As the digital landscape continues to evolve rapidly, organizations are grappling with the challenges posed by their legacy network infrastructure.
With outdated systems, keeping up with the demands of modern technology is challenging for businesses. In addition, security concerns have made upgrading to a more robust and secure network infrastructure essential.
Network modernization refers to the process of upgrading and optimizing existing network infrastructure to meet the needs of today’s digital age. It involves implementing new technologies, such as virtualization, cloud computing, software-defined networking, and network function virtualization.
By modernizing their networks, organizations can improve their ability to adapt to changing business requirements, reduce costs, and improve the user experience. This blog will discuss these benefits in detail and explore the different scenarios in which network modernization can be implemented.
Understanding the current network landscape
Today’s modern network infrastructure architectures have several key characteristics that differentiate them from traditional networks.
- Software-defined –Modern networks are software-defined, which means that network functionality is no longer tied to proprietary hardware devices. Instead, network functions are implemented using software running on commodity hardware. This allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as well as cost savings.
- Automation –Modern networks are highly automated, with software tools performing many routine tasks and configurations. This reduces the risk of errors and improves the speed and efficiency of network management.
- Virtualization –Modern networks extensively use virtualization technologies, which allow multiple virtual network devices to run on a single physical device. This can improve resource utilization and simplify network management.
- Advanced security –Modern networks prioritize security and incorporate advanced security features, such as micro-segmentation, into their design. This helps to protect against cyber threats and data breaches.
- Multi-cloud connectivity –Modern networks support multi-cloud connectivity, enabling organizations to connect to and manage resources across multiple cloud environments. This is increasingly important as more organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies.
Network modernizations are crucial to reducing the complexity of deployments. Increased endpoints and users with a distributed network multiply complexities. Despite massive cloud adoption, the 2023 Global Networking Trends Report indicates that 50% of workloads are still deployed on-premise.
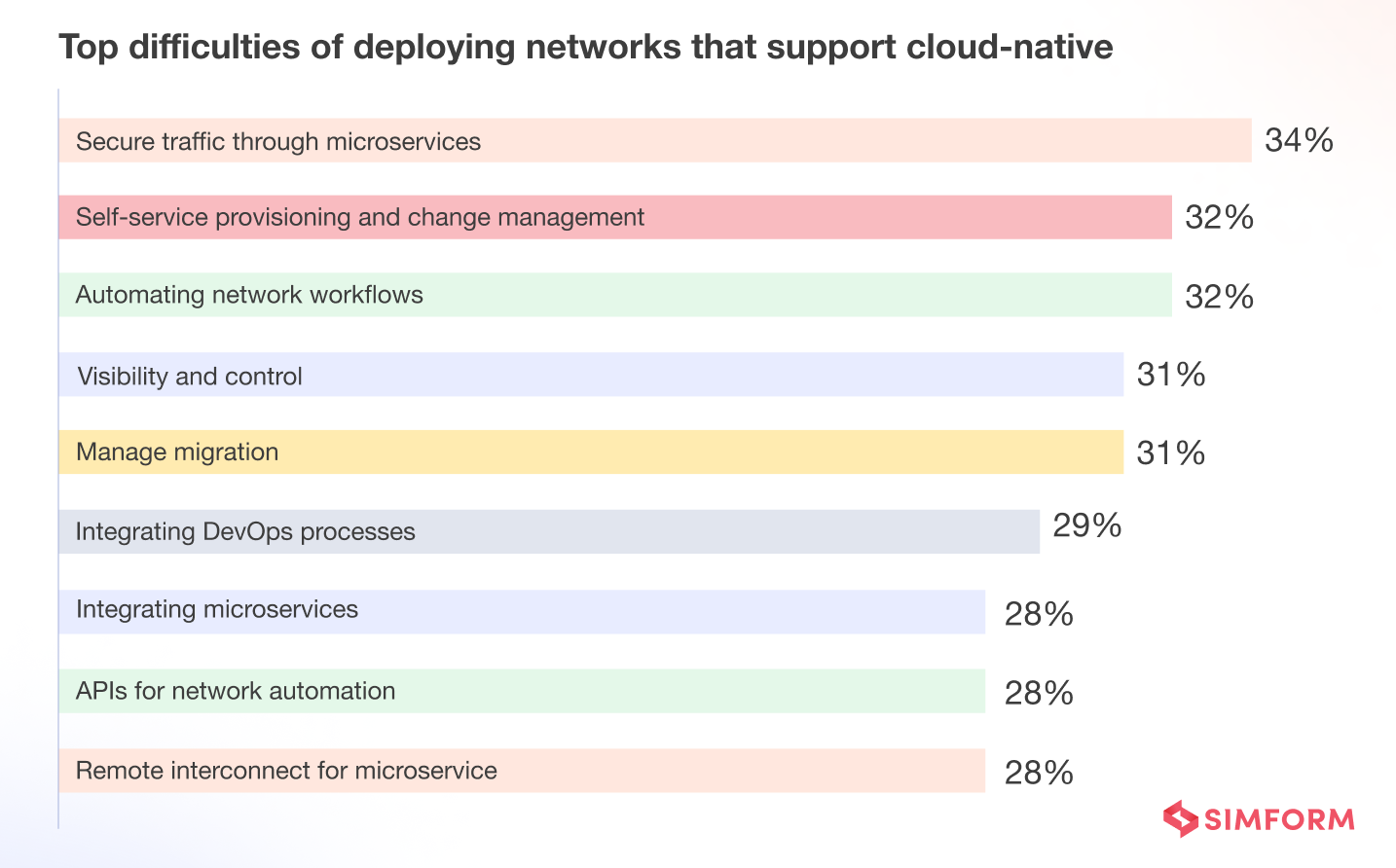
Provisioning, change management, and migration issues are reasons for resistance to the cloud. Network modernization addresses these issues and provides many other vital benefits.
Benefits of a modern network architecture
Network modernization benefits businesses by reducing operational costs and improving resilience and availability.
#1. Improve cost efficiency with network modernization
Network infrastructure modernization helps organizations optimize workflows and reduce downtime and licensing costs.
- Improved Resource Utilization – By implementing modern network technologies, such as virtualization and automation, organizations can improve resource utilization and reduce the need for expensive hardware devices. This can help to reduce capital and operational expenses.
- Simplified Network Management – Modern networks are easier to manage and require fewer resources, which can reduce the cost of network operations. Organizations can save time and money on network management by automating routine tasks and centralizing network management.
- Improved scalability – Modern networks are designed to be more scalable than traditional networks. Organizations can easily add or remove network resources without incurring high costs. This can help reduce the total ownership cost over the network’s lifespan.
- Reduced downtime – Modern networks are designed to be more resilient and reliable than traditional networks. This means that organizations can avoid costly downtime and reduce the risk of lost productivity due to network outages.
Now, if you are using cloud computing resources, the cost of operations depends on the instances used. Network modernization reduces the number of instances needed to improve cost efficiency.
Cost efficiency also requires identifying idle resources and reducing wastage of instances. This is where right-sizing comes into play.
#2. Right-size your infrastructure with network modernization
“Right-sizing your infrastructure” means optimizing your network infrastructure to meet the organization’s needs without overprovisioning resources. Network modernization can help organizations achieve the right size of infrastructure by
- Consolidating network resources on fewer devices
- Optimizing resource utilization, and reducing the need for additional resources, further reducing costs
- Add or remove resources to meet changing demands
- By automating routine tasks and centralizing network management
Organizations can achieve a more cost-effective and efficient network infrastructure for specific needs by leveraging modern network technologies and best practices.
#3. Improve operational efficiency with a modernized network
With the increasing complexity of user environments, modern networks have become a vital tool for organizations. These networks provide a means of managing and organizing highly distributed user environments in a simplified way.
One of the key benefits of modern networks is their ability to provide management interfaces that make complex tasks much more manageable. This feature alone can save organizations countless hours and resources that would otherwise be spent on cumbersome manual processes.
Moreover, modern networks give DevOps and SRE teams greater autonomy, enabling them to work more efficiently and effectively.
By embracing modern networks, organizations can streamline operations, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business landscape.
Moreover, network modernization also enables organizations to deploy zero-touch provisioning(ZTP). It uses a network switch feature that automatically configures new hardware devices added to a network. ZTP reduces the need for manual provisioning and configurations of hardware devices.
Modernization is critical if you need network support for remote worker environments quickly. It reduces manual processes, eliminates repetitive tasks, and improves business focus.
#4. Enhance end-user experience with network modernization
Modernized networks allow end-users to have a reliable and seamless application experience. They achieve this by ensuring higher availability and lower disruptions in the app experience.
Companies can use automated lifecycle management to deploy patches and upgrades without disruptions. So, there is no gap in user experience, and customer retention is also higher.
Network modernization approaches
Network modernization approaches include moving to compute off-site through cloud migration, investing in bigger pipes, evaluating SD-WANs, deploying virtual devices to support network functions virtualization (NFV) capabilities, and more.
#1. Cloud-based networking
Cloud-based networking is an approach that leverages cloud technology to provide remote network services to businesses. Such an approach enables organizations to host network infrastructure and services on the cloud.
Moreover, cloud service providers offer many features and services to manage and maintain the network on the cloud, which takes the burden of manual network management off your team’s shoulders.
Cloud-based networking facilitates,
- Ability to quickly scale networking capabilities and meet the changing demands of a business without the need for expensive hardware upgrades
- Outsourcing network infrastructure and services to cloud providers to reduce operational costs
- Higher flexibility for organizations to access network services from any location, time, and device
- Highly reliable infrastructure with backup options if service failure or an error occurs
Cloud-based networking as a network modernization approach has been widespread, with the market size estimated to reach $56.18 billion in revenue by 2026.
These numbers emphasize that many organizations are migrating to cloud-based infrastructure to modernize their networks for enhanced digital transformations.
Verizon deployed more than 8000 virtualized Radio Access Networks (vRAN) leveraging the cloud
Verizon leverages virtual infrastructure to serve 4G LTE and 5G networks across the United States. So, it required virtualized Radio Access Networks (vRAN) to ensure low latency network experience.
Verizon didn’t want to lose network control by migrating all the infrastructure to the cloud. Further, the telco giant did not want to outsource its entire infrastructure management to cloud service providers.
So the engineers at Verizon created a cloud-native architecture optimized for telco workloads. The new architecture also provided better compliance with industry regulations and performance standards. Its telco cloud has several control units running and enabling network management.
Additionally, Verizon leveraged AWS Wavelength compute platform to build private Mobile Edge Compute(MEC) like functions and deploy more than 8000 vRAN cells.
Considering the core, edge, and far edge of the network thus created, Verizon’s network infrastructure is the largest virtual infrastructure deployment in telecom.
#2. Software-defined networking (SDN)
Network policy management ensures high-performance networks and low latency experience. SDN enables network policy management by decoupling network control logic from devices executing functions.
SDN provides controllers that overlay above the hardware in the cloud and enables policy-based management. In this approach, the network control and forwarding planes are decoupled from the data plane, allowing the organization to program the network control easily.
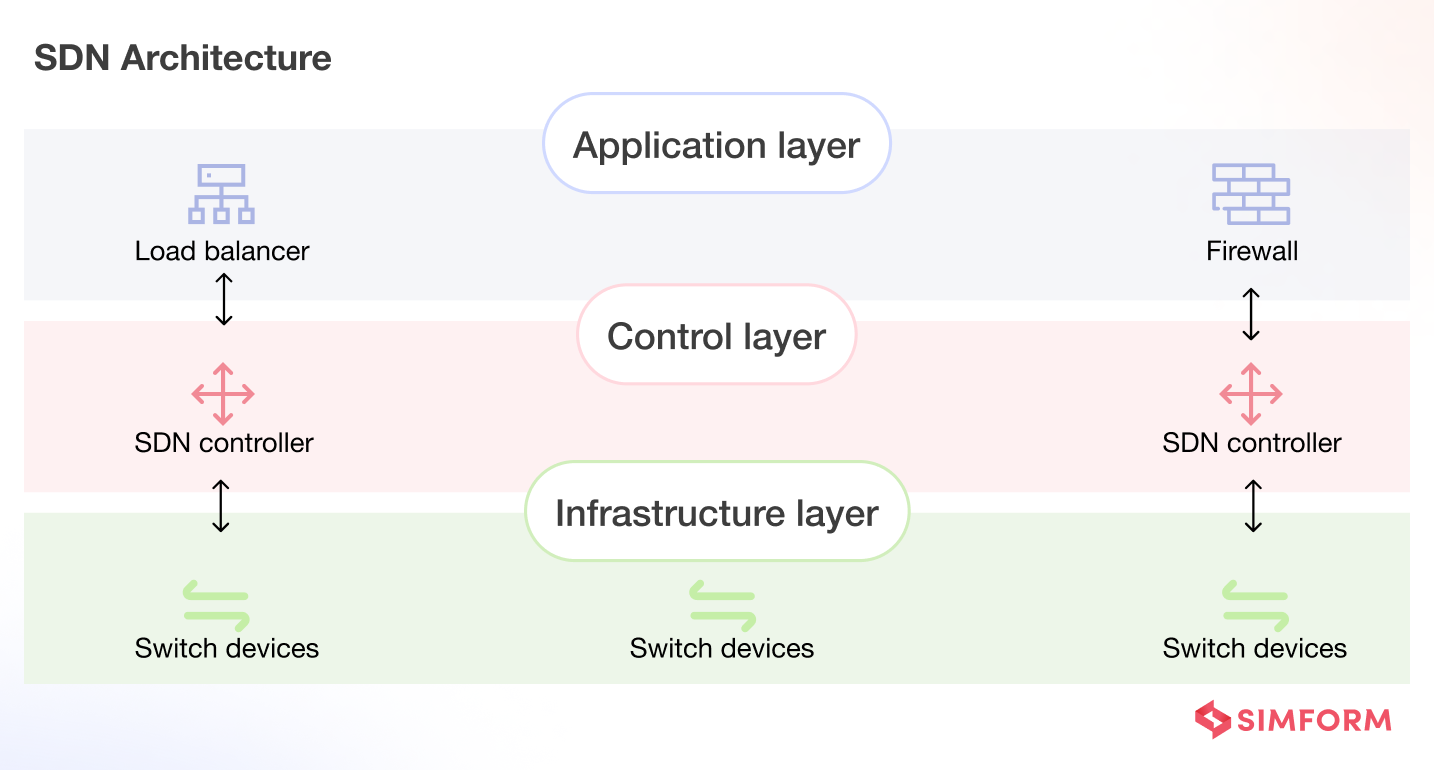
SDN consists of
- Apps that relay information to the network or ask for specific data allocation
- SDN controllers/load balancers that communicate with applications to determine where data packets will be transmitted
- Network devices that receive routing information from controllers
Traditionally, companies used a router or switch in the cloud or on-premise data center to control the network. However, organizations didn’t have enough visibility into network management. SDN provides complete control over the network and reduces the reliance on hardware devices.
SDN, as a network modernization approach, provides
- Higher reliability due to enhanced automation of network management
- Centralized management of network policies
- Higher visibility of network traffic and better control
- Traffic programmability to allow agile and adaptive network-driven policy creation
#3. SD-WAN
Software-defined Wide Area Network(SD-WAN) is similar to SDN but on a macro-level. SDN provides network management at the micro-level or within a local area network. At the same time, SD-WAN offers network management across geographical locations.
It is a virtual WAN architecture that combines transport services – including MPLS, LTE, and broadband internet services to connect users to applications securely.
SD-WAN provides
- Efficient routing mechanism for business-critical traffic for optimized operations
- Boosts security through support for integrations of encryptions and sandboxing capabilities
- Centralized management of the network across WAN through a dashboard
- Reduced overhead costs and improved network performance
#4. Network function virtualization (NFV)
NFV is a virtualization approach for network modernization. It separates communication services from hardware devices like routers and firewalls. Businesses can take advantage of NFV to deliver applications on demand.
Leveraging NFV for modernization reduces operating costs as you don’t need dedicated hardware for each network function. European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has proposed a standard NFV architecture that you can follow for enhanced network performance. The architecture includes
- Virtualized network functions (VNFs) are software applications facilitating functions like file sharing, IP configurations, and more.
- Network functions virtualization infrastructure (NFVi) has several computing, storage, and networking components to support software or a container management platform required to run applications.
- Management, automation, and network orchestration (MANO) offer the framework for provisioning and managing NFV infrastructure.
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) approach provides
- Reduced cost of equipment as you can use standard servers with a software layer
- Efficient usage of space, power, and cooling for on-premise data centers due to virtualization
- Faster time to market with higher network performance through virtualized architecture
- Elastic scaling capacity based on networking demands
#5. Network slicing
The network slicing approach allows you to divide the bandwidth into smaller slices to improve application reliability. Slicing the network enables organizations to multiplex virtualized and independent logical networks on the same physical infrastructure
Operators can build and manage networks on demand for different applications. Such an approach also allows organizations to isolate networks in “slices.” So, if specific applications are attacked, isolation makes sanitization easy.
Network slicing provides
- Focused network performance for critical applications and operations
- Higher availability and streaming performance for applications
- Enhanced security through isolation of malicious network slices
- Better support for value-added services through optimized network performance
#6. Network architecture redesign
Network architecture has several components, including software and hardware. The redesigning approach involves changing how these components function and adding new devices to the architecture.
There are many ways to redesign the network architecture,
- Segmentation is an approach to creating a layer-based architecture for separating internet-facing systems from internal components.
- Hybrid architecture is where you leverage on-premise physical infrastructure with cloud-based services.
- Multi-cloud network architecture is an approach to leverage multiple cloud services to deploy networks on demand.
- Modular redesign is an approach to group functions based on specific domains in different modules.
Network architecture redesign offers
- Improved performance by redesigning a network architecture to improve its accuracy, speed, and efficiency
- Increased scalability through redesigning allows organizations to handle more input features with less overhead on the infrastructure
- Enhanced flexibility with a well-designed network architecture with adaptability to changing requirements
- Reduced over lifting by redesigning a network architecture by adding regularization techniques like dropout or early stopping
#7. Network automation
Network automation is an approach where you automate key aspects like managing, provisioning, testing, and deploying workloads. Automation of networks involves leveraging software to manage infrastructure and automate configurations.
Further, with the integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning models, you can leverage model-driven network programmability to analyze specific patterns. Analyzing the network patterns and behaviors can help design data access policies for enhanced security.
Network automation
- Enables enhanced planning and network management across environments
- Facilitatesdevice testing and configuration management
- Provides advanced provisioning of physical and virtual network devices
- Helps ensure configuration compliance for all network devices
Critical considerations for network modernization
Modernizing the network requires elaborate planning, monitoring, and analysis of different environments. Before upgrading your network infrastructure, you must consider aspects such as change management, resistance within the organization, and costs.
#1. Network assessment And design
Before modernizing your network, existing infrastructure assessment and design analysis become vital to ensure the whole process aligns with the end goal. Some of the key reasons why you need to take into account network assessment and design considerations are,
- Comprehensive understanding: The assessment phase provides a comprehensive understanding of the current network infrastructure’s performance, configurations, and capabilities. This information is crucial for designing a modern network that meets the organization’s needs.
- Requirements gathering: During the design phase, organizations gather necessary data for the modernization requirements of a network. This includes identifying the organization’s specific needs, such as performance, security, and scalability requirements. This information is then used to design a modern network that meets these requirements and addresses any issues identified during the assessment phase.
- Aligning business goals: Network assessments allow companies to align their modernization efforts with organizational goals.
- Cost-effectiveness: Assessing the network infrastructure and design can help identify and reduce redundant components saving operational costs.
- Higher security: Design analysis allows businesses to make changes and introduce new security measures for data protection.
#2. Implementation and management
Implementation and management of network modernizations are crucial to determine project sustainability. If you don’t consider the requirements to implement modernization, the project costs and efforts can be higher. Other reasons why you need to consider the implementation and management of network modernizations are
- Project management: The implementation phase of modernization requires proper planning to ensure a modernized network within budget. So, you must consider aspects like time, budget, and quality standards before initiating the process.
- Change management: Modernization of network infrastructure can mean several organizational changes. So, you must ensure that the transition to the new network architecture is seamless and smooth.
- Advanced training: You also need to consider the need for advanced IT staff training to ensure no disruptions. Further, you need to train your users for changes in the systems due to modernization.
- Monitoring and maintenance: Considering monitoring and maintenance requirements is vital to ensure the system is secure. Additionally, it also helps in maintaining the system’s performance and security.
#3. Budget constraints
Not just network modernization but any sort of IT modernization makes budget a crucial factor. You need to analyze the costs of modernization and plan them accordingly. Some of the critical factors to consider are
- Cost optimization needs: You need to identify and capitalize on crucial cost optimization opportunities which you can include in your modernization plan.
- Need for a phased approach: Organizations with budget constraints may need faster modernization outcomes. So, you need to consider a phased approach to ensure that budget restrictions do not affect the pace of modernization.
- Modernization tradeoffs: Businesses often make trade-offs between low-code hardware or software solutions compared to expensive but high-performance devices.
#4. Resistance to change
Organizations modernize the network infrastructure and policies for data access. However, it continues beyond infrastructure, and companies must also change the process flow to accommodate network modernization.
Such changes may face resistance within the organizations, which you must consider before implementing modernization plans.
One of the critical aspects of this resistance to change is clarity on roles. Many employees need clarification about their roles in the new process flows and how to ensure no conflicting priorities. This is why you need to design the modernization plan keeping key roles and responsibilities defined.
#5. Technical challenge
Many significant technical challenges make modernization complex, including compatibility of new architecture with existing systems, the need for scaling on demand, and security requirements.
So, you must consider all such challenges before planning and implementing network infrastructure modernization.
Further, you need to consider integrating technologies and services like cloud, IoT, AI, and more for your modernized network.
Conclusion
Network modernization is one of the essential steps to achieving a truly modern IT environment. Businesses can improve their infrastructure, reduce costs, and increase efficiency by implementing network modernization strategies.
Many modernization strategies include network redesign, re-architecting the architecture, network slicing, segmentations, and more. However, choosing which approach for your project requires assessing existing network infrastructure and design analysis.
For example, cloud-based networking is an excellent approach if you want to optimize your network performance and coach. However, the implementation of cloud-based network modernization requires improved visibility.
Here is a guide on cloud cost optimization that will also help you understand how to improve project visibility. You also can reach out to discuss your needs.