealth app that satisfies all interested parties, it is wise to mind the key challenges that we discussed and focus on the crucial points.
1. Decide on a platform
When opting for native health apps, platform-specific languages like Swift for iOS while Java or Kotlin for Android work best; the choice depends on specific project needs. This ensures seamless interaction with device services such as geolocation, microphone, or media files.
Alternatively, for cross-platform mHealth applications, developers often use frameworks like React Native, Flutter, or Ionic. These frameworks allow developers to write code in languages like JavaScript, Dart, or TypeScript, which can then be compiled into native apps for both iOS and Android platforms. This approach offers adaptability across various mobile devices, eliminating the need for separate products for iPhone and Android users.
| Factor | Native mHealth Apps | Hybrid mHealth Apps |
| Development speed | Slower, requiring separate development for each platform, which can delay time-to-market | Faster development due to shared codebase, ideal for quickly launching simple mHealth apps such as appointment schedulers |
| User Experience | Typically offers a smoother and more responsive user experience, critical for complex medical applications like telemedicine platforms | May encounter slight performance differences and UI inconsistencies, suitable for less complex mHealth apps such as health trackers |
| Access to device features | Full access to device features like GPS, sensors, and camera, essential for advanced functionalities like medical imaging apps | Access to device features may be limited, impacting the functionality of hybrid apps in areas such as real-time data capture for monitoring apps |
| Performance | Generally offers better performance, crucial for real-time data processing in applications like remote patient monitoring | Performance may be slightly compromised, affecting the responsiveness of hybrid apps in critical scenarios such as emergency medical alerts |
| Maintenance | Requires separate updates for each platform, which can increase maintenance efforts, important for apps handling sensitive patient data | Simplified maintenance with updates applied uniformly, suitable for less critical apps such as health education resources |
| Cost | Higher development costs due to separate codebases and longer development cycles, relevant for comprehensive healthcare platforms | Lower development costs due to shared codebase, suitable for budget-constrained projects like symptom checkers |
| Offline Capability | Offers better offline capability with local data storage, essential for apps used in remote areas with limited connectivity | Hybrid apps can offer offline capability but may require additional configurations, impacting usage in offline scenarios like rural healthcare clinics |
2. Confidentiality compliance
Adhere to data protection regulations such as HIPAA (for the United States), GDPR (for the European Union), and relevant local regulations worldwide to safeguard patient data. Failure could lead to legal penalties and reputational damage, as seen in the Medical Informatics Engineering data breach in the U.S. and various GDPR-related fines in the
3. Data security measures
Implement robust encryption, authentication, and security audits to prevent breaches like the Anthem data breach, which resulted in substantial losses.The Anthem medical data breach exposed the information of approximately 80 million current and former customers, leading to potential costs exceeding $100 million for damage control and outreach efforts.
4. Device interoperability and compatibility
Healthcare facilities utilize various software and medical devices, such as Practice Management Systems, EHR solutions, and sensors. Your app should seamlessly interact with these existing applications.
Consider hosting options carefully. While the cloud offers benefits like data protection and high performance, some hospitals still prefer traditional hosting for cost reasons. Incorporating a compatibility layer into your app ensures it works smoothly with existing setups.
5. UI/UX considerations
Both doctors and patients invest significant time in medical apps, emphasizing the need for simplicity and ease of use. Design should focus on clarity, relevant visuals, and a soothing atmosphere, particularly considering the vulnerable state of many users.
Thoughtful choices regarding fonts, sizes, and colors enhance readability and prevent user confusion or frustration, ultimately retaining users.
Watch the interesting TEDx Talk on how to improve healthcare UX
How much does healthcare mobile app development cost?
The cost of developing a healthcare app can vary based on its complexity and features. On average, a basic healthcare app can cost between $30,000 to $70,000, while more complex apps can range upwards of $100,000 to as much as $500,000.
Here are specific elements that contribute to the overall expenditure:
- Development team expenses consist of salaries for developers, designers, project managers, QA specialists, impacting the total cost based on team size, expertise, and location.
- Design and user experience costs ensure a visually appealing, user-friendly interface, with customization potentially increasing costs.
- Backend infrastructure, including databases and servers, is essential for app functionality, data management, and scalability, impacting development costs.
- Testing fees ensure app performance, security, and longevity, while maintenance fees cover ongoing updates and technological advancements, contributing to the overall development cost.
- Marketing expenses, including social media campaigns and digital advertising, drive user engagement, brand visibility, and app success.
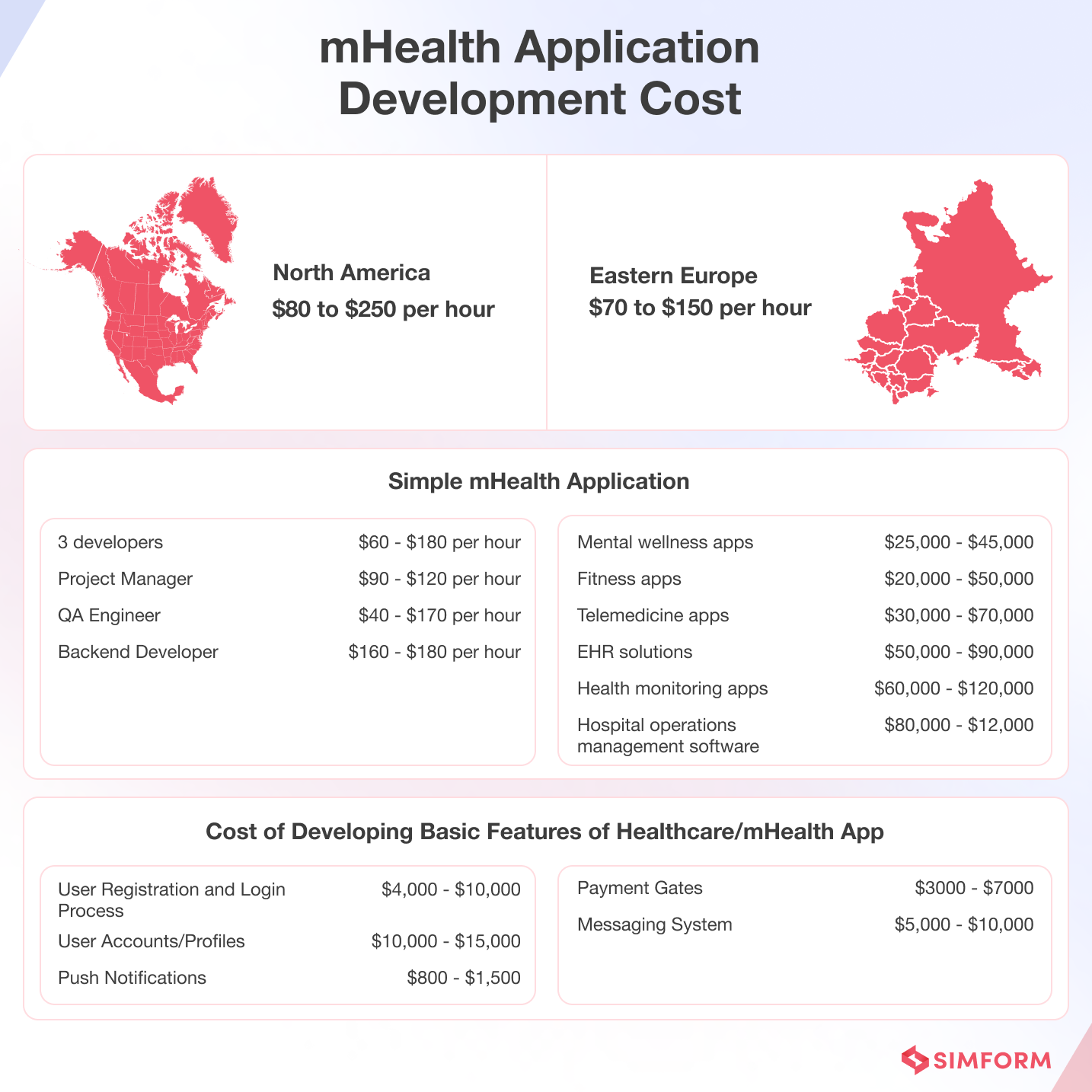
A reliable and experienced mHealth app development company can very well optimize resource allocation and help create cost-efficient and user-centric apps that enhance accessibility, usability, and overall engagement, ultimately improving patient care and streamlining healthcare processes.
Simform as your mHealth app development partner
At Simform, we understand the complexities and challenges of developing robust and secure mHealth solutions. Our team of experts specializes in the advanced technologies such as AI/ML, blockchain, Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), AR/VR, 3D imaging, and image recognition and analysis.
We have developed various types of mHealth applications, from telemedicine platforms and remote patient monitoring systems to medical imaging analysis tools and EHR management solutions. Our comprehensive services cover the entire development lifecycle, ensuring seamless integration, scalability, and compliance with industry regulations. Simform can help healthcare organizations utilize AWS cloud solutions to improve patient care, drive innovation, ensure compliance, and reduce costs. Let Simform help you create innovative mHealth applications!
